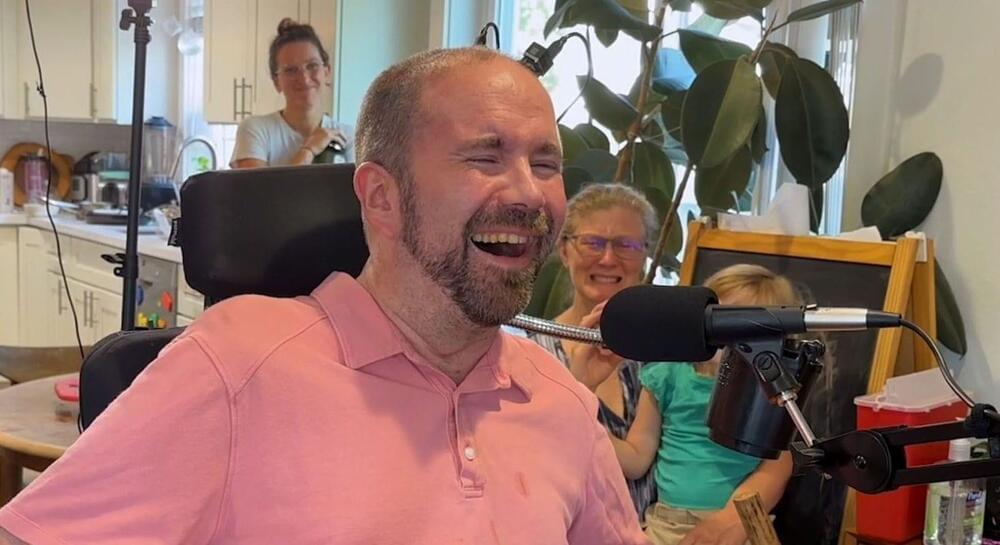
“Not being able to communicate is so frustrating and demoralizing. It is like you are trapped,” Harrell said. “Something like this technology will help people back into life and society.”
For the researchers involved, seeing the impact of their work on Harrell’s life has been deeply rewarding. “It has been immensely rewarding to see Casey regain his ability to speak with his family and friends through this technology,” said the study’s lead author, Nicholas Card, a postdoctoral scholar in the UC Davis Department of Neurological Surgery.
Leigh Hochberg, a neurologist and neuroscientist involved in the BrainGate trial, praised Harrell and other participants for their contributions to this groundbreaking research. “Casey and our other BrainGate participants are truly extraordinary. They deserve tremendous credit for joining these early clinical trials,” Hochberg said. “They do this not because they’re hoping to gain any personal benefit, but to help us develop a system that will restore communication and mobility for other people with paralysis.”