“Not all of these satellites are known to have oceans, but we know that some do,” said Dr. Max Rudolph. [ https://www.labroots.com/trending/space/30266/ocean-world-boiling-seas-2](https://www.labroots.com/trending/space/30266/ocean-world-boiling-seas-2)
Could ocean worlds in the outer solar system have boiling water underneath their icy crusts? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated the geochemical processes that could be occurring on ocean worlds orbiting in the outer solar system. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions on ocean worlds throughout the solar system and where we can best search for life beyond Earth.
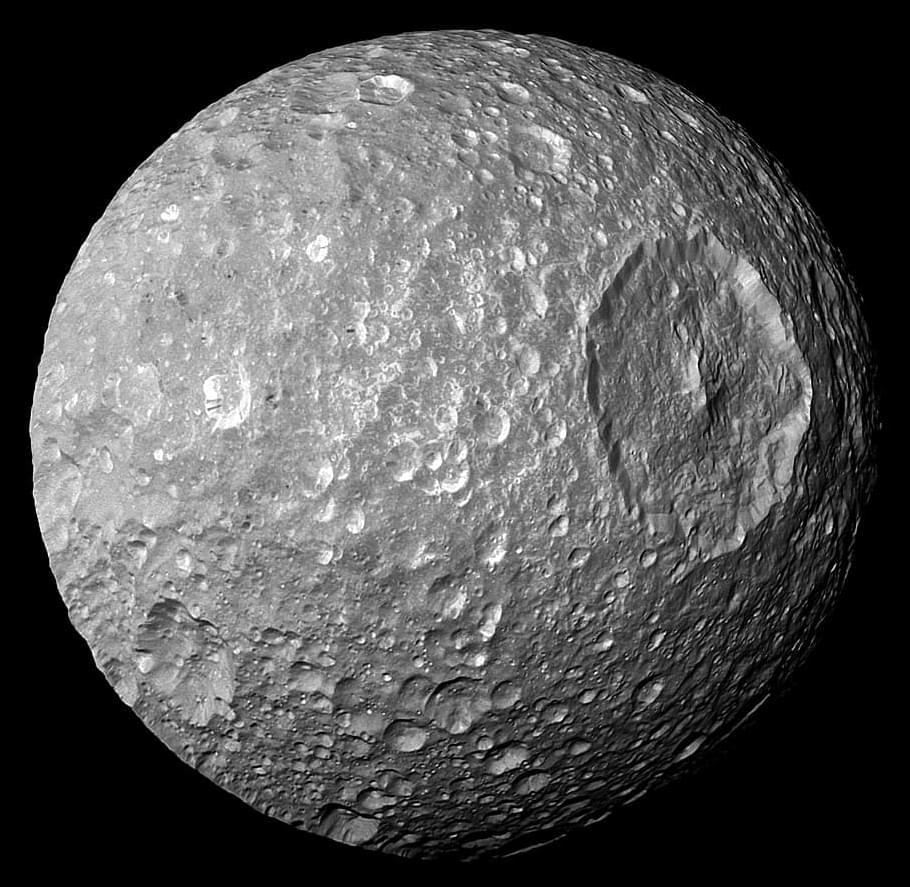
For the study, the researchers examined several icy moons orbiting Saturn and Uranus and what could happen as the ice shell on these moons becomes thinner over time. Specifically, they explored changes to the interior oceans beneath the icy shells, as some icy moons currently have oceans while others have evidence of past oceans that have since completely frozen over or escaped to space as water vapor.
In the end, the researchers identified different outcomes depending on the size of the moons. For example, if the ice shells on smaller moons like Saturn’s Mimas and Enceladus and Uranus’ Miranda become thinner, this could cause underlying oceans to boil from the decrease in pressure. However, if the ice shells on larger moons like Saturn’s Iapetus and Uranus’ Titania become thinner, this could lead to the ice shell collapsing, resulting in a type of plate tectonics.