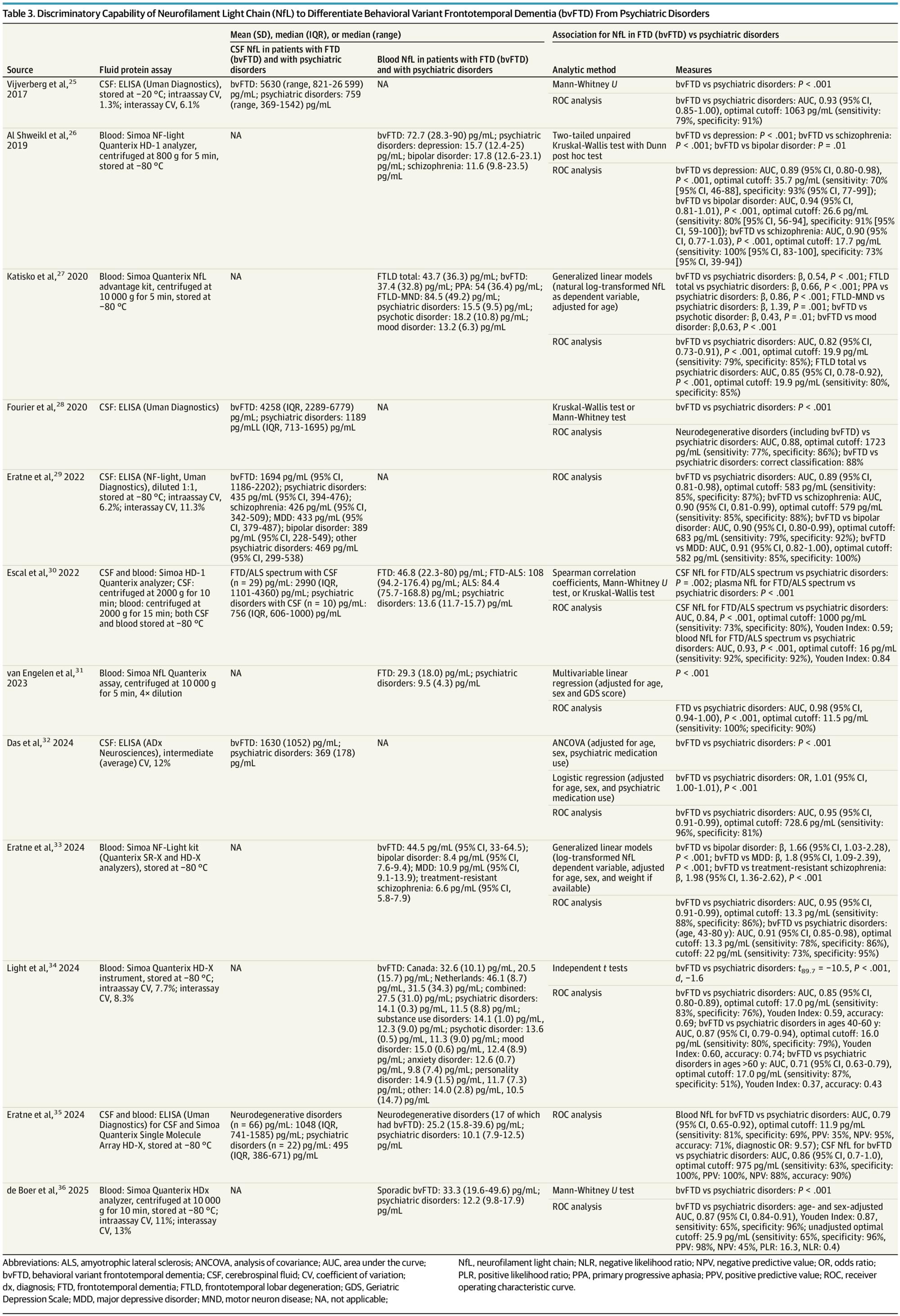
Neurofilament light chain levels in cerebrospinal fluid and blood are higher in patients with behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia than psychiatric disorders, suggesting its potential as a biomarker to aid in differentiating these conditions.
This systematic review aimed to determine whether elevated CSF or blood NfL can aid clinicians in differentiating bvFTD from psychiatric disorders. Across 12 studies reviewed, CSF and blood NfL levels were consistently significantly higher in patients with bvFTD than patients with psychiatric disorders at the group level. Furthermore, CSF and blood NfL demonstrated reasonable sensitivity and specificity to differentiate bvFTD from psychiatric disorders,38 though classification accuracy varied somewhat by study. While some of the AUCs for NfL differentiating bvFTD from psychiatric disorders had wide confidence intervals, these findings suggest a possible role for NfL in diagnostic clarification of patients with neuropsychiatric presentations. Misdiagnosing bvFTD as a psychiatric disorder may delay patients with bvFTD from early access to clinical trials when treatments may be more effective. Conversely, misdiagnosing a psychiatric disorder as bvFTD may worsen quality of life and delay treatment of ameliorable conditions.39-41
The existing literature has important limitations. Most studies were case control in design since they enrolled patients meeting diagnostic criteria for bvFTD or psychiatric disorders and then examined the association of NfL with these diagnoses. While these studies are essential for determining construct validity, they are not representative of the real-world clinical conditions by which NfL would be used. Also, such methods risk biased interpretations of the relationship of NfL with these conditions. Further studies are needed that prospectively recruit patients with neuropsychiatric symptoms and obtain NfL using clinically available assays to aid in real-time differential diagnosis.
An additional limitation of the reviewed studies is the selection and heterogeneity of psychiatric disorders. Several of the reviewed studies included patients with primary substance use, adjustment, or functional neurological disorder diagnoses.27, 31, 32,34, 35 Mood disorders, schizophrenia, and OCD may have the greatest symptom overlap with bvFTD.42 However, only 5 studies reported enrolling a total of 9 patients with OCD,25, 29, 31, 35, 36 a condition with an estimated OR of onset of 4.9 among individuals aged 45 to 59 years,43 suggesting a need for studies that include more patients with psychiatric disorders more likely to mimic core features of bvFTD despite absence of suspected neurodegenerative pathology. Moreover, FTD phenocopy syndromes (phFTD), clinical features that mimic FTD of mid-to late-life onset but do not progress to dementia, are understudied.44 Only 1 study in this review included a total of 2 patients with phFTD.