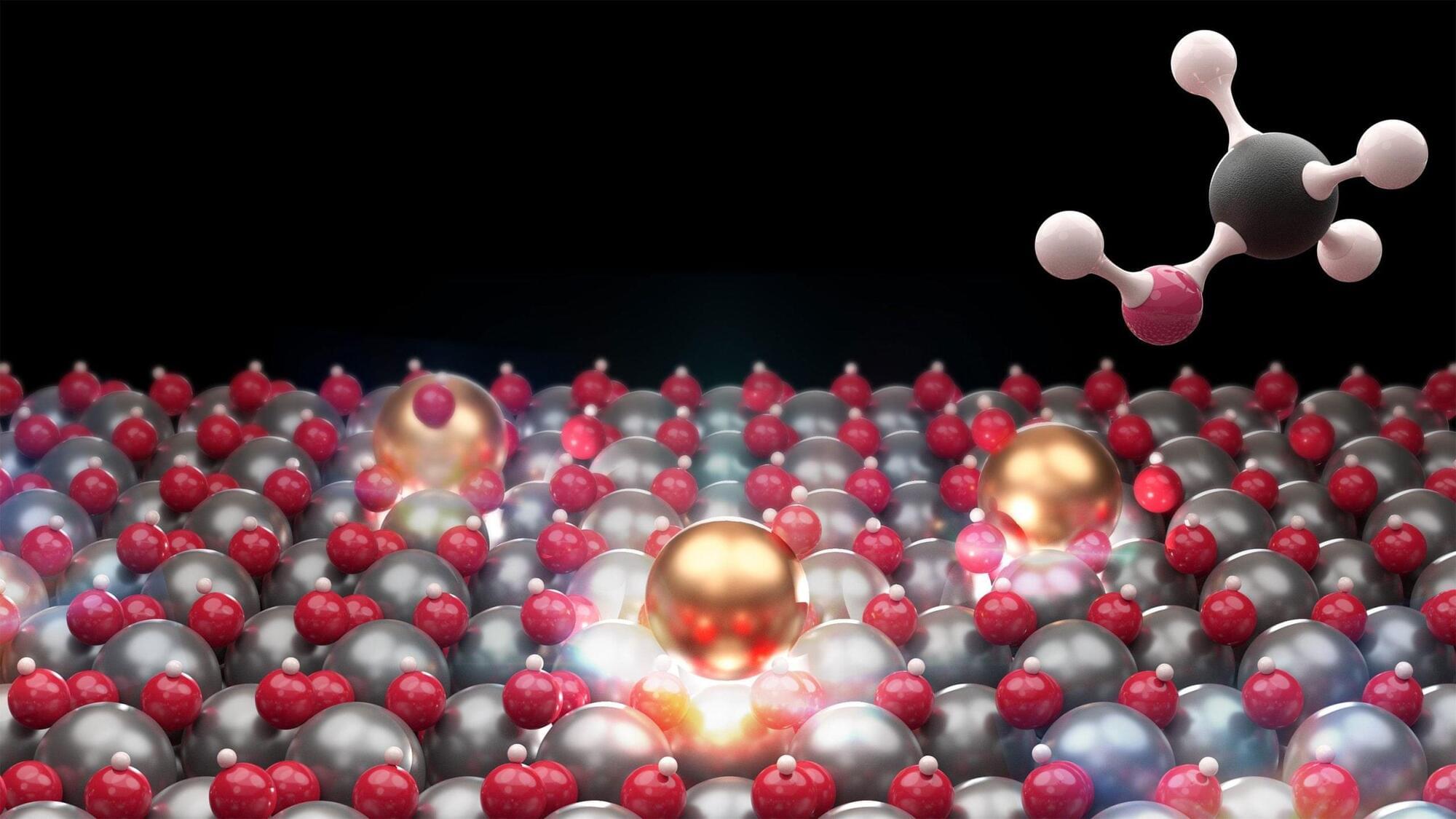
A new catalyst built from isolated indium atoms allows scientists to convert CO2 into methanol more efficiently while revealing the hidden chemistry that drives the reaction.


Imine-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) have been explored for various applications; however, chemical recycling of end-of-life COFs is an undeveloped area of research. Here, we report closed-loop recycling methods for imine-linked COFs, realizing their chemical depolymerization and reconstruction through d.
Austria’s scientists have created a leather made from mycelium. Growing mushrooms in low-oxygen chambers allows researchers to craft an alternative material that feels and looks like traditional leather. The finished textile is strong, flexible, and even fire-resistant.
Manufacturers grow the material instead of harvesting it from animals. After it reaches the desired thickness, they apply non-toxic enzymes to keep it fully biodegradable. The vegetative part of the fungus grows into a dense mat over a matter of days. Above all, it avoids the environmental impact of traditional leather production…
…This is not science fiction; fungal fabric has grown from a curiosity into reality. A 2025 report listed the benefits of mushroom leather as having a lower carbon footprint. It begins with a substantial reduction in water use. Growing mushrooms, compared to raising cattle, requires a fraction of the water.
Scientists created a mushroom leather made from mycelium that looks and feels like traditional leather. It’s grown in a matter of days.

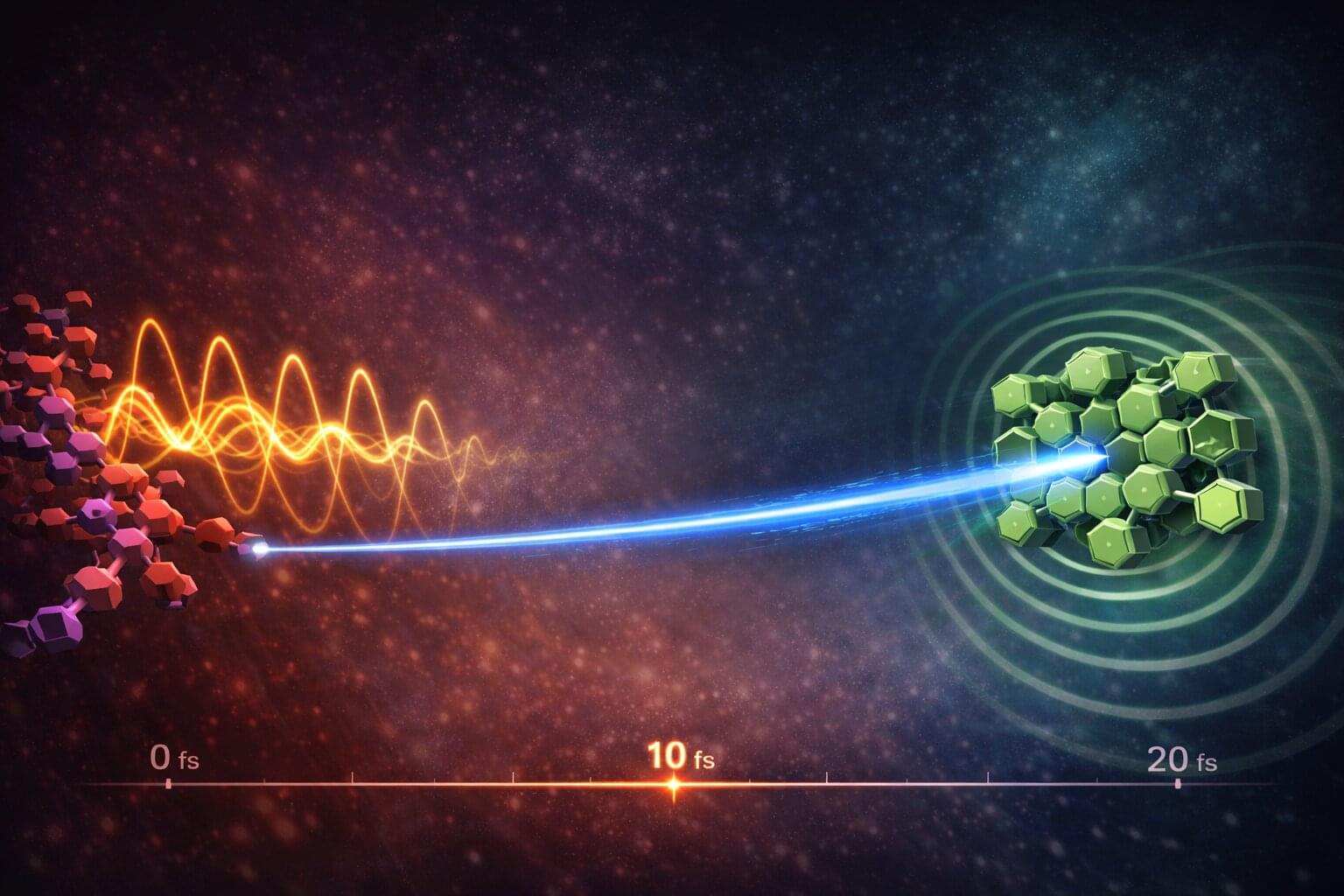
Electrons can be “kicked across” solar materials at almost the fastest speed nature allows, scientists have discovered, challenging long-held theories about how solar energy systems work. The finding could help researchers design more efficient ways of harvesting sunlight and converting it into electricity. The research is published in Nature Communications.
In experiments capturing events lasting just 18 femtoseconds —less than 20 quadrillionths of a second—researchers at the University of Cambridge observed charge separation happening within a single molecular vibration.
“We deliberately designed a system that—according to conventional theory—should not have transferred charge this fast,” said Dr. Pratyush Ghosh, Research Fellow, at St John’s College, Cambridge, and first author of the study. “By conventional design rules, this system should have been slow, and that’s what makes the result so striking.

Photocatalysis promises an efficient conversion of abundant solar energy into usable chemical energy. Polyheptazine imides have some key structural and functional twists that make them especially interesting for photocatalysis. So far, there is only limited knowledge about how structural changes affect the electronic and optical properties of the many material candidates in this class. A team led by researchers from the Center for Advanced Systems Understanding (CASUS) at HZDR has now presented a reliable and reproducible theoretical method to solve this challenge that was confirmed by measurements done on genuine candidate materials.
Polyheptazine imides belong to the family of carbon nitrides, which are layered, graphene-like compounds composed of nitrogen-rich, ring-shaped units. Unlike graphene, which exhibits excellent electrical conductivity but lacks photocatalytic activity, polyheptazine imides possess band gaps suitable for visible-light absorption.
Carbon nitride-based materials impress due to their low production cost, nontoxicity and thermal stability. However, the first generation of such materials were not ideal photocatalysts as the materials possessed properties that hindered charge separation. If a material has a low charge separation, the electron excited by an incoming photon quickly recombines with the hole it was propelled from—and releases energy only as heat or light. No energy is available to drive chemical reactions.
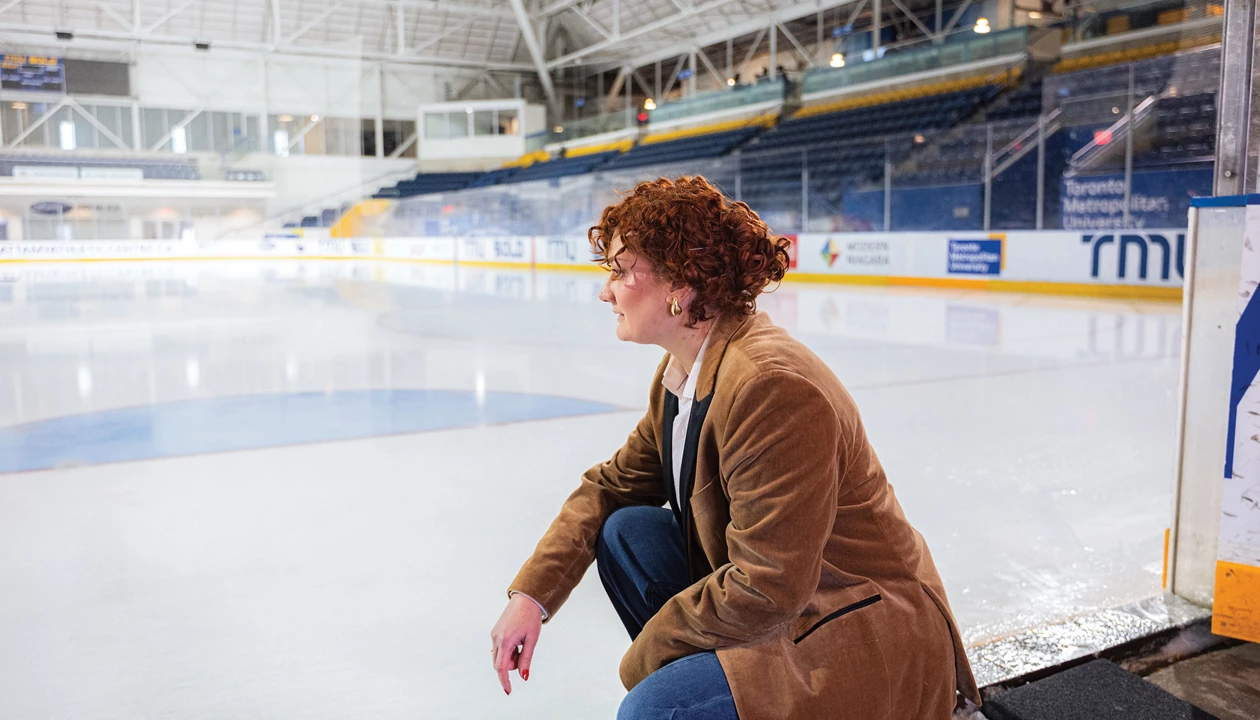

Stefania Impellizzeri, a sustainable-materials chemist at Toronto Metropolitan University, is trying to make ice rinks more efficient and sustainable by fine-tuning water chemistry and rink-related materials.
Rinks use energy, water, and refrigerants, and they create microplastics. People are trying to reduce this footprint by Prachi Patel.

Renewable energy is lowering electricity costs in some parts of the country, but those benefits aren’t being seen by consumers everywhere because they’re typically placed far away from demand centers. Better integrating electricity transmission networks across regions could significantly reduce generation costs, new research from the University of Michigan shows—at the expense of generation companies’ profits. The study is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Economist Catherine Hausman, associate professor at the Ford School of Public Policy, and colleagues found that improving interregional connectivity could have saved anywhere from $5.8 billion to $7.1 billion in electricity generation costs in 2022, and $3.4 billion to $5 billion in 2023.
At the same time, investing in regional connectivity could cost some power plants over $20 million in annual net revenue—giving them financial incentives to block or delay transmission network improvements.
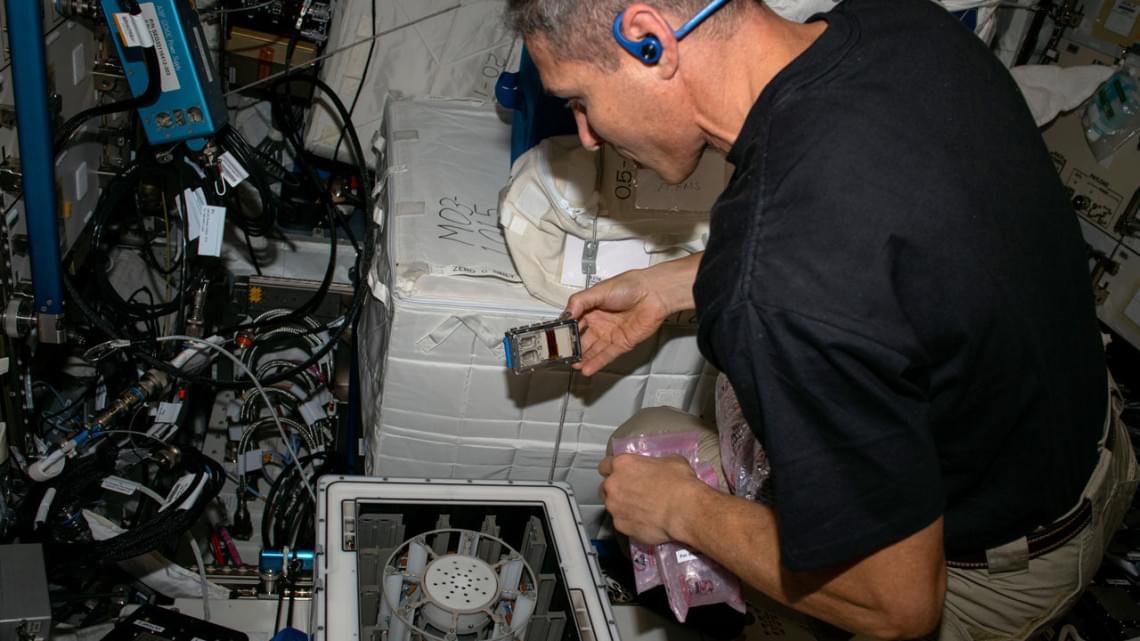

If humankind is to explore deep space, one small passenger should not be left behind: microbes. In fact, it would be impossible to leave them behind, since they live on and in our bodies, surfaces and food. Learning how they react to space conditions is critical, but they could also be invaluable fellows in our endeavor to explore space.
Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi can harvest crucial minerals from rocks and could provide a sustainable alternative to transporting much-needed resources from Earth.
Researchers from Cornell and the University of Edinburgh collaborated to study how those microbes extract platinum group elements from a meteorite in microgravity, with an experiment conducted aboard the International Space Station. They found that “biomining” fungi are particularly adept at extracting the valuable metal palladium, while removing the fungus resulted in a negative effect on nonbiological leaching in microgravity.

When we hear about moving objects with electricity, most of us imagine a “pulling force.” Positive and negative charges attract each other, drawing objects together. It is natural to think that this attractive force—known as electrostatic force—is what makes things move.
However, this force is not very strong, and it has not been suitable for driving large machines in our daily lives. For that reason, most practical motors rely on a different mechanism. For example, the motors in electric fans and electric vehicles do not use electricity directly to create motion. Instead, they use electricity to generate a magnetic field, and then use that magnetic force to rotate.