Meta is letting the US military and defense contractors use its Llama AI model for national security purposes.
Latest posts
Revealing hidden layers in superconducting nickelates.
In a collaborative effort, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research (MPI-FKF) have discovered a new crystal structure in La₃Ni₂O₇, a material known to exhibit high-temperature superconductivity under high pressure.
Nov 4, 2024
AI Designs Antibodies From Scratch In ‘Landmark Moment’ For Science
Posted by Jose Ruben Rodriguez Fuentes in categories: biotech/medical, robotics/AI, science
Marking a major breakthrough in medical development, scientists have used AI to design antibodies from scratch.
Nov 4, 2024
Starlink pauses new subscriptions in Nairobi, cites network overload
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in category: internet
Oh my. And here I was about to get Starlink.
Starlink has suspended new subscriptions in Nairobi and neighbouring Kiambu, Machakos, Narok, Murang’a and Nakuru regions, citing a network capacity overload due to increased demand.
Nov 4, 2024
Coarse-Grained Simulations of Adeno-Associated Virus and Its Receptor Reveal Influences on Membrane Lipid Organization and Curvature
Posted by Logan Thrasher Collins in categories: biotech/medical, virtual reality
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a well-known gene delivery tool with a wide range of applications, including as a vector for gene therapies. However, the molecular mechanism of its cell entry remains unknown. Here, we performed coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations of the AAV serotype 2 (AAV2) capsid and the universal AAV receptor (AAVR) in a model plasma membrane environment. Our simulations show that binding of the AAV2 capsid to the membrane induces membrane curvature, along with the recruitment and clustering of GM3 lipids around the AAV2 capsid. We also found that the AAVR binds to the AAV2 capsid at the VR-I loops using its PKD2 and PKD3 domains, whose binding poses differs from previous structural studies. These first molecular-level insights into AAV2 membrane interactions suggest a complex process during the initial phase of AAV2 capsid internalization.
Nov 4, 2024
New Research May Vindicate Einstein’s Theoretical Prediction of Massless Gravitons
Posted by Chavis Srichan in category: futurism
New research sets the most stringent limit yet on the mass of the graviton, suggesting it may indeed be massless as predicted by Einstein’s theory of gravity.
Nov 4, 2024
First data emerges from ‘direct-to-brain’ Alzheimer’s stem cell therapy trial
Posted by Arthur Brown in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
The small-scale FDA-cleared trial is designed to evaluate both the safety and initial efficacy of RB-ADSCs in nine patients with Alzheimer’s. Regeneration Biomedical’s CTAD presentation focused on the first three enrolled patients, who each received a single dose of RB-ADSCs delivered directly into the lateral ventricles of the brain using an “Ommaya reservoir” – a device implanted under the scalp to bypass the blood-brain barrier, a major obstacle in Alzheimer’s treatments.
Biomarker analysis at the 12-week mark demonstrated reductions in both p-Tau and amyloid-beta – two proteins strongly associated with Alzheimer’s disease progression. In cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from the three patients, p-Tau levels decreased to “normal” levels, while amyloid PET scans also showed a reduction in amyloid buildup.
Regeneration Biomedical also reported its treatment produced signs of cognitive improvement, with two of the three patients showing increased Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores, a common measure of cognitive function.
Nov 4, 2024
Towards Fine-Tuned Control of Gene Expression
Posted by Arthur Brown in category: biotech/medical
In a groundbreaking Nature paper, researchers have developed synthetic regulatory sequences that could prevent targeted gene therapies from having effects in unwanted cell types.
More than methylation
While methylation is the most well-known regulator of gene expression, it isn’t the only thing that determines what is to be expressed when. Cis-regulatory elements (CREs), so called because they sit near the DNA sequences they regulate, are responsible for expressing the genes that are specific to each cell type [1]. While they are technically non-coding, as they do not directly code for functional proteins, CREs are critical to epigenomic function.
Nov 4, 2024
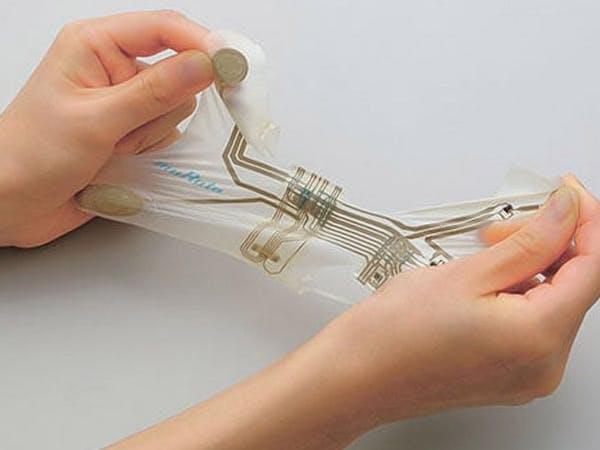
Murata Goes Flexible with Its Stretchable Printed Circuit Platform
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, wearables
Murata is branching out from its usual ceramic components with the launch of flexible, stretchable electronics — a Stretchable Printed Circuit (SPC) platform it says is ideally positioned for wearable and medical devices.
In recent years, in the medical field, to make more accurate diagnoses, the…
Bendy, soft, stretchy devices target the wearable and medical markets.
Continue reading “Murata Goes Flexible with Its Stretchable Printed Circuit Platform” »