A newly mapped form of superconductivity in uranium ditelluride emerges only under extremely strong magnetic fields, defying long-held expectations about how superconductors behave.



Chiral amines are privileged chiral building blocks with extensive applications in pharmaceuticals, advanced materials, and asymmetric catalysis owing to their unique structural features and functional diversity. Although palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic C–H amination offers an efficient strategy for constructing these motifs, the simultaneous challenges of coordinating sterically hindered internal alkenes and suppressing catalyst deactivation by Lewis basic amines have severely limited the development of asymmetric oxidative amination systems. In this study, we disclose a novel ester, an unmodified native functional group-directed strategy that enables the palladium-catalyzed asymmetric oxidative allylic amination of internal α,β-unsaturated esters with basic amines. This protocol yields a diverse array of non-natural γ-amino acid derivatives with excellent yields and high enantioselectivity (93% to >99% e.e.). Comprehensive mechanistic investigations, incorporating controlled experiments and density functional theory calculations, elucidate the intricate reaction pathway. The synthetic utility is further demonstrated through various product derivatizations and the streamlined synthesis of bioactive compounds. This work establishes a general platform for accessing enantioenriched nitrogen-containing architectures from readily available alkenes and amines.

Electron movement and structures described in quantum physics allow researchers to better understand how and why materials like superconductors behave as they do. Rice University researchers Jianwei Huang and Ming Yi have developed a new capability, magnetoARPES, building on angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) that allows researchers to study quantum behaviors they have been unable to resolve using ARPES alone. The work has been published in Nature Physics.
MagnetoARPES adds a tunable magnetic field, external to the sample, to ARPES. This allows researchers to probe the full electronic response to a magnetic field, giving insights into why certain collective behaviors of electrons develop.
Magnetic fields have, historically, been excluded from ARPES experiments, but over the course of a few years of experimentation and simulations, Yi’s team found a viable way to incorporate this capability into the ARPES sample environment.

Researchers from the Department of Physics and the University Institute of Materials at the University of Alicante (UA) and the Low Temperature and High Magnetic Field Laboratory at the Autonomous University of Madrid (UAM) have succeeded in measuring, for the first time, the electrical conductance of gold and silver atomic contacts subjected to extreme magnetic fields of up to 20 teslas, an intensity equivalent to 400,000 times Earth’s magnetic field.
The team observed that, when applying these fields, the conductance of the gold contacts decreases by around 15%, an unexpected result in noble metals such as gold (Au) and silver (Ag). Furthermore, they detected modifications in the formation process of the atomic contact itself, which were particularly marked in silver. These findings contradict previous theoretical predictions, which anticipated a practically non-existent magnetic dependence in pure Au and Ag.
The discovery, published in Physical Review Research, adds a new piece to the knowledge of electronic transport physics at the atomic scale. Achieving a noticeable response to a magnetic field from a conductor consisting of a single atomic channel, as occurs in these metals, is extremely difficult. The results suggest that functional materials can be designed by combining noble metals with magnetically active systems.

A research team has successfully designed and developed a proprietary non-precious metal oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalyst featuring a layered structure optimized for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) environments.
The study, published in the journal ACS Nano, is particularly significant in that it proposes a novel catalyst design strategy capable of simultaneously achieving high efficiency and durability while reducing reliance on expensive precious metal catalysts. The team was led by Dr. Sung Mook Choi of the Energy & Environment Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), in collaboration with a team headed by Professor Seung-Hwa Lee at Changwon National University.
Anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) operates under alkaline conditions, offering a structural advantage in that relatively low-cost non-precious metal catalysts can be employed in place of expensive precious metals. For this reason, AEMWE has attracted considerable attention as a cost-effective and inherently safe hydrogen production technology.
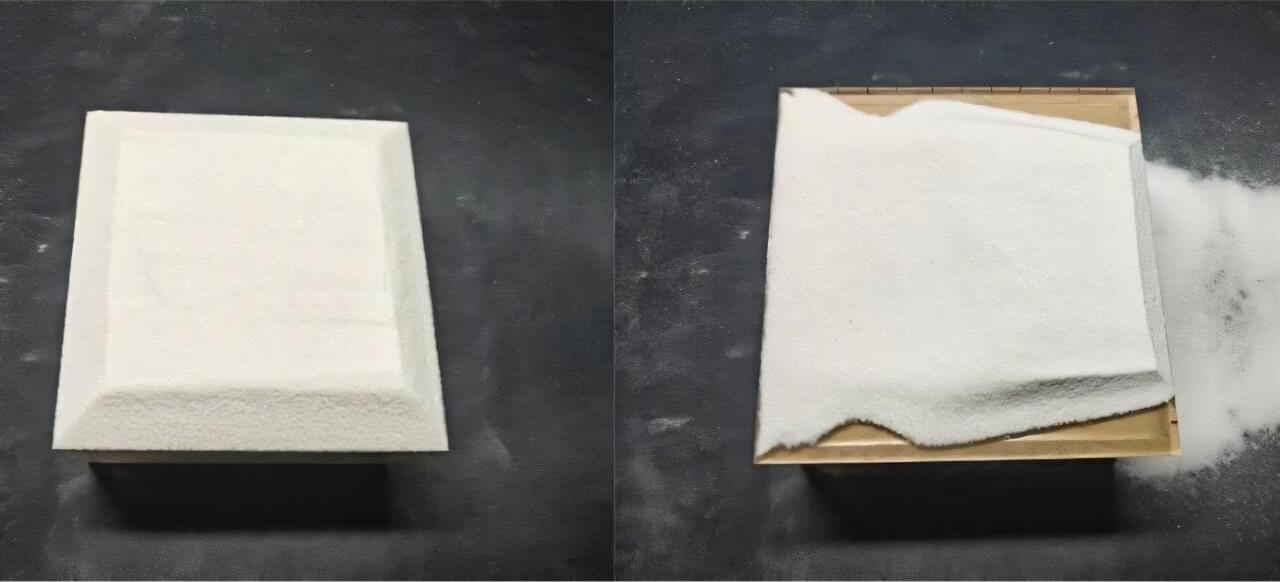
No two snowflakes may be the same, but models that fail to take these variations into consideration often fall short when calculating the way snow accumulates on roofs. In Physics of Fluids, researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology in China modeled the way snow gathers on a roof based on snowflake size and distribution.
“In cold regions, snow load is a critical factor in structural design,” said author Qingwen Zhang. “However, traditional models often simplify snow as a uniform material with a single particle size, overlooking the natural heterogeneity of snowflake sizes and distributions.”

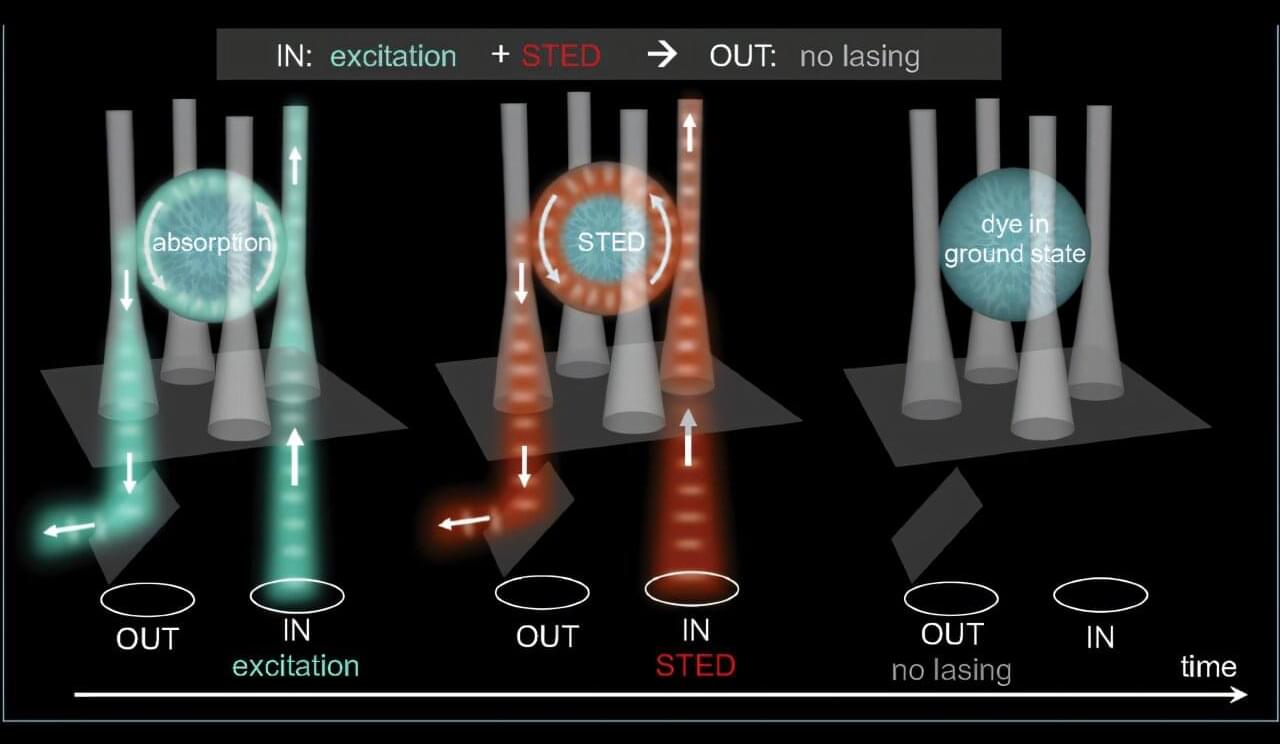
Controlling light with light is a long-sought goal for computing and communication technologies. Achieving this capability would allow optical signals to be processed without converting them into electrical signals, potentially enabling faster and more energy-efficient devices. In recent years, researchers have begun exploring an unexpected platform for this purpose: soft matter.
Soft-matter photonics investigates how materials such as liquids, liquid crystals, gels, and polymers can self-organize into structures that manipulate light. Unlike conventional solid-state photonic components, which require precise nanofabrication, soft materials can spontaneously form functional optical geometries. Some soft materials also exhibit nonlinear optical behavior. For example, through the Kerr effect, their refractive index can change in response to intense light, enabling one beam to influence another and allowing ultrafast optical switching on picosecond timescales.
As reported in Advanced Photonics, an international team of researchers introduced a different approach: a nanosecond optical switch based on resonant stimulated-emission depletion (STED) in a liquid crystal cavity. Rather than relying on refractive index changes, this method manipulates the stored optical energy inside a resonant structure.