Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is one of the most aggressive and hardest forms of breast cancer to treat, but a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine suggests a surprising way to stop it from spreading. Researchers have discovered that an enzyme called EZH2 drives TNBC cells to divide abnormally, which enables them to relocate to distant organs. The preclinical study also found drugs that block EZH2 could restore order to dividing cells and thwart the spread of TNBC cells.
“Metastasis is the main reason patients with triple negative breast cancer face poor survival odds,” said senior author Dr. Vivek Mittal, Ford-Isom Research Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery and member of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine. “Our study suggests a new therapeutic approach to block metastasis before it starts and help patients overcome this deadly cancer.”
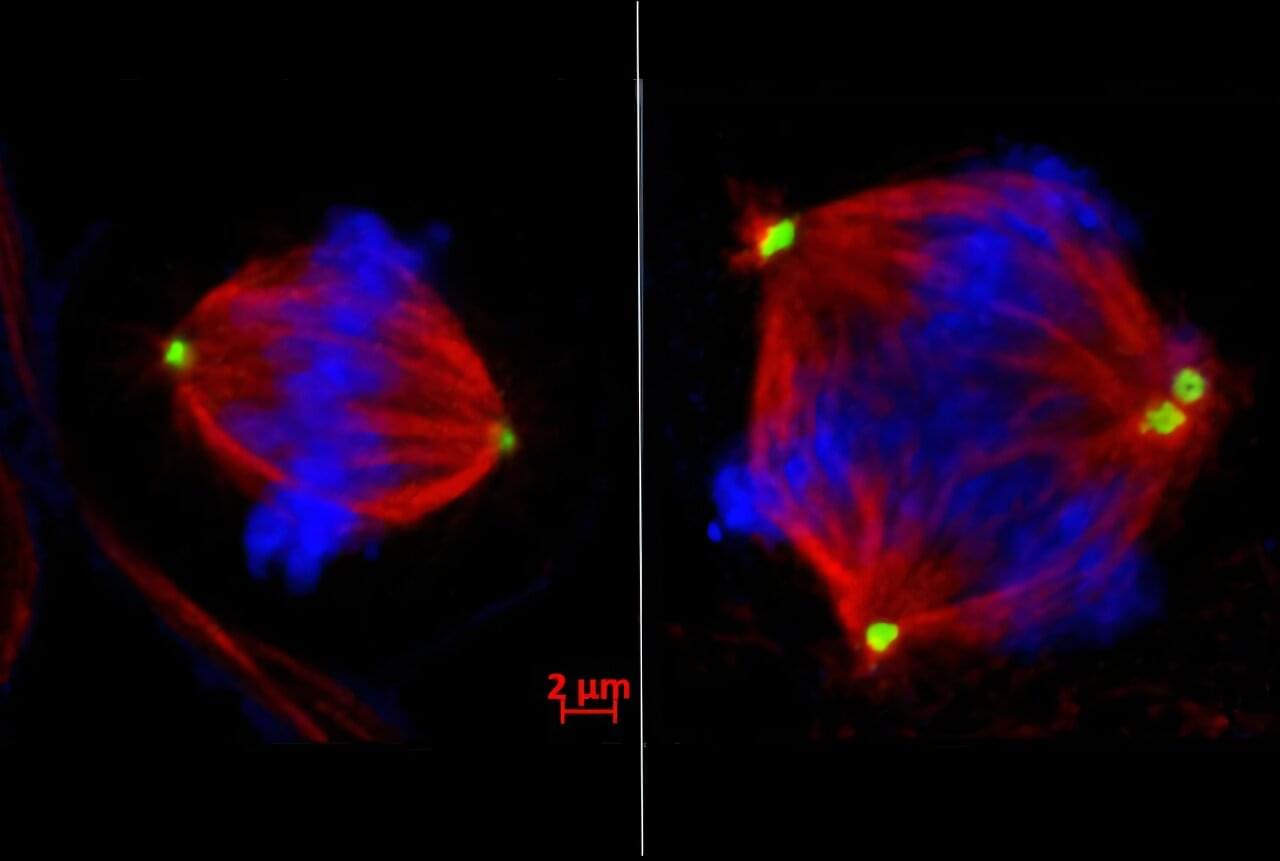
The findings, published Oct. 2 in Cancer Discovery, challenge the popular notion that cancer treatments should boost cell division errors already occurring in tumor cells beyond the breaking point to induce cell death. When normal cells divide, the chromosomes—DNA “packages” carrying genes—are duplicated and split evenly into two daughter cells. This process goes haywire in many cancer cells, leading to chromosomal instability: too many, too few, or jumbled chromosomes in multiple daughter cells.