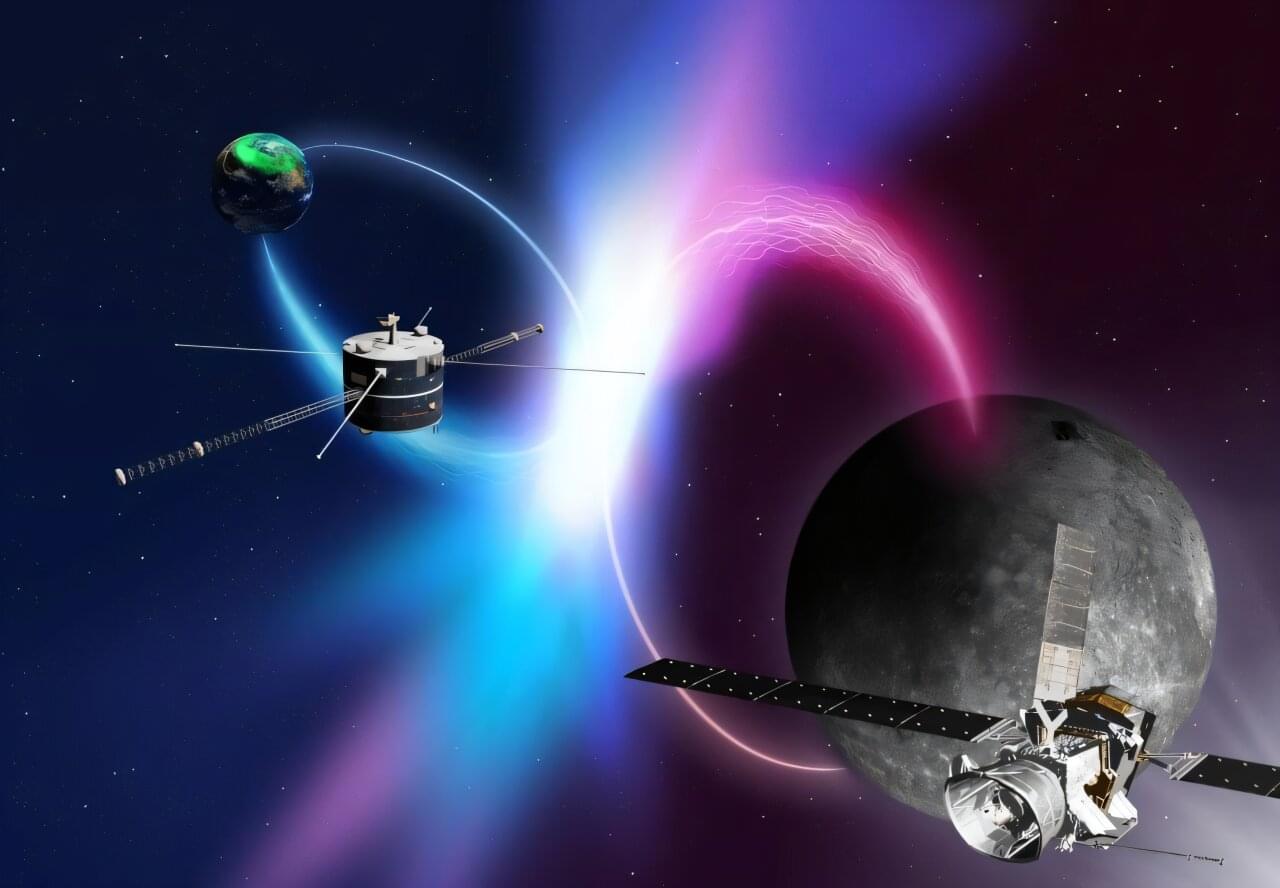
An international team from Kanazawa University (Japan), Tohoku University (Japan), LPP (France), and partners has demonstrated that chorus emissions, natural electromagnetic waves long studied in Earth’s magnetosphere, also occur in Mercury’s magnetosphere exhibiting similar chirping frequency changes.
Using the Plasma Wave Investigation instrument aboard BepiColombo’s Mercury orbiter Mio, six Mercury flybys between 2021 and 2025 detected plasma waves in the audible range. Comparison with decades of GEOTAIL data confirmed identical instantaneous frequency changes.
This provides the first reliable evidence of intense electron activity at Mercury, advancing understanding of auroral processes across the solar system.