Researchers have designed a material that can act as a superconductor in a room heated to close to 60 degrees Fahrenheit — the warmest temperature yet.
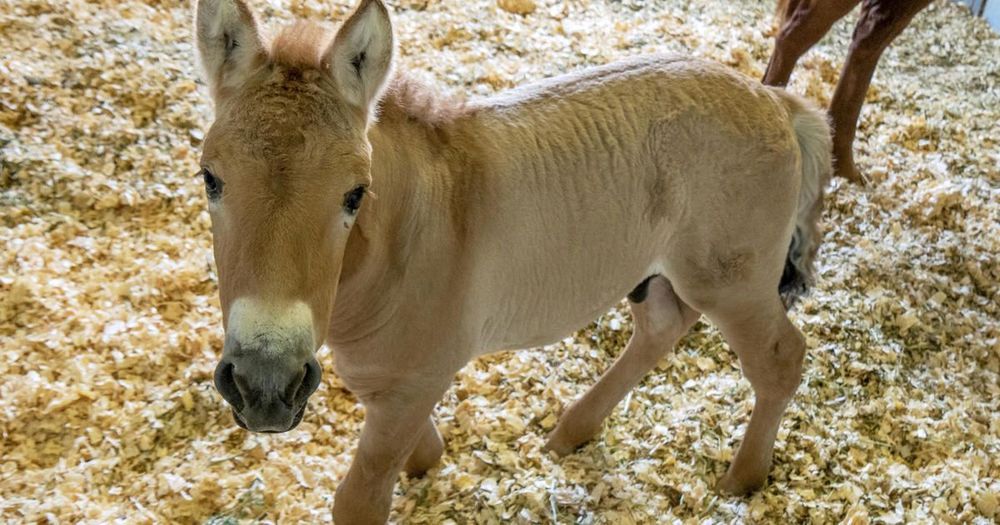


Little Kurt looks like any other baby horse as he frolics playfully in his pen. He isn’t afraid to kick or head-butt an intruder who gets in his way and, when he’s hungry, dashes over to his mother for milk.
But 2-month-old Kurt differs from every other baby horse of his kind in one distinct way: He’s a clone.
The rare, endangered Przewalski’s horse was created from cells taken from a stallion that had sat frozen at the San Diego Zoo for 40 years before they were fused with an egg from a domestic horse.


The research, out today from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and published in * Evolution and Human Behavior*, presents a hypothesis supporting a role for fructose, a component of sugar and high fructose corn syrup, and uric acid (a fructose metabolite), in increasing the risk for these behavioral disorders.
Johnson outlines research that shows a foraging response stimulates risk taking, impulsivity, novelty seeking, rapid decision making, and aggressiveness to aid the securing of food as a survival response. Overactivation of this process from excess sugar intake may cause impulsive behavior that could range from ADHD, to bipolar disorder or even aggression.” “Johnson notes, “We do not blame aggressive behavior on sugar, but rather note that it may be one contributor.”” “The identification of fructose as a risk factor does not negate the importance of genetic, familial, physical, emotional and environmental factors that shape mental health,” he adds.
Huh, want to know more.
“New research suggests that conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity syndrome (ADHD), bipolar disorder, and even aggressive behaviors may be linked with sugar intake, and that it may have an evolutionary basis.
The research, out today from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and published in Evolution and Human Behavior, presents a hypothesis supporting a role for fructose, a component of sugar and high fructose corn syrup, and uric acid (a fructose metabolite), in increasing the risk for these behavioral disorders.
“We present evidence that fructose, by lowering energy in cells, triggers a foraging response similar to what occurs in starvation,” said lead author Richard Johnson, MD, professor at the University of Colorado School of Medicine on the CU Anschutz Medical Campus.
In the largest clinical trial of its kind, researchers show that combining sound and electrical stimulation of the tongue can significantly reduce tinnitus, commonly described as “ringing in the ears.” They also found that therapeutic effects can be sustained for up to 12 months post-treatment.
The findings could potentially help millions of people since tinnitus affects about 10 to 15 percent of the population worldwide. The study was conducted by researchers from the University of Minnesota, Trinity College, St. James’s Hospital, University of Regensburg, University of Nottingham, and Irish medical device company Neuromod Devices Limited.
The research was published as the cover story of Science Translational Medicine, an interdisciplinary medical journal by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
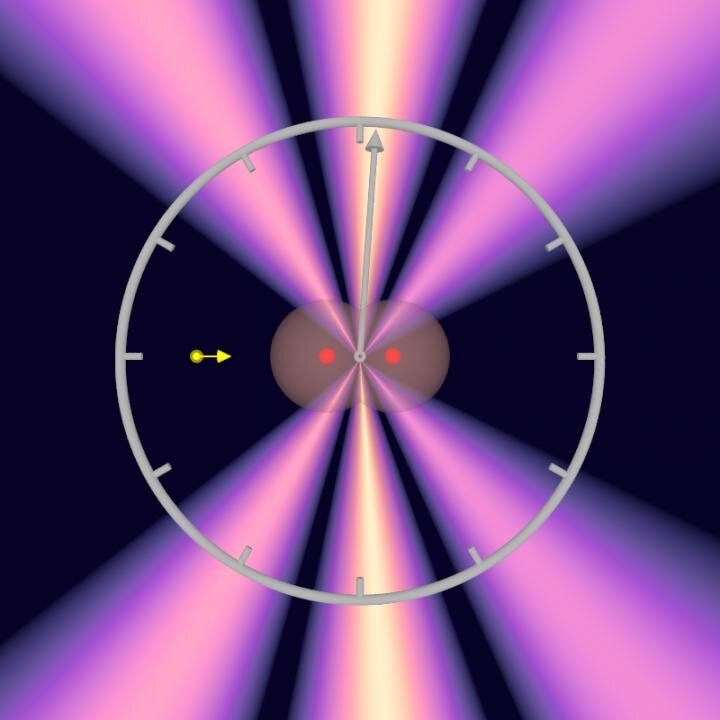
In 1999, the Egyptian chemist Ahmed Zewail received the Nobel Prize for measuring the speed at which molecules change their shape. He founded femtochemistry using ultrashort laser flashes: the formation and breakup of chemical bonds occurs in the realm of femtoseconds.
Now, atomic physicists at Goethe University in Professor Reinhard Dörner’s team have for the first time studied a process that is shorter than femtoseconds by magnitudes. They measured how long it takes for a photon to cross a hydrogen molecule: about 247 zeptoseconds for the average bond length of the molecule. This is the shortest timespan that has been successfully measured to date.
The scientists carried out the time measurement on a hydrogen molecule (H2) which they irradiated with X-rays from the X-ray laser source PETRA III at the Hamburg accelerator facility DESY. The researchers set the energy of the X-rays so that one photon was sufficient to eject both electrons out of the hydrogen molecule.

There’s rough terrain – then there are the craters and near-vertical cliffs on the Moon, Mars, and beyond. The DuAxel is a robot built for situations just like those. By creating two single-axle rovers that can combine into one with a central payload we could maximize versatility during future missions. See more details: go.nasa.gov/34QNo5T.

A peer-reviewed study by scientists at the Environmental Working Group estimates that more than 200 million Americans could have the toxic fluorinated chemicals known as PFAS in their drinking water at a concentration of 1 part per trillion, or ppt, or higher. Independent scientific studies have recommended a safe level for PFAS in drinking water of 1 ppt, a standard that is endorsed by EWG.
The study, published today in the journal Environmental Science & Technology Letters, analyzed publicly accessible drinking water testing results from the Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Geological Survey, as well as state testing by Colorado, Kentucky, Michigan, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Carolina and Rhode Island.
“We know drinking water is a major source of exposure of these toxic chemicals,” said Olga Naidenko, Ph.D., vice president for science investigations at EWG and a co-author of the new study. “This new paper shows that PFAS pollution is affecting even more Americans than we previously estimated. PFAS are likely detectable in all major water supplies in the U.S., almost certainly in all that use surface water.”
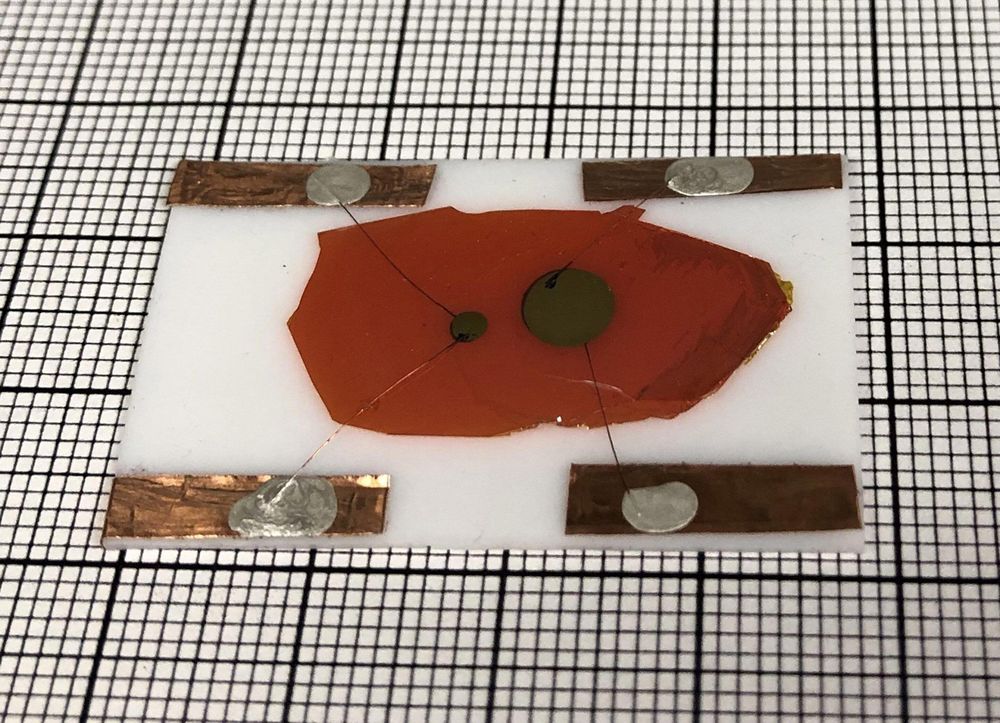
Homeland Security might soon have a new tool to add to its arsenal.
Researchers at Northwestern University and Argonne National Laboratory have developed a new material that opens doors for a new class of neutron detectors.
With the ability to sense smuggled nuclear materials, highly efficient neutron detectors are critical for national security. Currently, there are two classes of detectors which either use helium gas or flashes of light. These detectors are very large — sometimes the size of a wall.
PLEASE sign our petition in support of the Neuro-Specific Human Rights Bill here: http://chng.it/pkCvhRMS
Watch our latest video describing the bill here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gFLBrd3vuIw
Our website: http://www.globalneuroethics.com
Our GoFundMe campaign: https://www.gofundme.com/f/global-neuroethics-neurorights-bill-proposal
Please help us enact the Neuro-Specific Human Rights Bill into legislation by sharing the links above on all social media platforms!