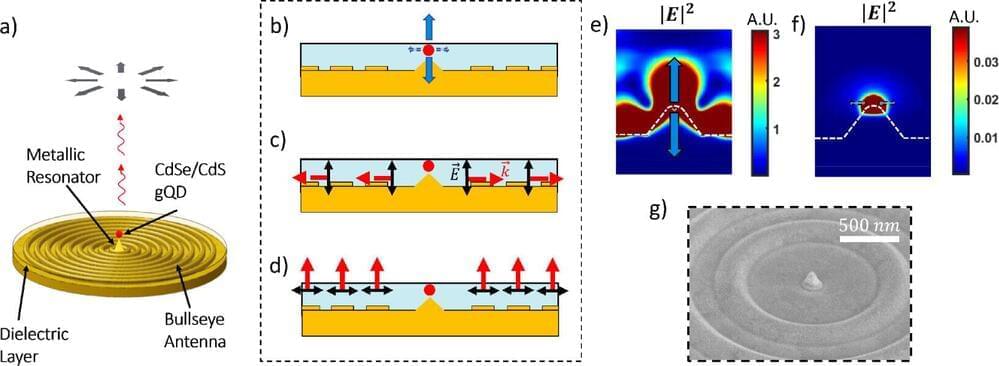
Researchers have developed a tiny, room-temperature device that creates a special type of structured light called radially polarized photons, which are highly useful for secure communication, advanced imaging, and precision optical tools.
By carefully designing and positioning a quantum dot within a nanoantenna, they achieved high-quality light with more than 93% polarization purity. This breakthrough helps improve the efficiency and practicality of devices that use structured light, paving the way for advancements in communication and optical technology.
A team led by Prof. Ronen Rapaport from the Racah School of Physics at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem has developed the new device that produces radially polarized photons at room temperature. This advancement offers new possibilities for both classical and quantum communication technologies.