Microsoft patches critical flaws in Azure Health Bot Service that could expose patient data. Researchers detail vulnerabilities and their potential im.



This is a ~50 minute conversation between Josh Bongard (https://www.uvm.edu/cems/cs/profiles/josh_bongard), Atoosa Parsa (https://www.atoosaparsa.com/), Rich…

New research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst shows that programming robots to create their own teams and voluntarily wait for their teammates results in faster task completion, with the potential to improve manufacturing, agriculture and warehouse automation. The study is published in 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).
This research was recognized as a finalist for Best Paper Award on Multi-Robot Systems at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2024.
“There’s a long history of debate on whether we want to build a single, powerful humanoid robot that can do all the jobs, or we have a team of robots that can collaborate,” says one of the study authors, Hao Zhang, associate professor at the UMass Amherst Manning College of Information and Computer Sciences and director of the Human-Centered Robotics Lab.


Variable renewables cannot, by themselves, reliably supply all of our electricity and heat. But we can change our demand for energy supply through targeted energy efficiency and smart demand management.
The ISP focuses on electricity supply, so it does not effectively address gas-related factors such as the impact of efficient building electrification on electricity demand. Assumptions that electrification will dramatically increase electricity demand are risky.
A lot of gas technologies are far less efficient than many believe, and deliver heat at temperatures higher than processes actually require. And gas equipment can use significant amounts of electricity for fans, pumps, controls and other functions.
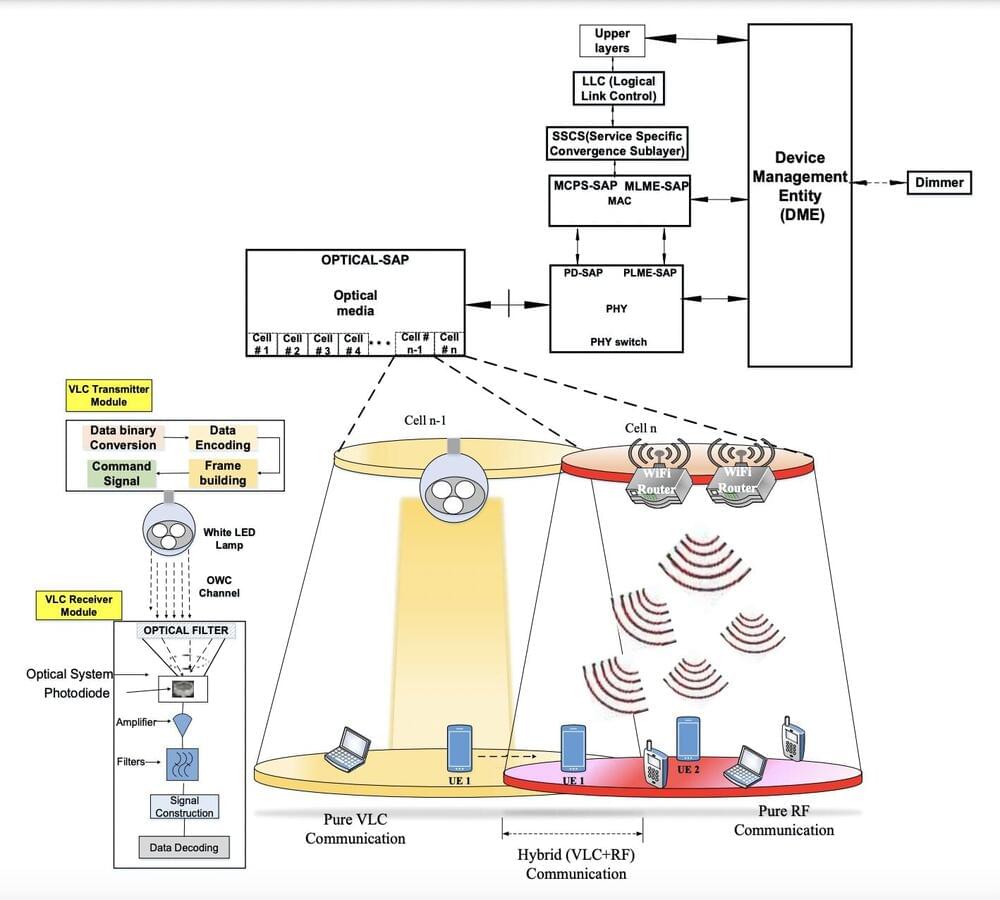
Wireless internet supports the daily activities of countless people worldwide, ranging from their professional communications to internet browsing and the streaming of movies or TV series. This spiking demand for wireless internet access goes hand in hand with greater power consumption, which in turn contributes to carbon emissions worldwide.
Future wireless networks should be able to support the high computational demands of many modern applications and internet services, while limiting power consumption. Some researchers have thus been developing energy efficient techniques supporting communication between devices and the sharing of media or other information online.
One of these solutions is known as visible light communication (VLC). This is a method to realize efficient wireless communication using visible light to transmit data, relying on light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or other artificial light sources.

$665 million in cash is nothing to sneeze at, and for AMD, the acquisition is the latest step in the company’s broader pivot that puts its main focus on AI and AI-related technologies. This is nothing new; we’ve seen the same shift happen in other companies like Google, Meta, Apple, and, of course, NVIDIA. However, NVIDIA’s AI focus started many years ago.
“AI is our number one strategic priority,” said Vamsi Boppana, AMD senior vice president, AIG. “We continue to invest in both the talent and software capabilities to support our growing customer deployments and roadmaps.”
“The Silo AI team has developed state-of-the-art language models that have been trained at scale on AMD Instinct accelerators, and they have broad experience developing and integrating AI models to solve critical problems for end customers,” Vamsi Boppana adds. “We expect their expertise and software capabilities will directly improve the experience for customers in delivering the best performing AI solutions on AMD platforms.”
The Geometric Langlands Correspondence. Edward Frenkel is a renowned mathematician and professor at the University of California, Berkeley, known for his work in representation theory, algebraic geometry, and mathematical physics. Edward is also the author of the bestselling book “Love and Math: The Heart of Hidden Reality”, which bridges the gap between mathematics and the broader public.
Listen on Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9…
Become a YouTube Member Here:
/ @theoriesofeverything.
Patreon: / curtjaimungal (early access to ad-free audio episodes!)
Join TOEmail at https://www.curtjaimungal.org.
LINKS: