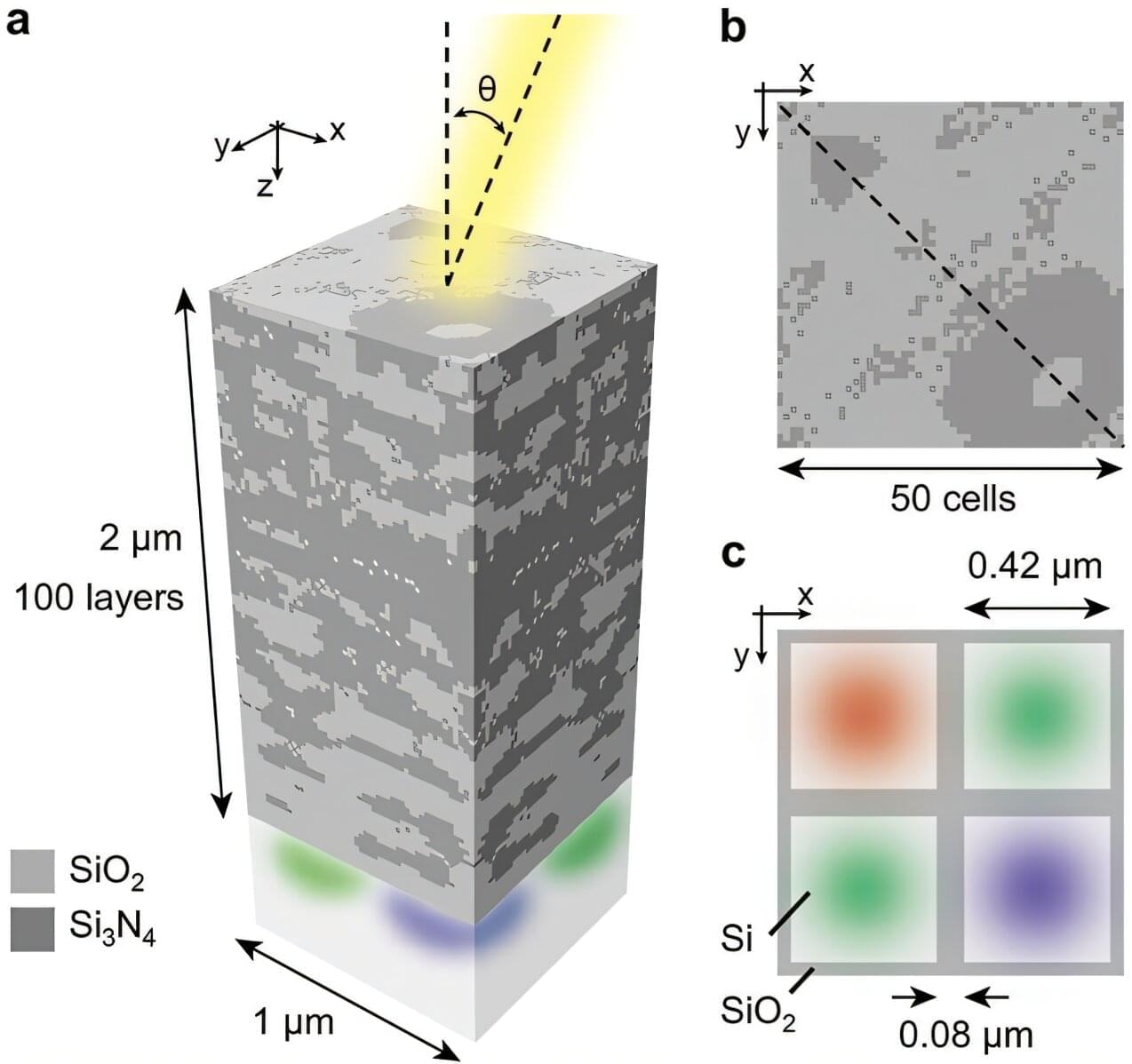
Smartphone cameras are becoming smaller, yet photos are becoming sharper. Korean researchers have elevated the limits of next-generation smartphone cameras by developing a new image sensor technology that can accurately represent colors regardless of the angle at which light enters. The team achieved this by utilizing a “metamaterial” that designs the movement of light through structures too small to be seen with the naked eye.
A research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang of the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Haejun Chung’s team at Hanyang, has developed a metamaterial-based technology for image sensors that can stably separate colors even when the angle of light incidence varies.
The findings were published in Advanced Optical Materials.