A super-tough microbe may be able to survive being blasted from Mars into space—opening the door to interplanetary life transfer.


The universe is old enough, large enough, and chemically rich enough to have produced countless civilizations. And yet, when we listen, we hear nothing. The Great Filter hypothesis offers one of the most disturbing explanations in modern science — somewhere between dead chemistry and starfaring intelligence, there exists a barrier so severe that almost nothing gets through. But the real question isn’t whether the filter exists. It’s whether we’ve already passed it — or whether it’s still ahead of us, waiting. This video explores the formal probability argument behind the silence, the candidate barriers hiding in the deep history of biology, the existential threats that scale with technological power, and what every new discovery about life beyond Earth actually tells us about our own survival odds.
Sources:
Robin Hanson, \
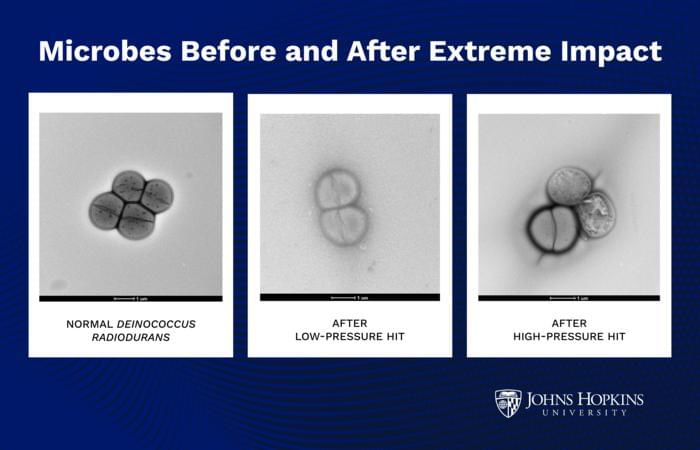
“Life might actually survive being ejected from one planet and moving to another,” said Dr. K.T. Ramesh. [ https://www.labroots.com/trending/space/30268/microbes-survi…-planets-2](https://www.labroots.com/trending/space/30268/microbes-survi…-planets-2)
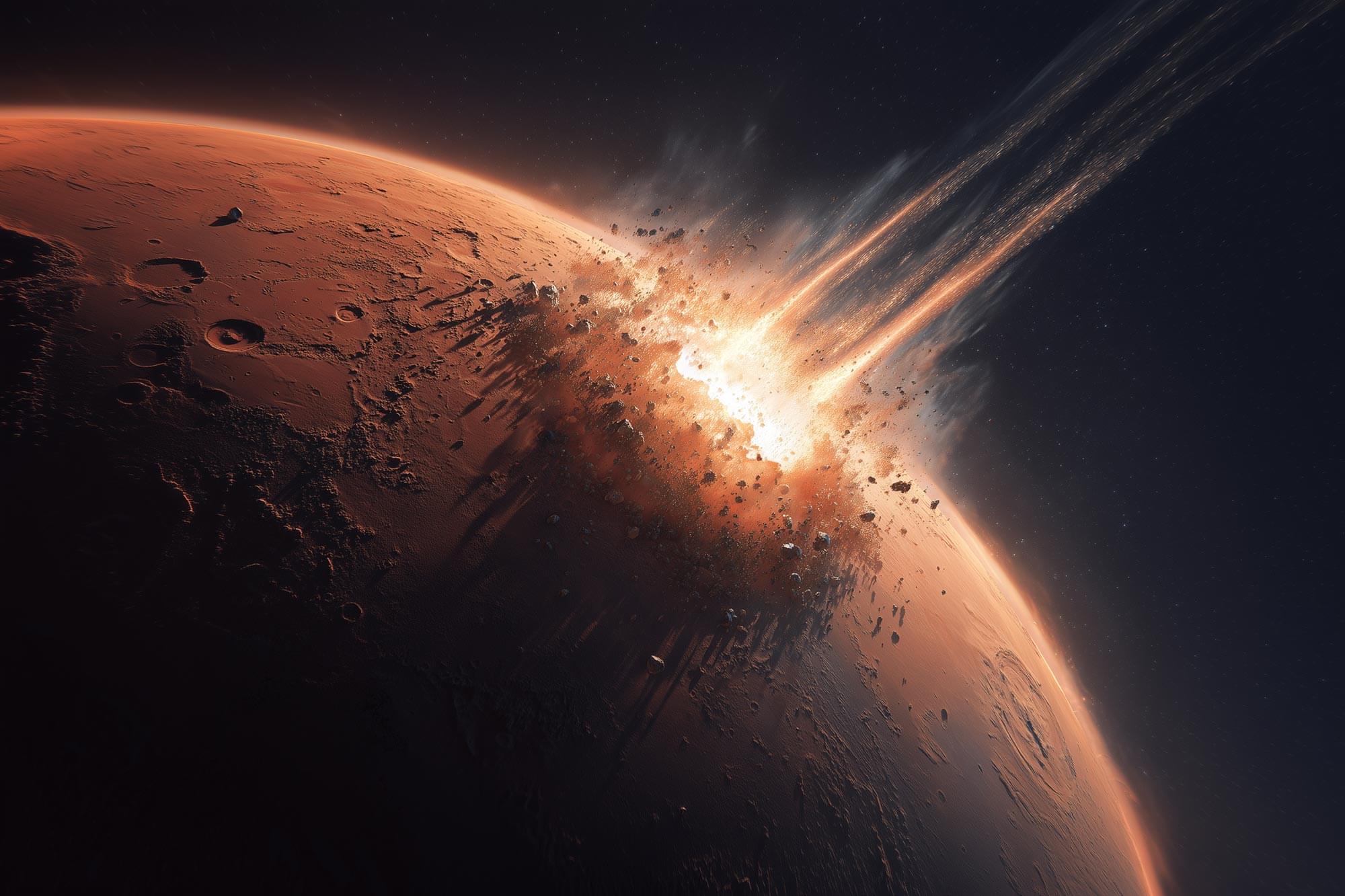
Can life transport between planets from impacts? This is what a recent study published in PNAS Nexus hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated how microbes could have come to Earth via asteroid impacts on planets like Mars. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand how life started on Earth and other worlds throughout the cosmos.
For the study, the researchers conducted a series of laboratory experiments where they subjected microorganisms to space-like conditions, specifically extreme pressure changes. The goal of the study was to ascertain the survival rate and overall response to the extreme environment, which could help determine if microorganisms could survive the extreme vacuum of space during a journey from Mars to Earth. This is because meteorites on Earth have been discovered to have originated from large impacts Mars, flinging chunks of rocks into deep space for millions of years, and crashing on Earth.
In the end, the researchers were surprised to find that the microorganisms in their experiments could survive the harshness of outer space, potentially even being able to travel from planet-to-planet. Potentially, if a large impact occurred on Mars, any microorganisms that existed there could survive the long and harsh journey to Earth.
⚠️⚠️⚠️Please note: The narration in this documentary is produced using advanced AI voice technology and is not voiced by a human narrator.⚠️⚠️⚠️
Sir David Attenborough: Have We Finally Solved the Fermi Paradox?
The universe contains hundreds of billions of galaxies. Each galaxy holds hundreds of billions of stars. Around many of those stars orbit planets — some potentially similar to Earth.
So where is everybody?
In 1950, physicist Enrico Fermi posed a simple yet unsettling question: if intelligent life is common in the cosmos, why have we found no evidence of it? This contradiction became known as the Fermi Paradox — one of the greatest mysteries in modern science.
In this immersive documentary, we explore whether recent discoveries in astronomy, astrobiology, and cosmology may finally offer an answer. From the staggering scale of the Milky Way to the discovery of thousands of exoplanets by missions like James Webb Space Telescope and Kepler Space Telescope, our understanding of the universe has transformed dramatically in just a few decades.
We examine the leading explanations: the Rare Earth hypothesis, the Great Filter theory, cosmic distance barriers, self-destruction scenarios, and the possibility that advanced civilizations may exist beyond our ability to detect them.
In this presentation, Dr. Roman V. Yampolskiy provides a rigorous examination of the fundamental limitations of Artificial Intelligence, arguing that as systems approach and surpass human-level intelligence, they become inherently unexplainable, unpredictable, and uncontrollable. He illustrates how the black box nature of deep learning prevents full audits of decision-making, while concepts like computational irreducibility suggest we cannot forecast the actions of a smarter agent without running it – often until it is too late for safety. He asserts that there is currently no evidence or mathematical proof to guarantee that a superintelligent system can be safely contained or aligned with human values.
Dr. Yampolskiy further bridges theoretical computer science with safety engineering by applying impossibility results, such as the Halting Problem and Rice’s Theorem, to demonstrate that certain safety guarantees for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) are mathematically unreachable. These technical impediments lead to a sobering discussion on existential risk, where the inability to verify or monitor advanced systems results in an alarmingly high probability of catastrophic outcomes. By analysing why advanced AI defies traditional engineering safety standards, he makes the case that current trajectories may lead to irreversible consequences for humanity.
To conclude, the talk shifts toward potential pathways for mitigation, emphasising the urgent need to prioritise specialised, narrow AI over the pursuit of general superintelligence. Dr. Yampolskiy argues that while narrow AI can solve global challenges within controllable parameters, the pursuit of AGI represents an existential gamble. He calls for a shift in the research community from a “move fast and break things” mentality to a mathematically grounded approach, urging that we must prove a problem is solvable before investing billions into its deployment.

Somewhere, out in the cold depths of space, there is a space rock that could destroy a large chunk of life on Earth. Is this fate inevitable? Could we find a way to stop it, or will we eventually suffer the same fate as the dinosaurs? And should this existential threat be keeping you up at night? Here’s what we know.
The asteroid that killed the dinosaurs 66 million years ago was at least 10 kilometres across, big enough to cause megatsunamis, ignite enormous forest fires and darken the skies the world over. Asteroids of that size are estimated to hit Earth about every 60 million years, based on the planet’s crater record. For the next size class down, asteroids about 1 kilometre across, estimates suggest they hit Earth about every million years, and the most recent one was about 900,000 years ago. Those numbers are enough to make you nervous.
But one of the things that sets humanity apart from the dinosaurs is our ability to look out into space and interpret what we see there. Naturally, researchers around the world have used this ability to attempt to learn how many asteroids are out there and what proportion of them are on trajectories that could be dangerous.
Image: angel_nt/Getty Images.
The dinosaurs were wiped out by an asteroid, but does that mean we risk suffering the same fate — and should you be worried about the possibility? Leah Crane sets the matter straight.
By Leah Crane
An exploration of extinction events for technological civilizations, but also extinction events that may happen to alien machine civilizations.
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
/ eventhorizonshow.
Music.
A exploration of the question of with Earth being 4.6 billion years old, then why wasn’t earth colonized by an alien civilization?
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
/ eventhorizonshow.
Music:
Fermi paradox the potentially extreme danger of mirror life.
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/eventhorizonshow.
Papers.
Subscribe: https://goo.gl/r5jd1F
Some call it The Great Silence, others The Fermi Paradox.
For the last 60 years, we’ve had our eyes and ears glued to the cosmos looking and listening for some sign letting us know we’re not all alone in the galaxy. And the more we discover, the harder it is to believe we’re the only ones.
Think about this for a moment; there’s around 2 trillion [2,000,000,000,000 galaxies] galaxies in the observable universe. Each one of those galaxies have on average 100 million stars. Some supergiants have one hundred trillion stars, and our Milky Way Galaxy has between 100 to 400 billion stars alone. It is likely that there’s at least this many planets floating around all those stars, and complex planetary systems that may resemble our own Solar System.
It brings us to the big question: where is everyone, and why haven’t we been contacted by an extra-terrestrial civilization from even inside our own galaxy? There should be many advanced civilizations out there, and we should have heard something from someone by now.
There are quite a few possible explanations for the ‘Great Silence’, and some researchers think they may have found some answers to this so-called paradox.