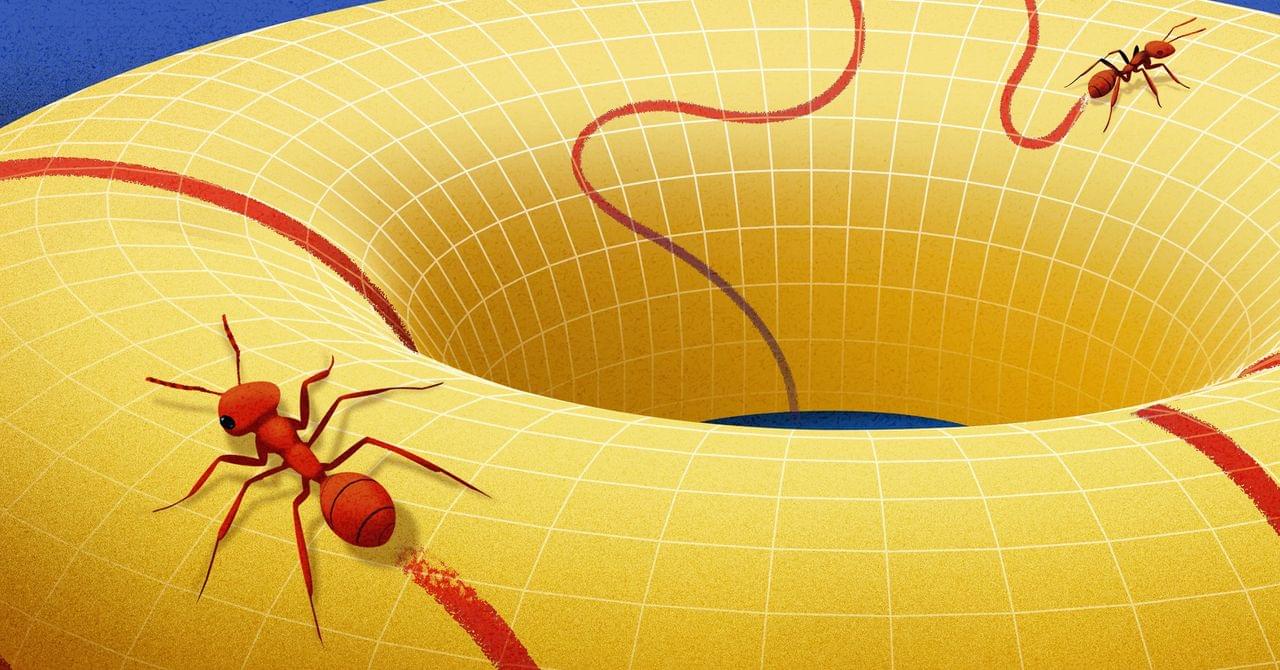
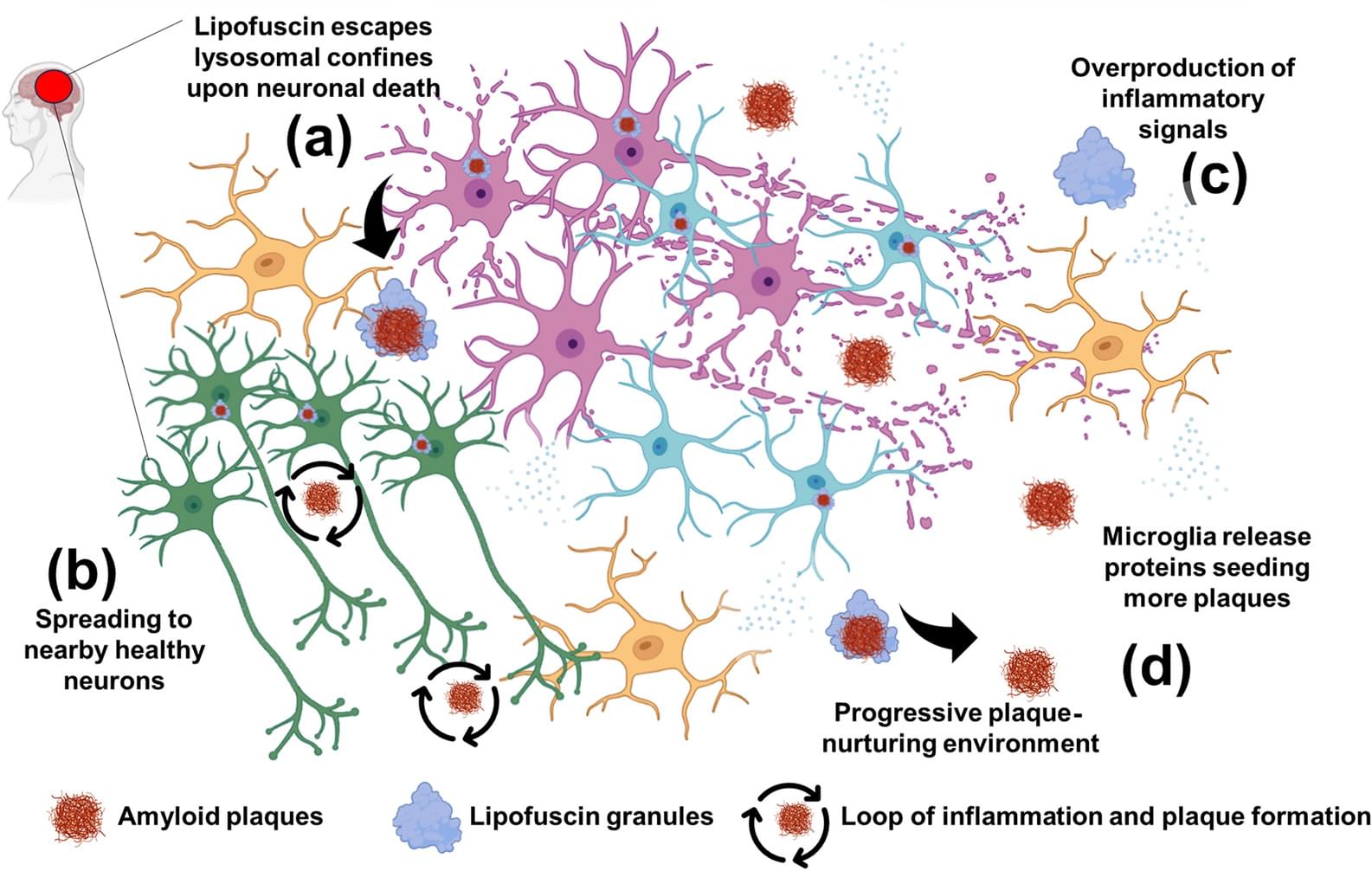
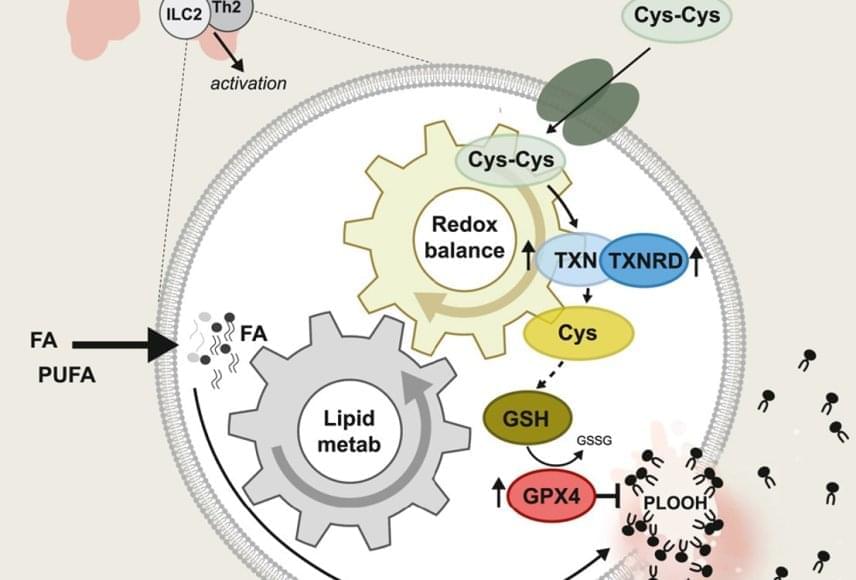
The world is full of such shapes—ones that look flat to an ant living on them, even though they might have a more complicated global structure. Mathematicians call these shapes manifolds. Introduced by Bernhard Riemann in the mid-19th century, manifolds transformed how mathematicians think about space. It was no longer just a physical setting for other mathematical objects, but rather an abstract, well-defined object worth studying in its own right.
This new perspective allowed mathematicians to rigorously explore higher-dimensional spaces—leading to the birth of modern topology, a field dedicated to the study of mathematical spaces like manifolds. Manifolds have also come to occupy a central role in fields such as geometry, dynamical systems, data analysis, and physics.