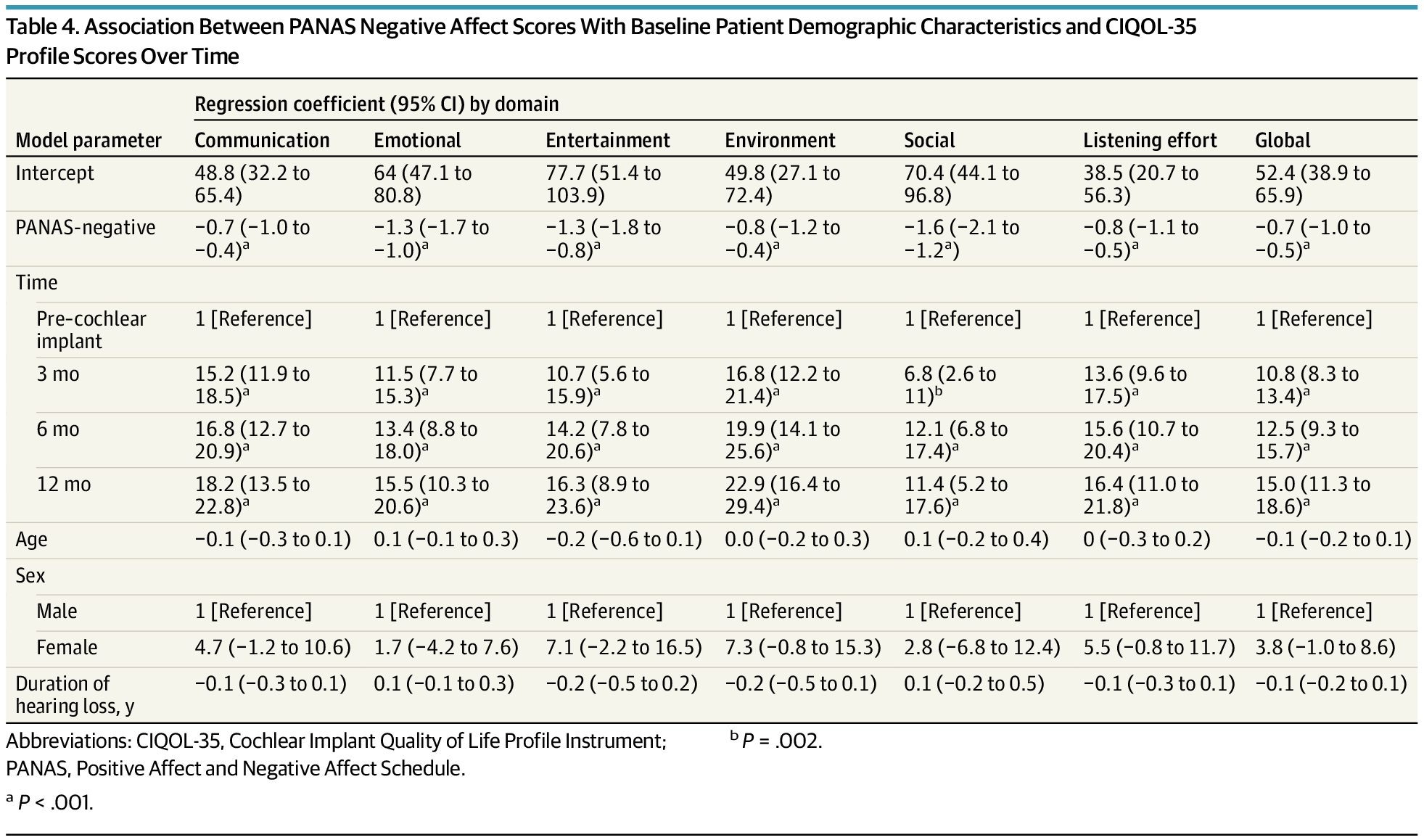
In adults receiving cochlear implants, gains in positive affect and reductions in negative affect corresponded with improvements in quality-of-life scores across listening, communication, and participation domains. Strongest statistical associations were observed in social and emotional CIQOL areas, but effect sizes were small.
Importance The use of patient-reported outcome measures to assess outcomes in adults who use cochlear implants has increased, as highlighted by the inclusion of the Cochlear Implant Quality of Life (CIQOL) instruments in the Minimal Speech Testing Battery, version 3. However, the self-reported nature of these instruments raises questions regarding how psychosocial characteristics impact responses.
Objective To assess whether affect and CIQOL domain scores change over time and whether affect is associated with CIQOL domain scores.
Design, Setting, and Participants Prospective longitudinal cohort study in adult cochlear implant candidates (aged 18–89 years) meeting indications for cochlear implantation based on bilateral moderate to profound hearing loss with aided sentence recognition scores 60% or less between September 19, 2019, and October 8, 2021, in a single tertiary otolaryngology referral center. Patients receiving a second cochlear implant and those without Montreal Cognitive Assessment scores were excluded. Follow-up duration was 1 year. Data analysis was performed between October 15, 2023, and August 5, 2025.