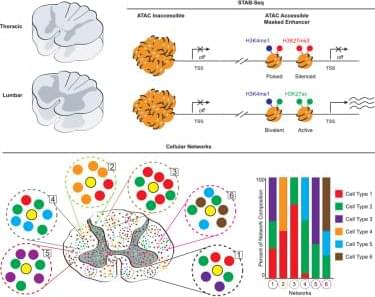
High-altitude survival gene in mammals may help reverse nerve damage from conditions like multiple sclerosis.
Neuron.
Li et al. report that a gain-of-function Retsat variant, associated with high-altitude adaptation, promotes myelination by boosting neuronal synthesis of the signaling metabolite ATDRA. This molecule activates RXR-γ in oligodendrocyte progenitors. Administration of the prodrug ATDR promotes remyelination in models of myelin disease.