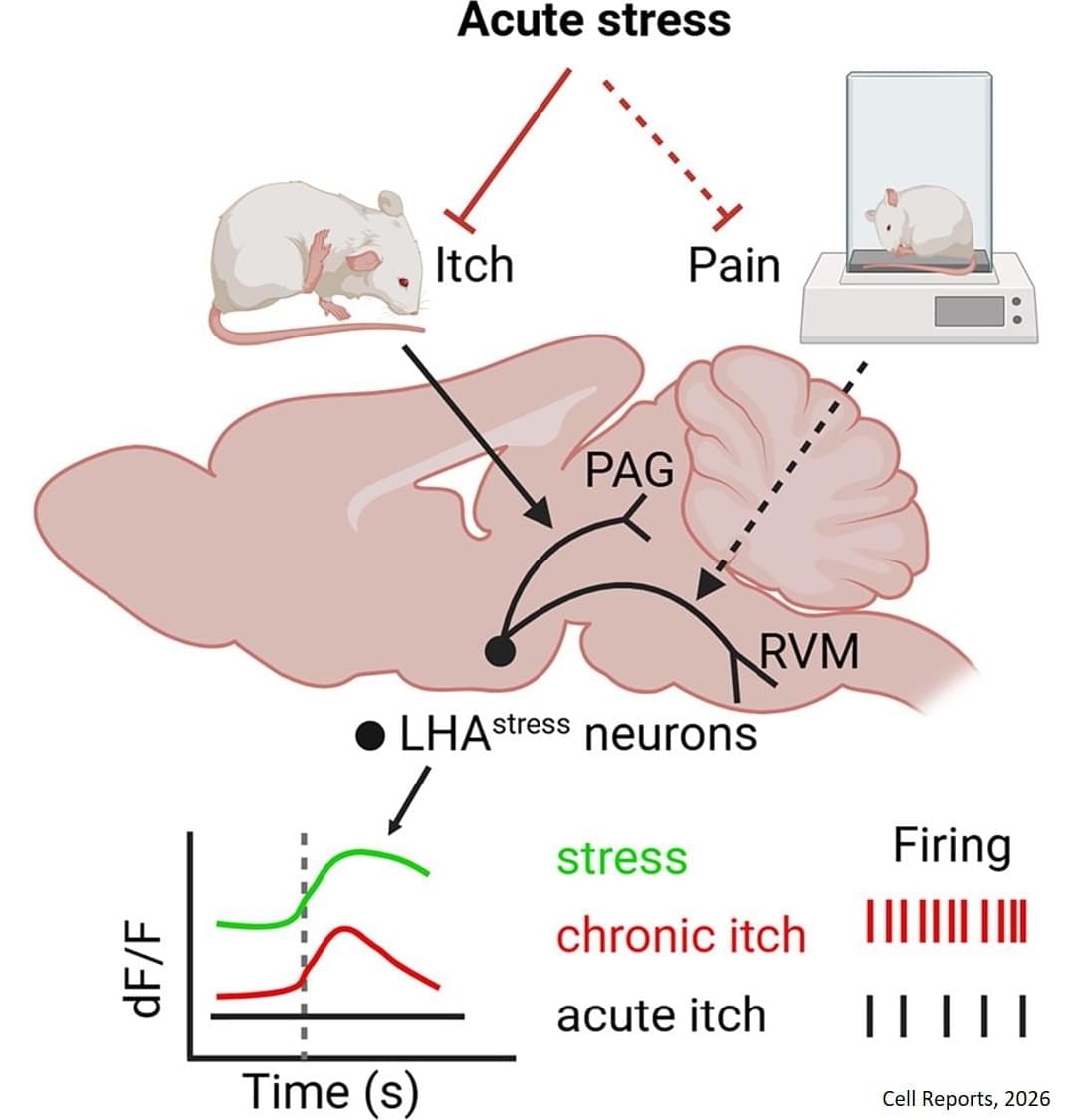
The researchers then tested whether these stress-activated neurons directly influence itch. “We ran some pilot experiments, and we saw that surprisingly, acute stress was able to suppress acute itching,” says the first author of the study.
When the team artificially activated the stress neurons, scratching behaviour decreased in both short-term chemically induced itch and a psoriasis-like chronic itch model. Conversely, when these neurons were silenced, stress no longer reduced scratching. These results showed that these neurons are both necessary and sufficient for stress-induced suppression of itch.
“We show that a specific circuit in the lateral hypothalamus can suppress itch during acute stress, revealing how the brain directly links emotional states to sensory perception,” says the corresponding author. “By identifying the specific neural circuit that links stress to itch, we are opening the possibility of targeting these brain mechanisms to better manage chronic stress-induced worsening of itch.” ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.
Researchers have mapped a neural circuit in the brain involved in the complex relationship between itch and stress. Their findings, published in Cell Reports, reveal how specific neurons activated during stress can directly regulate itch.
Itch and pain are both unpleasant sensations triggered by harmful or irritating stimuli, but they lead to different behavioural responses. While pain typically causes us to withdraw (such as pulling our hand away from a fire), itch drives scratching. Scientists have long known that emotional states such as stress and anxiety can influence the intensity of these sensations. While the neural mechanisms linking stress and pain have been studied extensively, the effect of stress on itch has remained poorly understood.
In the new study, the team focused on the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), a brain region known to regulate stress, motivation, and emotional states. Using genetically engineered mouse models, the researchers identified a specific population of neurons in the LHA that become active during acute stress.