Mar 31, 2023
Microsoft lays off entire AI ethics team while going all out on ChatGPT
Posted by Claudio Soprano in categories: ethics, robotics/AI
A new report indicates Microsoft will expand AI products, but axe the people who make them ethical.
A new report indicates Microsoft will expand AI products, but axe the people who make them ethical.
Aurora Borealis can cause damage to satellites in severe solar storms. Scientists are experimenting to understand near-space weather better.
Dune Scene Stars: Kyle MacLachlan, Francesca Annis, Jürgen Prochnow, Silvana Mangano Director: David Lynch Writers: Frank Herbert, David Lynch Producer: Raffaella De Laurentiis Music: TOTO Production: Dino De Laurentiis Company, Estudios Churubusco Azteca S.A. Distributon: Universal Pictures Released: 1984
► watch Dune https://play.google.com/store/movies/details/Dune?id=BB5433C0E07FCF5BMV
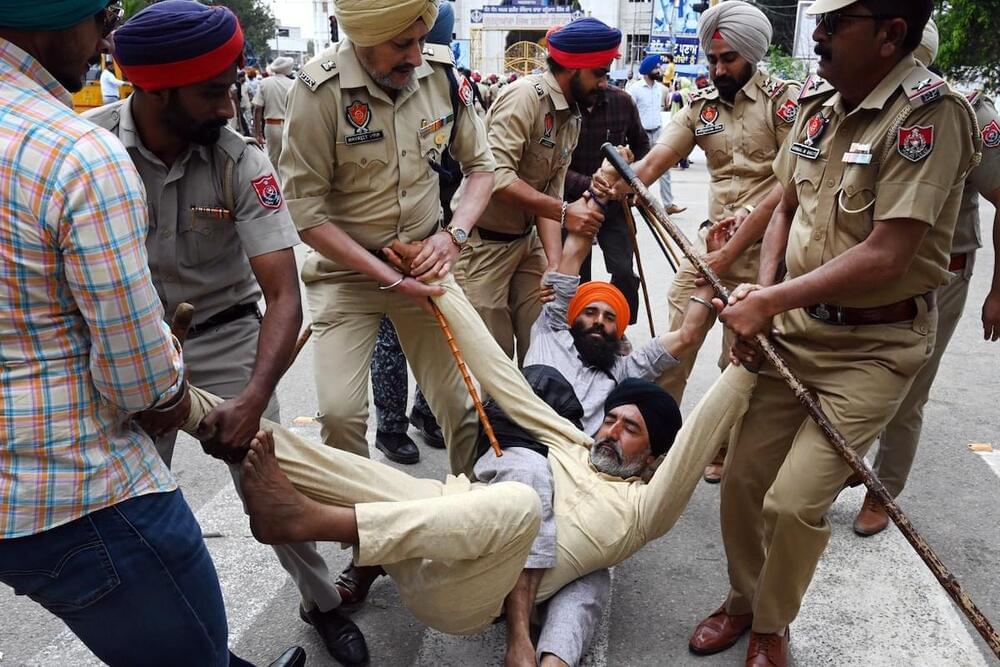

Two months ago, Musk said he was too busy to look into his company’s role in mass censorship in India. It’s only gotten worse.
Why do cancer immunotherapies work so extraordinarily well in a minority of patients, but fail in so many others? By analyzing the role of neutrophils, immune cells whose presence usually signals treatment failure, scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), from Harvard Medical School, and from Ludwig Cancer Center have discovered that there is not just one type of neutrophil, but several. Depending on certain markers on their surface, these cells can either promote the growth of tumors, or fight them and ensure the success of a treatment. By boosting the appropriate factors, neutrophils could become great agents of anti-tumor immunity and reinforce the effects of current immunotherapies. These results have been published in the journal Cell.
Immunotherapy involves activating immune cells —mainly T cells—to recognize and destroy cancer cells. While this treatment is very efficient for some patients, and sometimes even exceeds expectations, it is unfortunately not the case in most cases. “The reasons for these failures remain largely unknown,” says Mikaël Pittet, full professor at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine, holder of the ISREC chair in immuno-oncology, director of the Centre for Translational Research in Onco-Hematology and member of the Ludwig Cancer Center, who directed this work. “This is why deciphering the immune components involved is key to develop more advanced treatments and make immunotherapies a real therapeutic revolution.”
Neutrophils are the most abundant immune cells in the blood and are very useful in infections or injuries by being quickly mobilized to the affected area and releasing antimicrobial factors. In the context of cancer, however, their presence is generally bad news as they promote vascularization and tumor progression.
In a recent study on the medRxiv preprint server, researchers identified an interleukin 6 (IL-6) dependent alternative pathway as a therapeutic strategy against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Study: A Complement Atlas identifies interleukin 6 dependent alternative pathway dysregulation as a key druggable feature of COVID-19. Image Credit: MarynaOlyak/Shutterstock.com
“You won’t live forever” is a catchphrase which has often been touted and has so far remained the proven truth of life — of humans and almost every other living being on planet earth. But soon, this catchphrase may well become the truth of the past, as humanity steps forward to attain immortality.
A former Google scientist has made a prediction, which if proven right, may redefine human civilisation as we know it. Ray Kurzweil, whose over 85 per cent of 147 predictions have been proven right, has predicted that humans will become immortal by 2029.
The revelation came when the 75-year-old computer scientist dwelled upon genetics, nanotechnology, robotics and more in a YouTube video posted by channel Adagio.
The expanded availability of opioid use disorder-related telehealth services and medications during the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with a lowered likelihood of fatal drug overdose among Medicare beneficiaries, according to a new study.
“The results of this study add to the growing research documenting the benefits of expanding the use of telehealth services for people with opioid use disorder, as well as the need to improve retention and access to medication treatment for opioid use disorder,” said lead author Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, director of the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “The findings from this collaborative study also highlight the importance of working across agencies to identify successful strategies to address and get ahead of the constantly evolving overdose crisis.”
Published today in JAMA Psychiatry, this study is a collaborative research effort led by researchers at the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, a part of CDC; the Office of the Administrator and the Center for Clinical Standards and Quality, both part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS); and the National Institute on Drug Abuse, a part of the National Institutes of Health.

Physics-Astronomy: Home of the best science(focusing physics, astronomy) and technology news since 2012. Keep up with the latest news via email or social media. We are curious about the Universe, are you?
Advances in antiaging drug/lead discovery in animal models constitute a large body of literature on novel senotherapeutics and geroprotectives. However, with little direct evidence or mechanism of action in humans—these drugs are utilized as nutraceuticals or repurposed supplements without proper testing directions, appropriate biomarkers, or consistent in-vivo models. In this study, we take previously identified drug candidates that have significant evidence of prolonging lifespan and promoting healthy aging in model organisms, and simulate them in human metabolic interactome networks. Screening for drug-likeness, toxicity, and KEGG network correlation scores, we generated a library of 285 safe and bioavailable compounds. We interrogated this library to present computational modeling-derived estimations of a tripartite interaction map of animal geroprotective compounds in the human molecular interactome extracted from longevity, senescence, and dietary restriction-associated genes. Our findings reflect previous studies in aging-associated metabolic disorders, and predict 25 best-connected drug interactors including Resveratrol, EGCG, Metformin, Trichostatin A, Caffeic Acid and Quercetin as direct modulators of lifespan and healthspan-associated pathways. We further clustered these compounds and the functionally enriched subnetworks therewith to identify longevity-exclusive, senescence-exclusive, pseudo-omniregulators and omniregulators within the set of interactome hub genes. Additionally, serum markers for drug-interactions, and interactions with potentially geroprotective gut microbial species distinguish the current study and present a holistic depiction of optimum gut microbial alteration by candidate drugs. These findings provide a systems level model of animal life-extending therapeutics in human systems, and act as precursors for expediting the ongoing global effort to find effective antiaging pharmacological interventions.
Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
