Unlike fish, jellyfish lack bones and possess a sole rudimentary nerve net, yet they can travel considerable distances with minimal energy expenditure. A jellyfish’s seemingly effortless glide through the water is thanks to a ring of muscle within its soft belly, which creates a simple jet that propels it forward. Scientists refer to this intrinsic capability as “embodied intelligence,” which suggests that the organism’s physical structure plays a role in problem-solving.
When harnessed, this locomotion provides an efficient means to monitor coral reefs, track oil spills, and observe climate trends. “Jellyfish cyborgs” require minimal power and operate without engines, limiting the environmental impact associated with current methods of studying the vast expanse of the ocean.
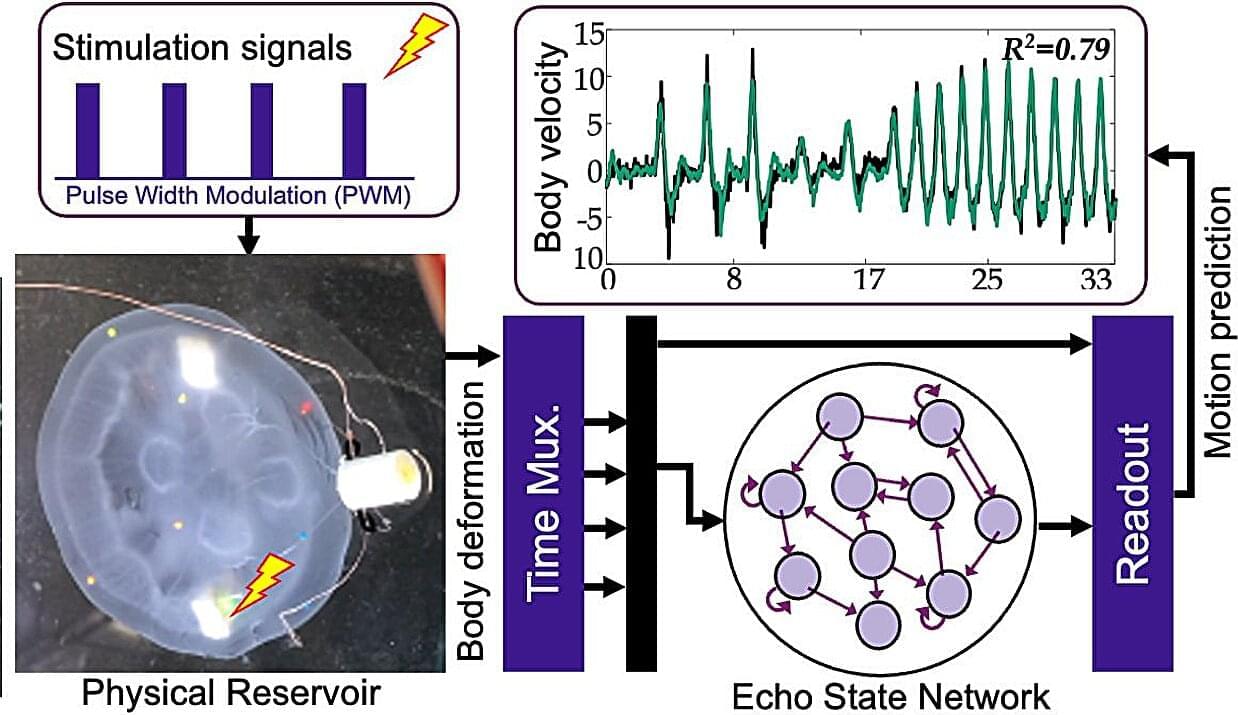
In a new study, a research team, led by Dai Owaki, an associate professor in the Department of Robotics at Tohoku University’s Graduate School of Engineering, successfully modulated the swimming behavior of jellyfish using gentle electric pulses. Moreover, they utilized a lightweight artificial intelligence (AI) model to predict the swimming speed of each jellyfish.