Microbial systems have been synthetically engineered to deploy therapeutic payloads in vivo.
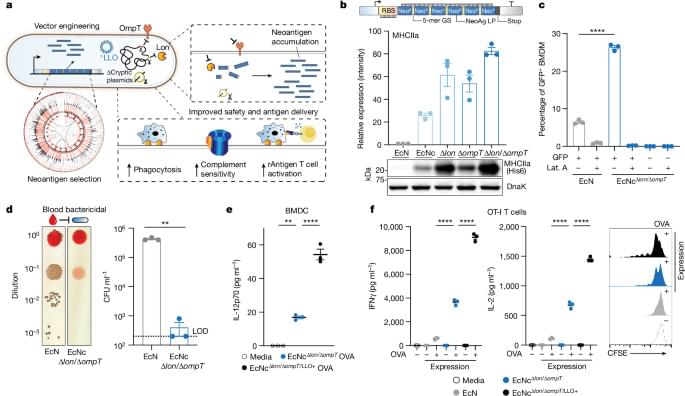
To enable effective cancer vaccination, we developed an engineered bacterial system in probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) to enhance expression, delivery and immune-targeting of arrays of tumour exonic mutation-derived epitopes highly expressed by tumour cells and predicted to bind major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II (Fig. 1a). This system incorporates several key design elements that enhance therapeutic use: optimization of synthetic neoantigen construct form with removal of cryptic plasmids and deletion of Lon and OmpT proteases to increase neoantigen accumulation, increased susceptibility to phagocytosis for enhanced uptake by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and presentation of MHC class II-restricted antigens, expression of listeriolysin O (LLO) to induce cytosolic entry for presentation of recombinant encoded neoantigens by MHC class I molecules and T helper 1 cell (TH1)-type immunity and improved safety for systemic administration due to reduced survival in the blood and biofilm formation.
To assemble a repertoire of neoantigens, we conducted exome and transcriptome sequencing of subcutaneous CT26 tumours. Neoantigens were predicted from highly expressed tumour-specific mutations using established methods14,15, with selection criteria inclusive of putative neoantigens across a spectrum of MHC affinity16,17. Given the importance of both MHC class I and MHC class II binding epitopes in antitumour immunity15,18,19, we integrated a measure of wild-type-to-mutant MHC affinity ratio—termed agretopicity17,20—for both epitope types derived from a given mutation, to help estimate the ability of adaptive immunity to recognize a neoantigen. Predicted neoantigens were selected from the set of tumour-specific mutations satisfying all criteria, notably encompassing numerous recovered, previously validated CT26 neoantigens15 (Extended Data Fig. 1a).
Continue reading “Probiotic neoantigen delivery vectors for precision cancer immunotherapy” »