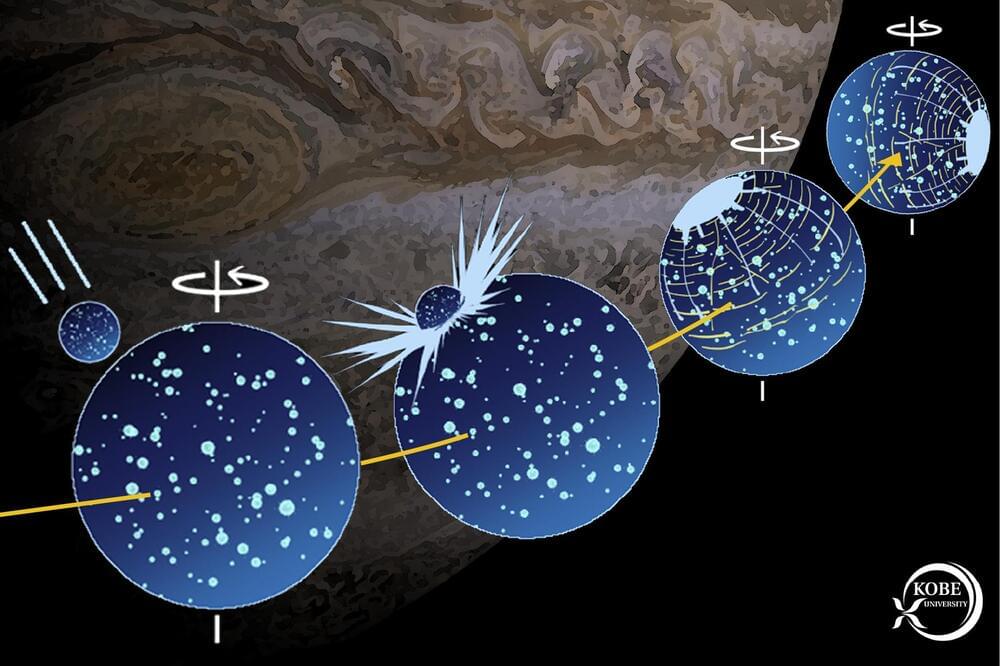
Around 4 billion years ago, an asteroid hit the Jupiter moon Ganymede. Now, a Kobe University researcher realized that the Solar System’s biggest moon’s axis has shifted as a result of the impact, which confirmed that the asteroid was around 20 times larger than the one that ended the age of the dinosaurs on Earth, and caused one of the biggest impacts with clear traces in the Solar System.
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System, bigger even than the planet Mercury, and is also interesting for the liquid water oceans beneath its icy surface. Like the Earth’s moon, it is tidally locked, meaning that it always shows the same side to the planet it is orbiting and thus also has a far side. On large parts of its surface, the moon is covered by furrows that form concentric circles around one specific spot, which led researchers in the 1980s to conclude that they are the results of a major impact event. “The Jupiter moons Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto all have interesting individual characteristics, but the one that caught my attention was these furrows on Ganymede,” says the Kobe University planetologist HIRATA Naoyuki. He continues, “We know that this feature was created by an asteroid impact about 4 billion years ago, but we were unsure how big this impact was and what effect it had on the moon.”
Data from the remote object is scarce making research very difficult, and so Hirata was the first to realize that the purported location of the impact is almost precisely on the meridian farthest away from Jupiter. Drawing from similarities with an impact event on Pluto that caused the dwarf planet’s rotational axis to shift and that we learned about through the New Horizons space probe, this implied that Ganymede, too, had undergone such a reorientation. Hirata is a specialist in simulating impact events on moons and asteroids, so this realization allowed him to calculate what kind of impact could have caused this reorientation to happen.