Nov 11, 2024
Assessing ways to gauge aging status
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: life extension
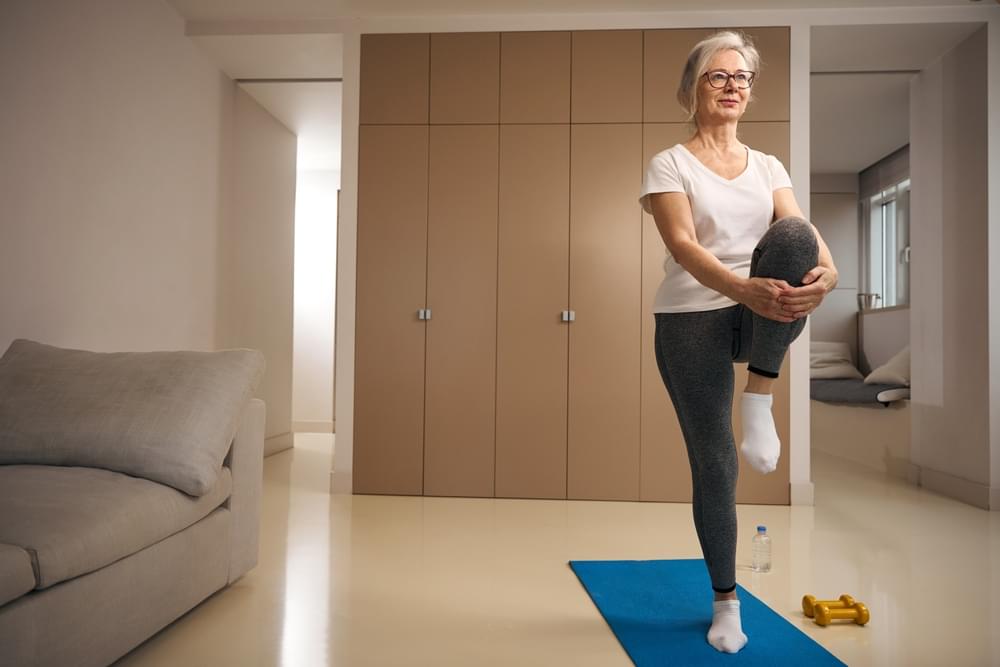
To learn more, a research team led by Drs. Asghar Rezaei and Kenton Kaufman of the Mayo Clinic set out to assess gait, balance, and strength in healthy people over age 50. Their study enrolled 40 participants. Half were between ages 50 and 64. The rest were ages 65 or older. In each group, half of the participants were female, and half were male.
Each participant underwent a series of tests in a motion analysis lab. Reflective markers were attached to specific locations on each participant’s feet, thighs, pelvis, head, and more. To assess gait, a 14-camera motion capture system recorded marker movements as people walked back and forth on an eight-meter-long walkway. Force plates on the floor measured ground reaction forces to detect changes in the center of pressure. Balance tests similarly used force plates to record movements and center of pressure data. The balance tests assessed the body’s sway as people stood on one leg with eyes open and on both legs with eyes open and closed. Grip strength and knee strength were measured by using specialized devices. Results were reported on October 23, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
The researchers found that gait characteristics—including walking speed and stride length—were not significantly affected by age. In contrast, several measures of balance and strength showed significant age-related reductions.