Russia admits building a substantial arsenal of intermediate-range missiles during a moratorium, says Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov.


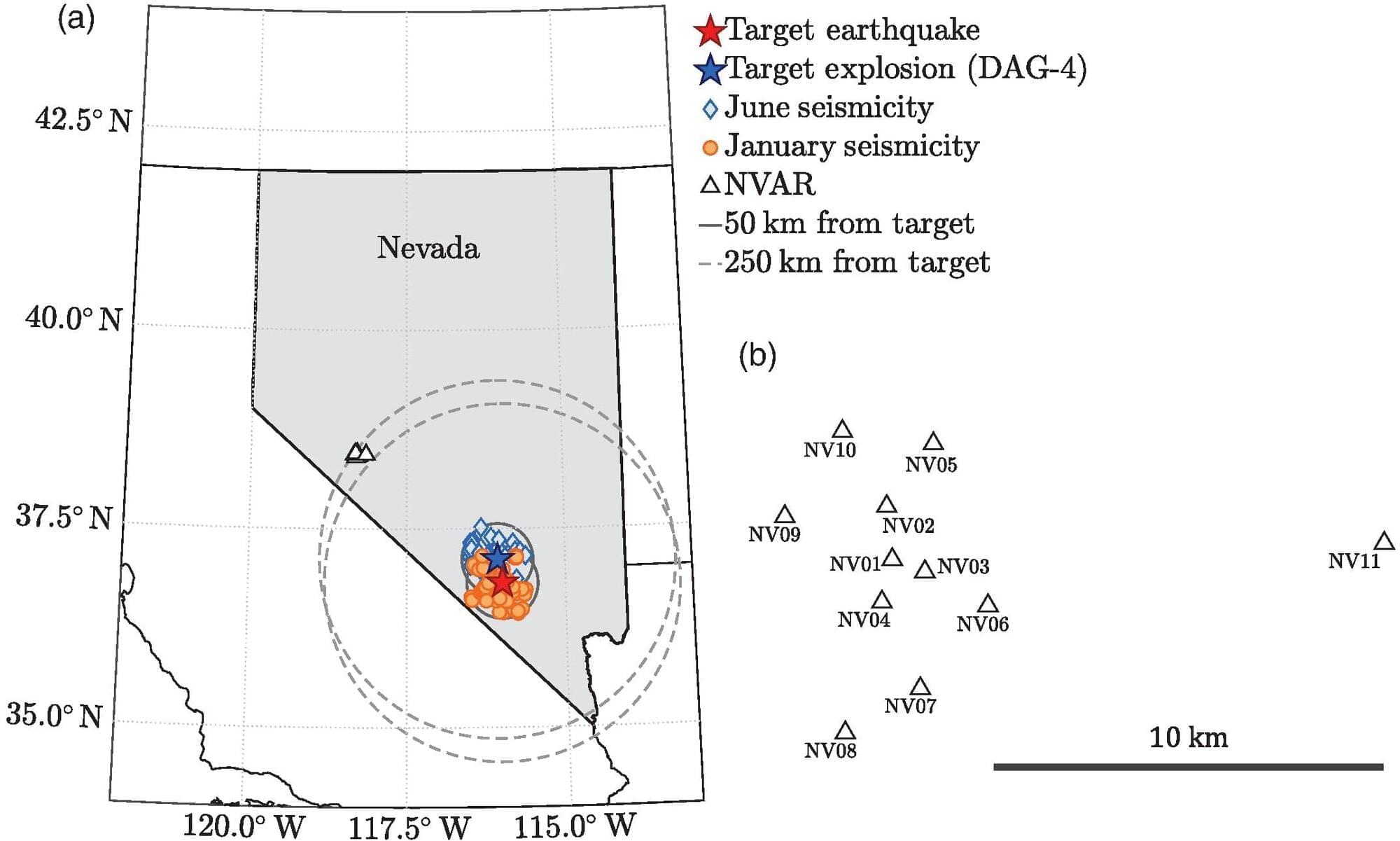
Could the seismic signal of an underground nuclear test explosion be “hidden” by the signal generated by a natural earthquake?
It’s possible, according to a new review article published in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America that contradicts the conventional wisdom about explosion “masking.”
The new analysis by Joshua Carmichael and colleagues at Los Alamos National Laboratory found that advanced signal detector technology that can identify a 1.7-ton buried explosion with a 97% success rate only has a 37% success rate when seismic signals from that explosion are hidden within the seismic waveforms of an earthquake that happens within 100 seconds and about 250 kilometers away from the explosion.
The following declassified nuclear test footage has been enhanced using AI with techniques such as slow motion, frame interpolation, upscaling, and colorization. This helps improve the clarity and visual quality of the original recordings, which were often degraded or limited by the technology of the time. Experiencing these shots with enhanced detail brings the devastating power of atomic weapons into focus and offers a clearer perspective on their catastrophic potential and impact.
Music generated with Suno AI.
Instagram: / hashem.alghaili \r.
Facebook: / sciencenaturepage.
A supersonic drone that will be propelled by a revolutionary new engine has taken to the skies for the first time. When Venus Aerospace’s aircraft does go supersonic on a later date, it will be powered by a Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE).
Supersonic drones may sound like something bleeding edge, but they’re surprisingly old hat as a basic concept. As far back as the early 1950s, the US Air Force was fielding remote-controlled supersonic jets for targets to test air defenses, as platforms for reconnaissance in dangerous areas, or as weapons armed with conventional or nuclear warheads.
However, the one thing they’ve all had in common over the past 75 years was a jet engine for propulsion to boost them past Mach 1. In recent years, advances in avionics, aerodynamics, and autonomous systems have allowed uncrewed aircraft to expand their roles, but at their heart, they were still jet propelled.

Thanks to a significant scientific breakthrough in detection methods, conducting secret underground nuclear tests could become obsolete.
A team of Earth scientists and statisticians say they can now tell with 99 percent accuracy if such an explosion has taken place. This is up from 82 percent and is based on a dataset of known tests in the US, according to the new study published in Geophysical Journal International. It has previously been tricky to differentiate between nuclear explosions and other seismic sources, such as naturally-occurring earthquakes or man-made noise above ground.
“The explosion goes off and you have all this energy that radiates out, which can be measured on seismometers,” said lead author Dr. Mark Hoggard, of The Australian National University (ANU). “So, the science problem becomes how do we tell the difference between that and a naturally-occurring earthquake?”
Ultimate fact presents top 15 Weapons Of The Future Will Blow Your Mind. We’ve come a long way since sticks and stones, and it’s almost inconceivable that only a few hundred years ago, Man was still waging war with bows, arrows, cannons, and muskets. Modern militaries are constantly in the process of developing new weapons, some of which will definitely make some mouths drop. We thought it would be fun to take a closer look at the most amazing offensive and defensive weapons currently in the works.
Autonomous weapons.
These are robotic vehicles, under development, that search and destroy enemy troops and equipment on the ground or in the air, without risk to friendly troops – theoretically.
Onboard computers interpret sensor data to identify and target hostile forces with built-in weapons. Robots may query human controllers at remote sites for the go-ahead to fire, and friendly forces may carry transponders that identify them as “friends”
High-energy lasers.
These are powerful energy beams that travel through air or space in straight lines. They travel at the speed of light and can strike over distances of thousands of kilometres. Large mirrors focus powerful laser beams onto a small spot on the target.
Space-based weapons.
Space is the ultimate high ground, so weapons in orbit would have the ability to see and zap anything on the ground, in the air, or nearby in space. The main mission of space-based weapons would be to defend against ballistic missiles fired at targets on Earth.
Hypersonic aircraft.
Launched from a standard runway, a hypersonic aircraft could fly faster than Mach 5 to strike anywhere in the world within two hours. It would also have enough thrust to deliver a satellite to low-Earth orbit. To get off the ground from a runway, a hypersonic plane would either hitch a ride on a conventional plane, or have its own conventional jet engine.
Active Denial System.
Millimetre-wave or microwave beams supposedly make people flee without injuring them. They might typically be powered by a generator fitted to a Humvee, in crowd control situations.
A 2-metre antenna and mobile generator produce and aim a beam of 95-gigahertz (3-millimetre) radiation.
Nuclear missiles.
Nuclear missiles are able to deliver unmatched destructive power anywhere in the world, making them the ultimate level of military power. One or more nuclear warheads are mounted on a ballistic missile, and launched vertically.
Stun guns (Tasers)
Tasers disable people with bursts of high-voltage electricity, allowing police to subdue them without lasting injury. A special gun fires darts on wires. These deliver a pulse of electricity that temporarily disrupts control of voluntary muscles.
E-bombs.
A rapid increase in electromagnetic field strength during a pulse, induces surges of electric current in conductors. This burns out electrical equipment – semiconductor chips are particularly vulnerable.
Layered missile defence.
Layered missile defence offers the best chance to shoot down attacking ballistic missiles.
Multiple anti-missile systems are deployed to target ballistic missiles during different stages of the attacking missile’s flight: Each phase, or layer, of defence increases the chance of successful destruction of the missile.
Information warfare.
This technique interferes with the flow of information vital to enemy operations, while defending friendly channels of communication. Information warfare specifically targets communication networks and computers.
‘Hyper Stealth’ or ‘Quantum Stealth’
Using naturally occurring metamaterials, scientists have been designing lightwave-bending materials that can greatly reduce the thermal and visible signatures of a target.
Electromagnetic Rail Guns.
EM rail gun launchers use a magnetic field rather than chemical propellants (e.g., gunpowder or fuel) to thrust a projectile at long range and at velocities of 4,500 mph to 5,600 mph. nautical miles using 32 megajoules.
The extended velocity and range of EM rail guns provides several benefits both in offensive and defensive terms, from precision strikes that can counter even the most advanced area defense systems to air defense against incoming targets.
Space Weapons.
Despite international pressure against the weaponization of space, major countries continue to explore technologies that would turn the sky above us into the next battleground.
Hypersonic Cruise Missiles and ‘Prompt Global Strike’
Had hypersonic cruise missiles existed in the mid-1990s, the U.S. might have rid itself of Al Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden much earlier than it did, and would have accomplished the feat in Afghanistan rather than in Pakistan.
Sentient’ Unmanned Vehicles.
Perhaps the single-most important development in the defense industry in the past decade is the emergence of unmanned vehicles.
Among this which one seems most terrible to you let us know in the comment section.
#UltimateFact #Weaon #Facts

Year 2017
North Korea claims it has again tested a hydrogen bomb underground and that it “successfully” loaded it onto the tip of an intercontinental ballistic missile, a claim that if true, crosses a “red line” drawn by South Korea’s president last month.
In a state media announcement, North Korea confirmed the afternoon tremors in its northeast were indeed caused by the test of a nuclear device, and that leader Kim Jong Un personally signed off on the test.
“North Korea has conducted a major Nuclear Test. Their words and actions continue to be very hostile and dangerous to the United States,” President Trump tweeted Sunday morning in response. “North Korea is a rogue nation which has become a great threat and embarrassment to China, which is trying to help but with little success.”

North Korean leader Kim Jong Un is “seriously preparing” for war as it builds its nuclear weapons arsenal, according to an expert on Korean history.
After decades of international pressure attempting to stop its development of nuclear weapons, North Korea announced during the administration of former President George W. Bush that it was conducting nuclear tests and had weapons. The country now has an arsenal that includes an estimated 35 to 63 warheads, according to the Institute for Science and International Security.
In an interview published by The Financial Times on Thursday, Kookmin University history professor Andrei Lankov said that Kim had been emboldened to build the nuclear arsenal due to Western leaders failing to take advantage of earlier opportunities to pressure the regime, wrongly believing that the nuclear program was not “a realistic threat.”
Although essentially the United Nations are now making nuclear weapons illegal with new treaties like nuclear disarmament. Russia currently has taken another route for globalization and possibly nuclear escalation. As currently the doomsday clock seems closer to midnight which could mean the end of the world scenarios due to Russias escalation and the possibility of all out nuclear war globally and then nuclear annihilation of the planet. Even with current wars are actually seemingly always going on but this global escalation of nuclear war is a zero sum game as no one would be the winner due to radiation levels circulating the planet. I do think that the us and china are in a treaty but so far Russia is still escalating which now holds the world now ransom.
This is a summary of Policy Brief 139 which is available with full references on the Toda Peace Institute’s website.
In January 2021, a global treaty came into force outlawing the bomb. The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW or Ban Treaty) is the most significant multilateral development in nuclear arms control since the Non-Proliferation Treaty’s (NPT) entry into force in 1970. It establishes a new normative settling point on the ethics, legality and legitimacy of the bomb.
The possession of nuclear weapons by nine countries did not suddenly became illegal with the treaty’s entry into force in January 2021. However, it would be false to claim that a UN-negotiated treaty, following a UN-authorised process and conference, has no implications for the legality and legitimacy of nuclear-weapon possession and practices.
