A new method for checking the reliability of a quantum computer can be scaled up to devices of any size.
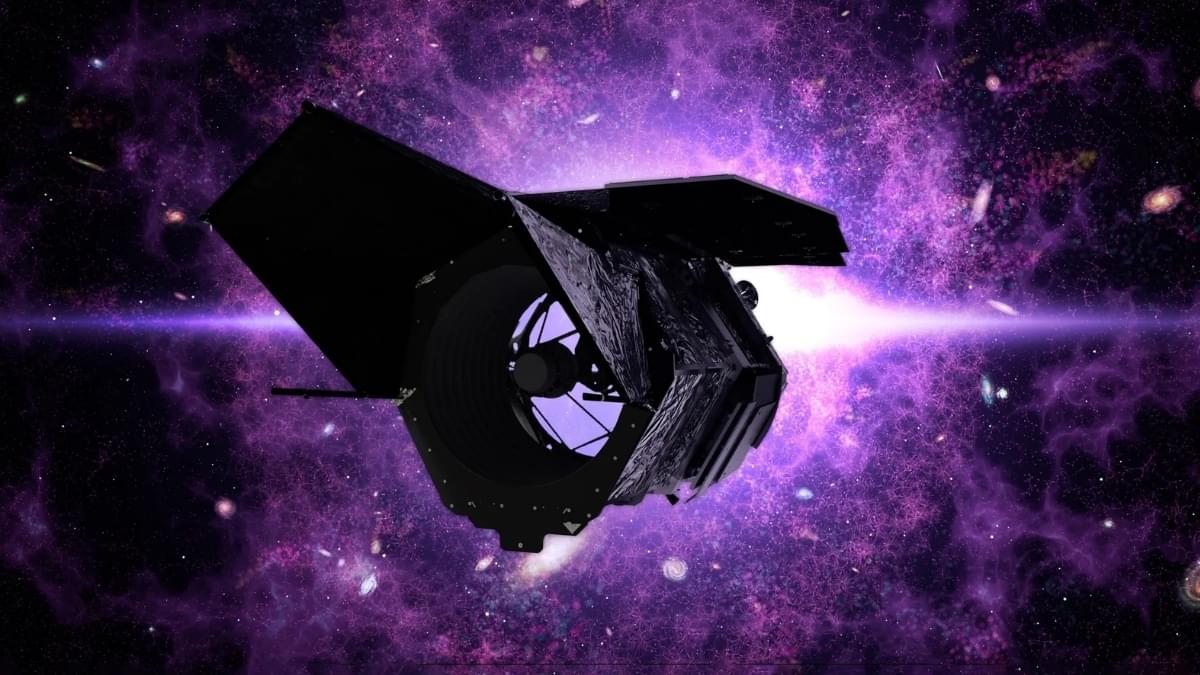


If you feel a thrill every time we discover something new about the cosmos, then November 25th may have been a noteworthy day to you. That’s the day that NASA completed assembly of the Nancy Grace Roman Telescope.
The two main segments of the powerful space telescope were joined together in the large clean room at Goddard Space Flight Center that day. This means that the telescope is on track for launch as early as Fall 2026.
The Roman is an infrared telescope that’s set to become a flagship in the telescope fleet. It has only two instruments, the Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) and the Coronagraph Instrument (CGI).
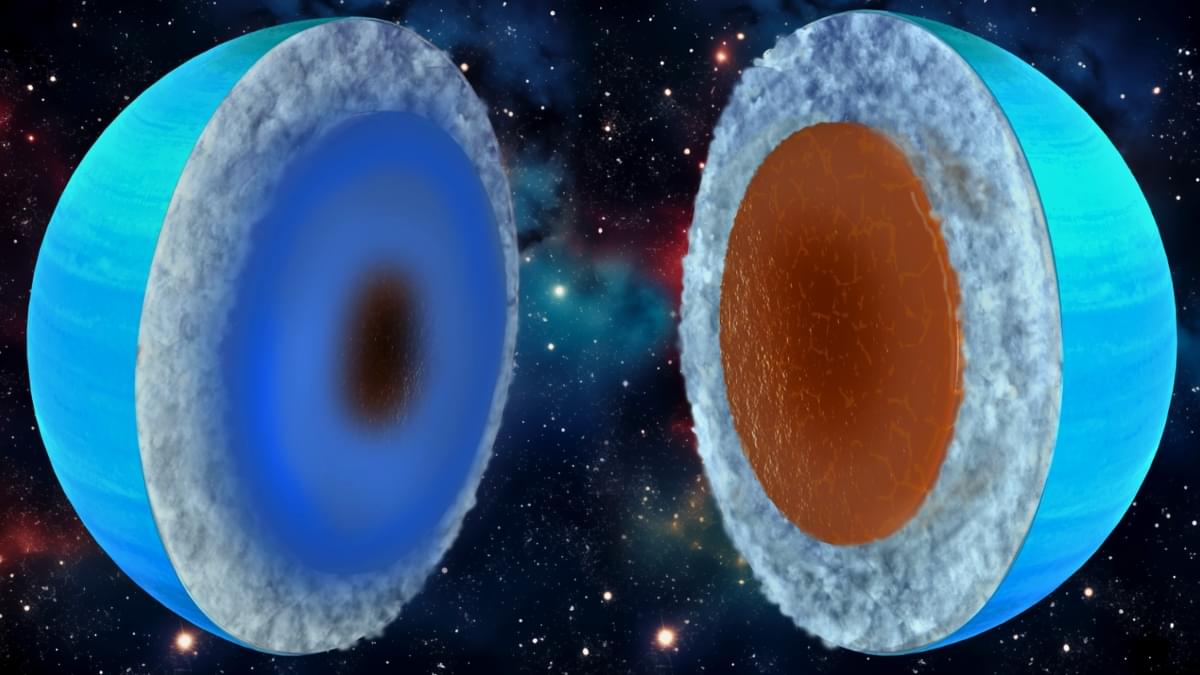
Although they are technically gas giants, Uranus and Neptune are referred to as “ice giants” due to their composition.
This refers to the fact that Uranus and Neptune have more methane, water, and other volatiles than their larger counterparts (Jupiter and Saturn).
Given the pressure conditions in the planets’ interiors, these elements become solid, essentially becoming ‘ices.’

Scientists have used a specially engineered virus to help track the brain changes caused by psilocybin in mice, revealing how the drug could be breaking loops of depressive thinking.
This may explain why psilocybin keeps showing positive results for people with depression in clinical trials.
“Rumination is one of the main points for depression, where people have this unhealthy focus, and they keep dwelling on the same negative thoughts,” says Cornell University biomedical engineer Alex Kwan.





Ransomware groups are targeting hypervisors to maximize impact, allowing a single breach to encrypt dozens of virtual machines at once. Drawing on real-world incident data, Huntress explains how attackers exploit visibility gaps at the hypervisor layer and outlines steps orgs can take to harden virtualization infrastructure.