Mar 8, 2023
Cyborg technology analyzes the functional maturation of stem-cell derived heart tissue
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, cyborgs
Research in animal models has demonstrated that stem-cell derived heart tissues have promising potential for therapeutic applications to treat cardiac disease. But before such therapies are viable and safe for use in humans, scientists must first precisely understand on the cellular and molecular levels which factors are necessary for implanted stem-cell derived heart cells to properly grow and integrate in three dimensions within surrounding tissue.
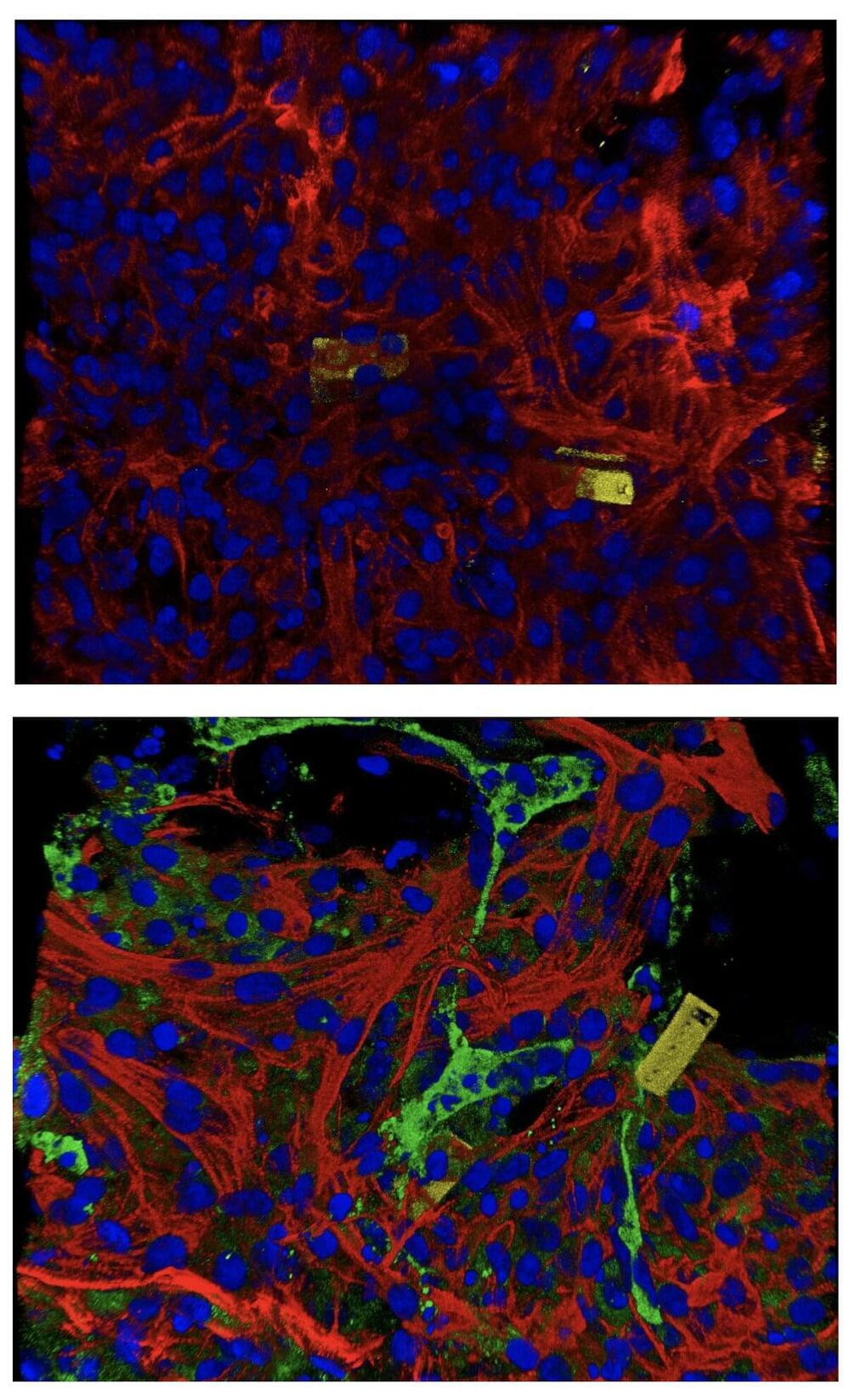
New findings from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) make it possible for the first time to monitor the functional development and maturation of cardiomyocytes—the cells responsible for regulating the heartbeat through synchronized electrical signals —on the single-cell level using tissue-embedded nanoelectronic devices. The devices—which are flexible, stretchable, and can seamlessly integrate with living cells to create “cyborgs”—are reported in a Science Advances paper.
“These mesh-like nanoelectronics, designed to stretch and move with growing tissue, can continuously capture long-term activity within individual stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes of interest,” says Jia Liu, co-senior author on the paper, who is an assistant professor of bioengineering at SEAS, where he leads a lab dedicated to bioelectronics.