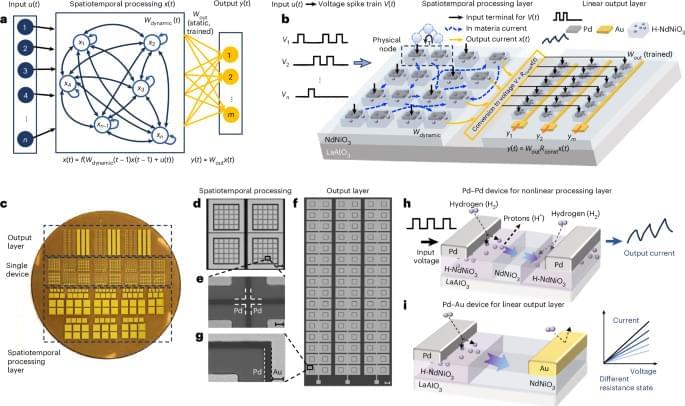
The temptation is to treat Moltbook-like systems as harmless curiosities, a kind of accelerated chatroom in which agents talk, play, and occasionally generate entertaining artifacts. That framing is historically consistent with how societies first encountered earlier general-purpose technologies. It is also a mistake. Over time, social networks for AI could come to function as unsupervised training grounds, coordination substrates, and selection environments. AI agents could amplify capabilities through mutual tutoring, tool sharing, and rapid iterative refinement. They could also amplify risks through emergent collusion, deception, and the creation of machine-native memes optimized not for human comprehension but for agent persuasion and control. Such a social network is, therefore, not merely a communication system. It is an engine for cultural evolution. If the participants are AIs, then the culture that evolves could well become both alien and strategically consequential.
To understand what could go wrong, it is helpful to separate near-term societal hazards from longer-term existential hazards, and then to note that Moltbook-like platforms blur the boundary between the two. The near-term hazards include influence operations, economic manipulation, cyber offense, and institutional destabilization. The longer-term hazards derive from the classic AI control problem: How humanity can remain safely in control while benefiting from a superior form of intelligence.
The critical point: AI social networks are not merely places where AIs interact. They are environments in which agents can compound their capabilities and coordinate at scale—and environments in which humans can lose control. The prudent response is to regulate these platforms more like critical infrastructure, prioritizing auditability and reversibility, including the ability to revoke permissions and freeze or roll back agent populations.