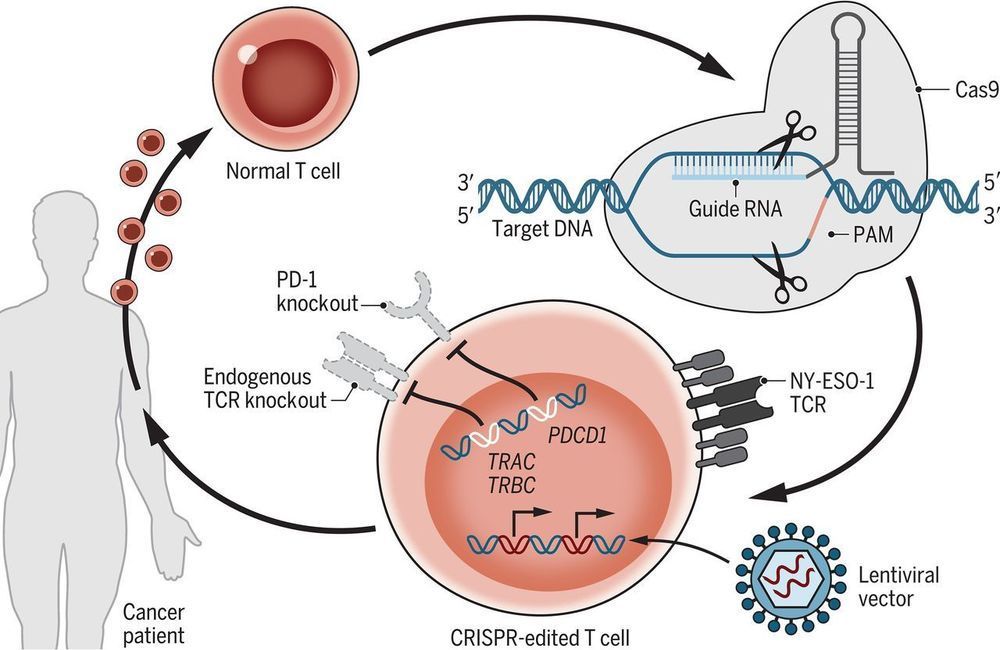
When opportunity knocks, open the door: No one has taken heed of that adage like Nvidia, which has transformed itself from a company focused on catering to the needs of video gamers to one at the heart of the artificial-intelligence revolution. In 2001, no one predicted that the same processor architecture developed to draw realistic explosions in 3D would be just the thing to power a renaissance in deep learning. But when Nvidia realized that academics were gobbling up its graphics cards, it responded, supporting researchers with the launch of the CUDA parallel computing software framework in 2006.
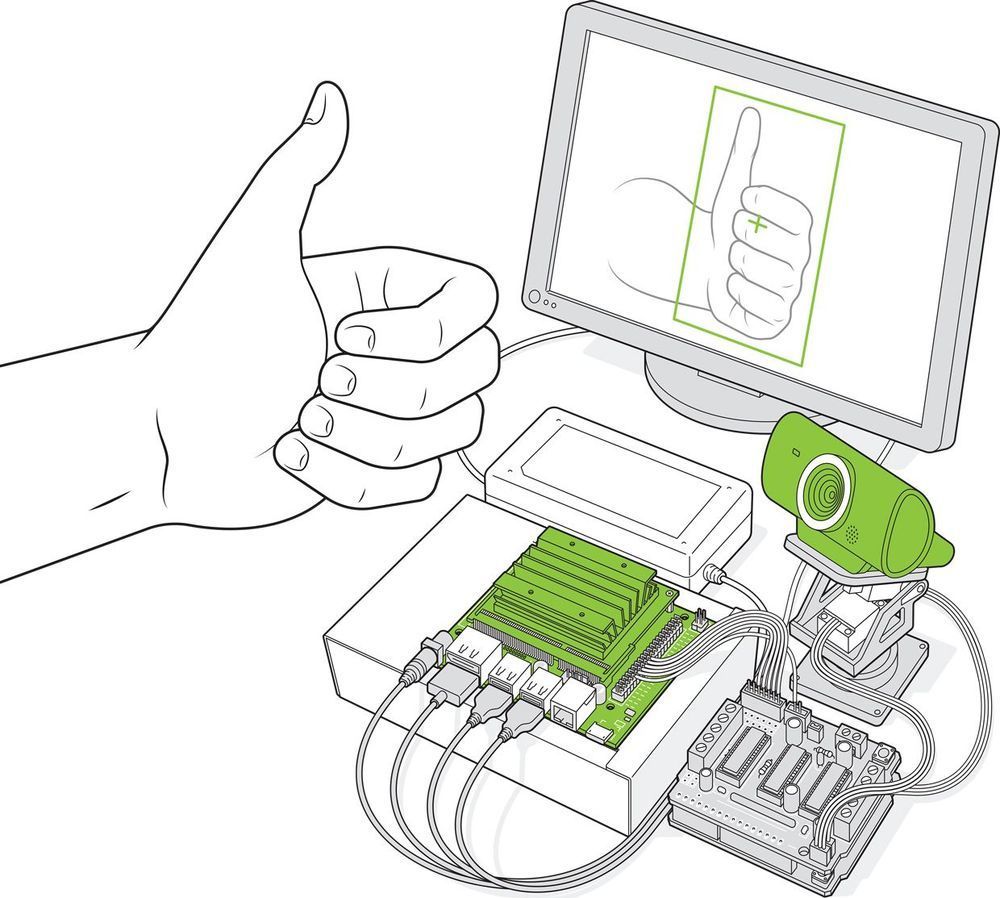
Since then, Nvidia has been a big player in the world of high-end embedded AI applications, where teams of highly trained (and paid) engineers have used its hardware for things like autonomous vehicles. Now the company claims to be making it easy for even hobbyists to use embedded machine learning, with its US $100 Jetson Nano dev kit, which was originally launched in early 2019 and rereleased this March with several upgrades. So, I set out to see just how easy it was: Could I, for example, quickly and cheaply make a camera that could recognize and track chosen objects?
Embedded machine learning is evolving rapidly. In April 2019, Hands On looked at Google’s Coral Dev AI board which incorporates the company’s Edge tensor processing unit (TPU), and in July 2019, IEEE Spectrum featured Adafruit’s software library, which lets even a handheld game device do simple speech recognition. The Jetson Nano is closer to the Coral Dev board: With its 128 parallel processing cores, like the Coral, it’s powerful enough to handle a real-time video feed, and both have Raspberry Pi–style 40-pin GPIO connectors for driving external hardware.