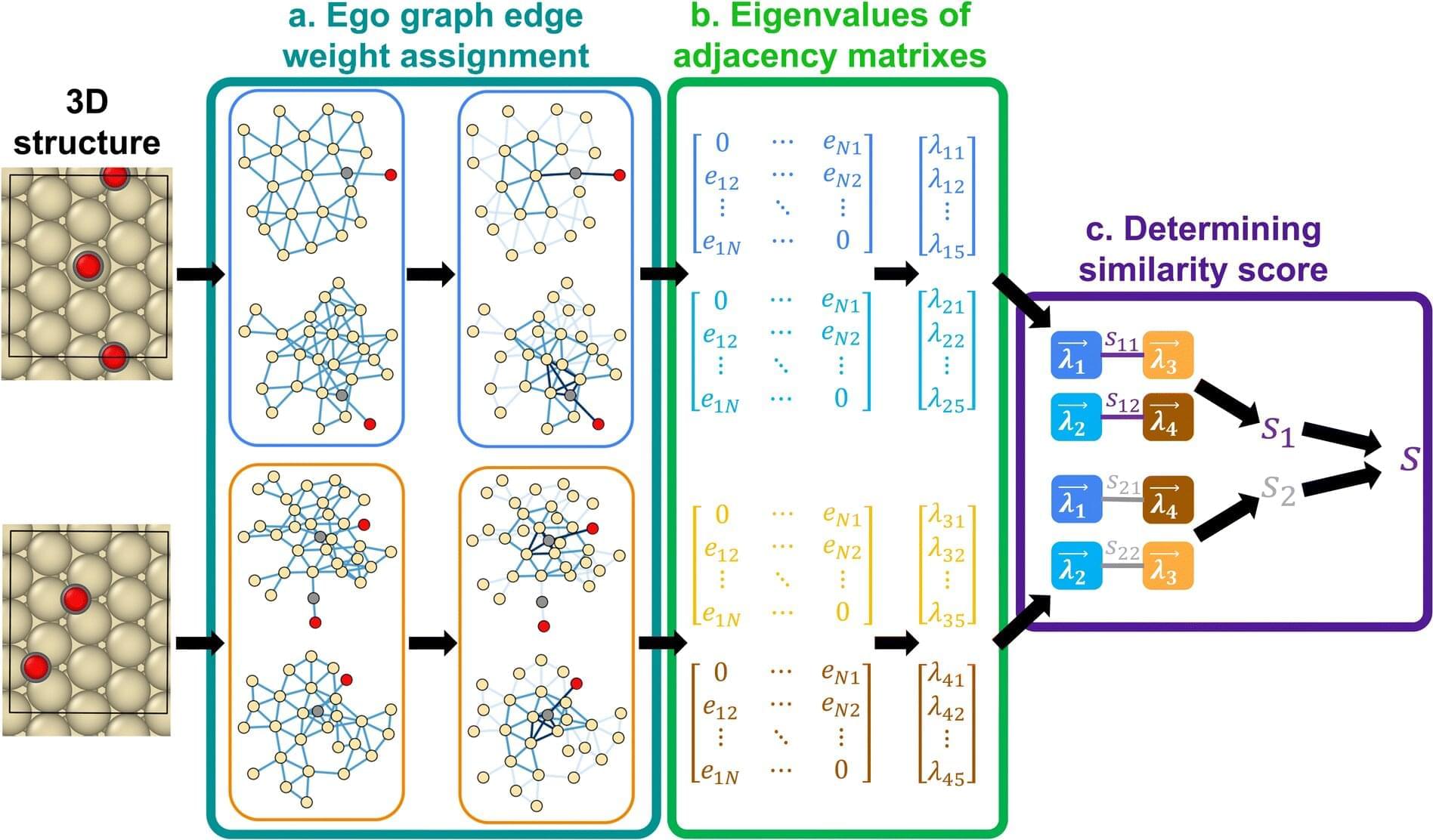
Time, not space plus time, might be the single fundamental property in which all physical phenomena occur, according to a new theory by a University of Alaska Fairbanks scientist.
The theory also argues that time comes in three dimensions rather than just the single one we experience as continual forward progression. Space emerges as a secondary manifestation.
“These three time dimensions are the primary fabric of everything, like the canvas of a painting,” said associate research professor Gunther Kletetschka at the UAF Geophysical Institute. “Space still exists with its three dimensions, but it’s more like the paint on the canvas rather than the canvas itself.”