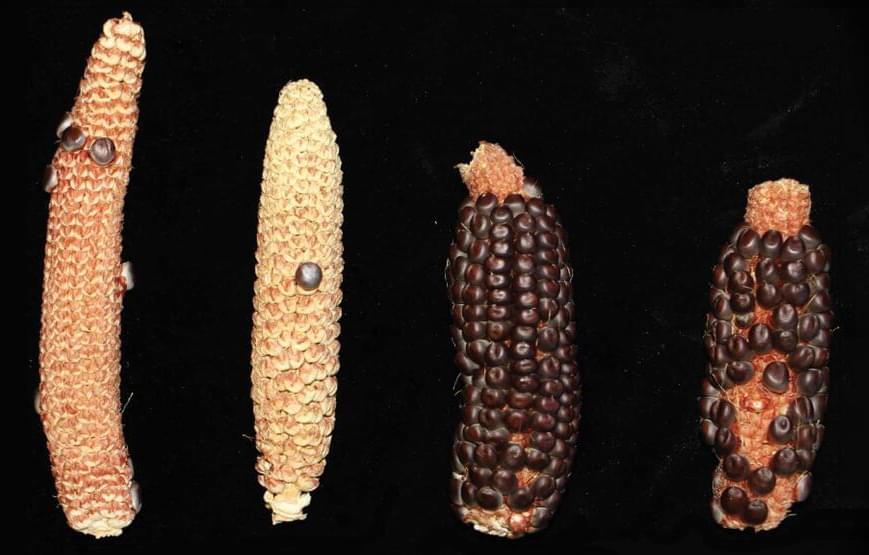
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have traced the domestication of maize back to its origins 9,000 years ago, highlighting its crossbreeding with teosinte mexicana for cold adaptability.
The discovery of a genetic mechanism known as Teosinte Pollen Drive by Professor Rob Martienssen provides a critical link in understanding maize’s rapid adaptation and distribution across America, shedding light on evolutionary processes and potential agricultural applications.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) scientists have begun to unravel a mystery millennia in the making. Our story begins 9,000 years ago. It was then that maize was first domesticated in the Mexican lowlands. Some 5,000 years later, the crop crossed with a species from the Mexican highlands called teosinte mexicana. This resulted in cold adaptability. From here, corn spread across the continent, giving rise to the vegetable that is now such a big part of our diets. But how did it adapt so quickly? What biological mechanisms allowed the highland crop’s traits to take hold? Today, a potential answer emerges.