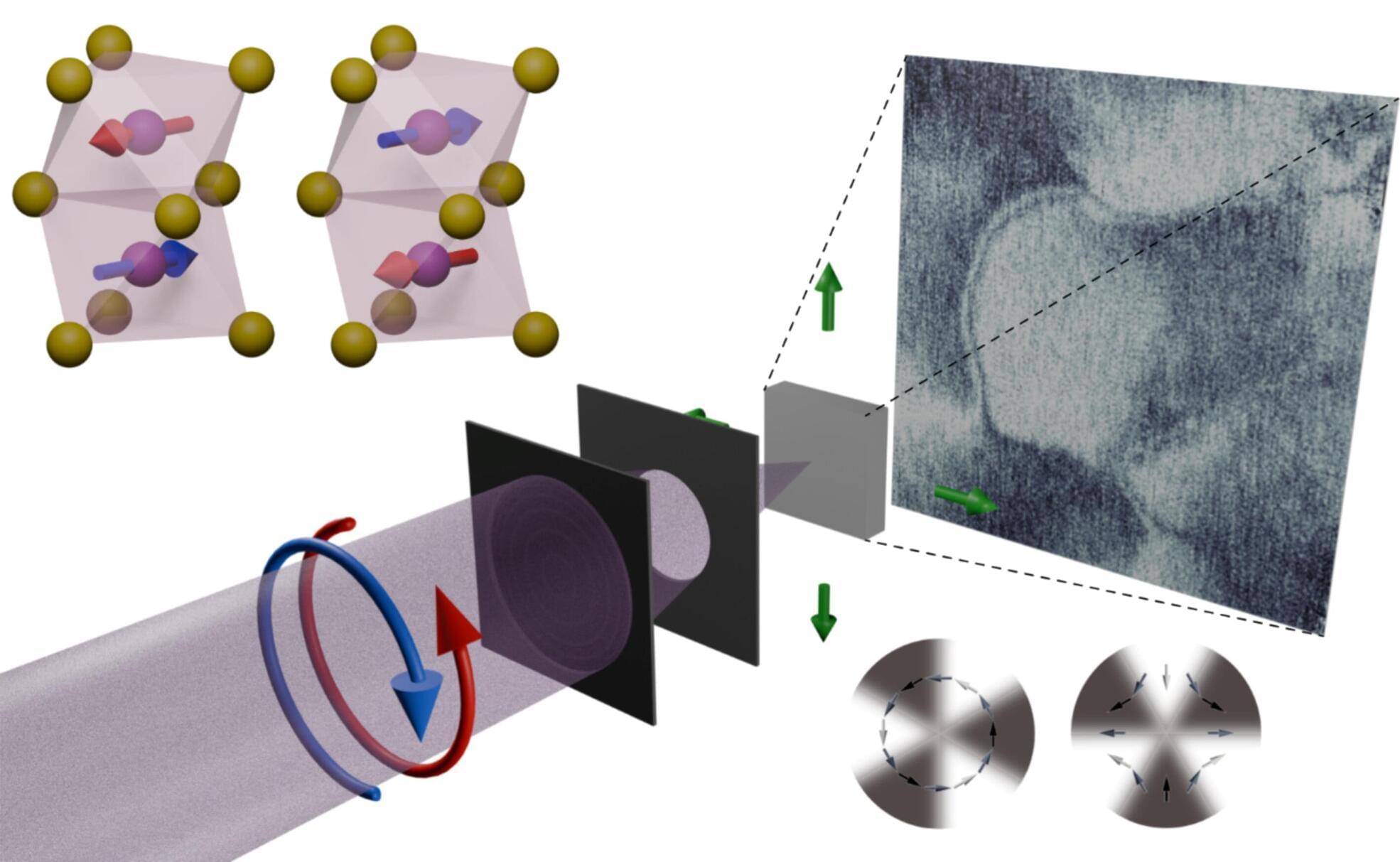
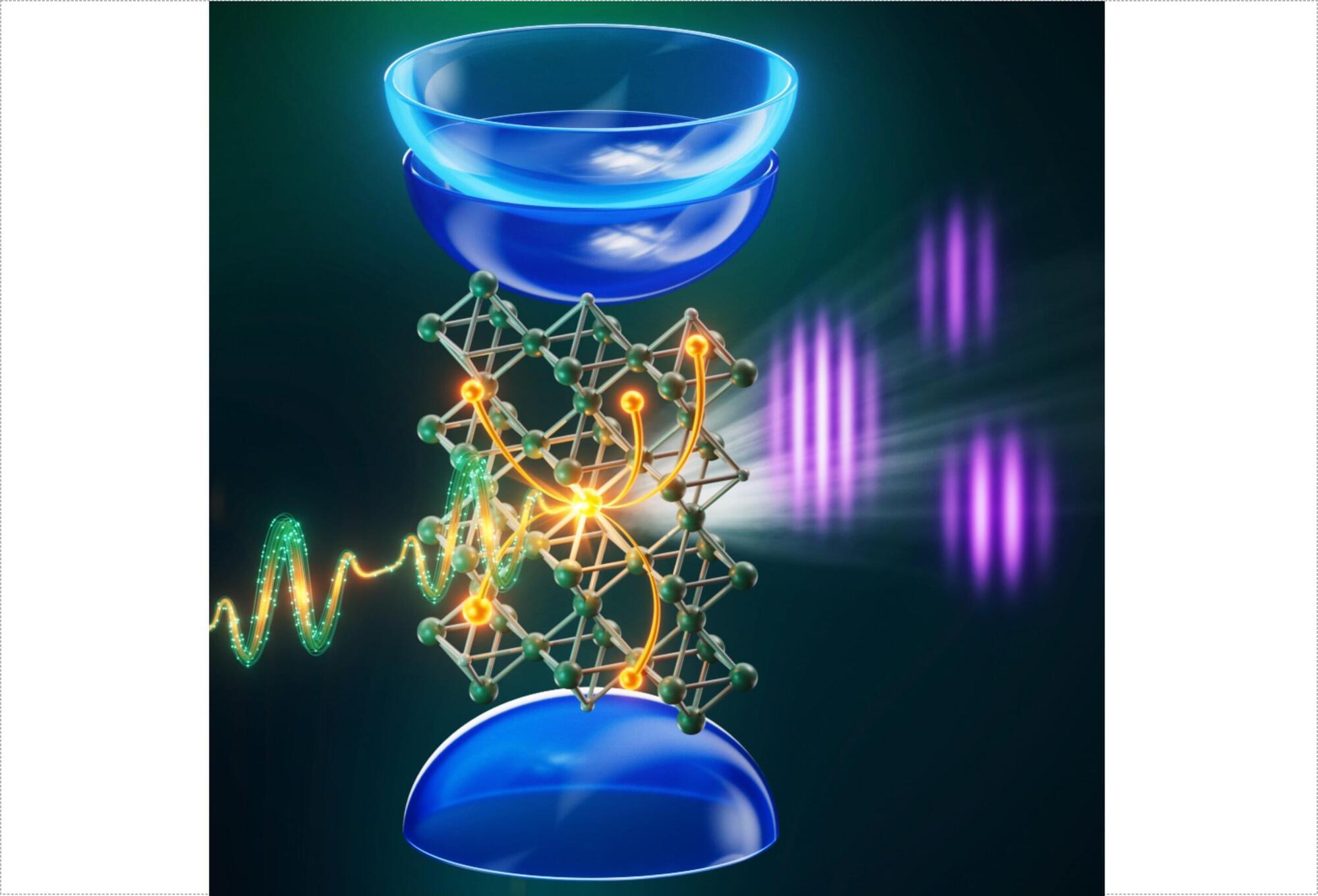
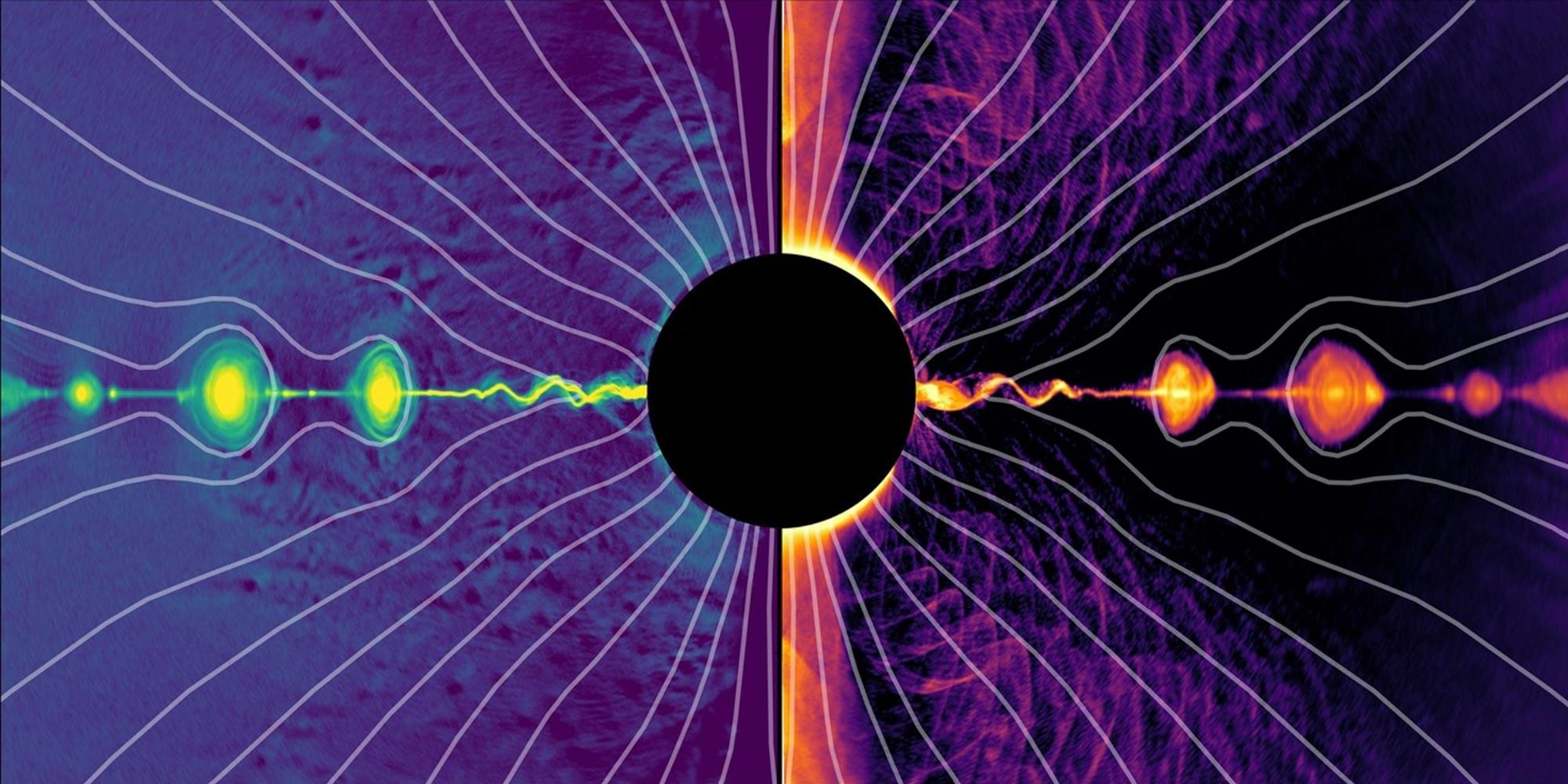
Magnetic materials have been known since ancient times and play an important role in modern society, where the net magnetic order offers routes to energy harvesting and data processing. It is the net magnetic moment of ferromagnets that has so far been key to their applications, with an alternative type of magnetic material, the antiferromagnet, deemed “useless” by their discoverer Louis Néel in his Nobel Prize lecture.
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in antiferromagnets, which offer a number of exciting advantages for technologies including robust order and ultrafast dynamics—however with the challenge that they are hard to detect and manipulate electrically.
The recent discovery of a new type of magnetic order—the altermagnet—has overturned this view: by combining antiferromagnetic ordering with ferromagnet-like properties such as spintronic effects, they promise a multitude of advantages for future applications.