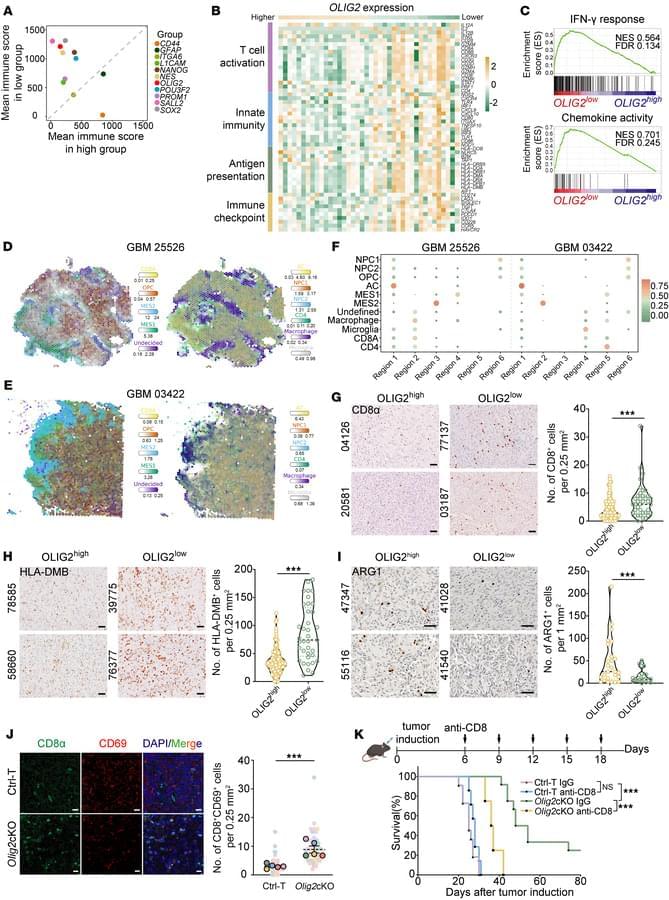
This actually offers some significant new insights for both cancer treatment research and the development of anti-aging therapies. 🧠
Read more👇
A group of natural compounds attracting attention for their anti-aging potential has a dark side.
New research shows how a family of chemicals called polyamines speeds up the growth of cancer cells. Led by a team from the Tokyo University of Science in Japan, the study offers some significant new insights for both cancer treatment research and the development of anti-aging therapies.
Polyamines are essential molecules found in all living cells. Including compounds with colorful names like spermidine and putrescine, they regulate processes involving cell growth and protein synthesis.