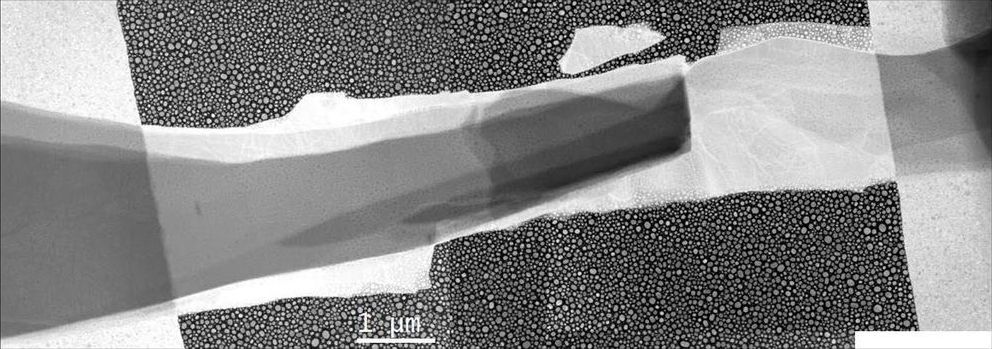
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a new method of 3D-printing gels and other soft materials. Published in a new paper, it has the potential to create complex structures with nanometer-scale precision. Because many gels are compatible with living cells, the new method could jump-start the production of soft tiny medical devices such as drug delivery systems or flexible electrodes that can be inserted into the human body.
A standard 3D printer makes solid structures by creating sheets of material—typically plastic or rubber—and building them up layer by layer, like a lasagna, until the entire object is created.
Using a 3D printer to fabricate an object made of gel is a “bit more of a delicate cooking process,” said NIST researcher Andrei Kolmakov. In the standard method, the 3D printer chamber is filled with a soup of long-chain polymers—long groups of molecules bonded together—dissolved in water. Then “spices” are added—special molecules that are sensitive to light. When light from the 3D printer activates those special molecules, they stitch together the chains of polymers so that they form a fluffy weblike structure. This scaffolding, still surrounded by liquid water, is the gel.