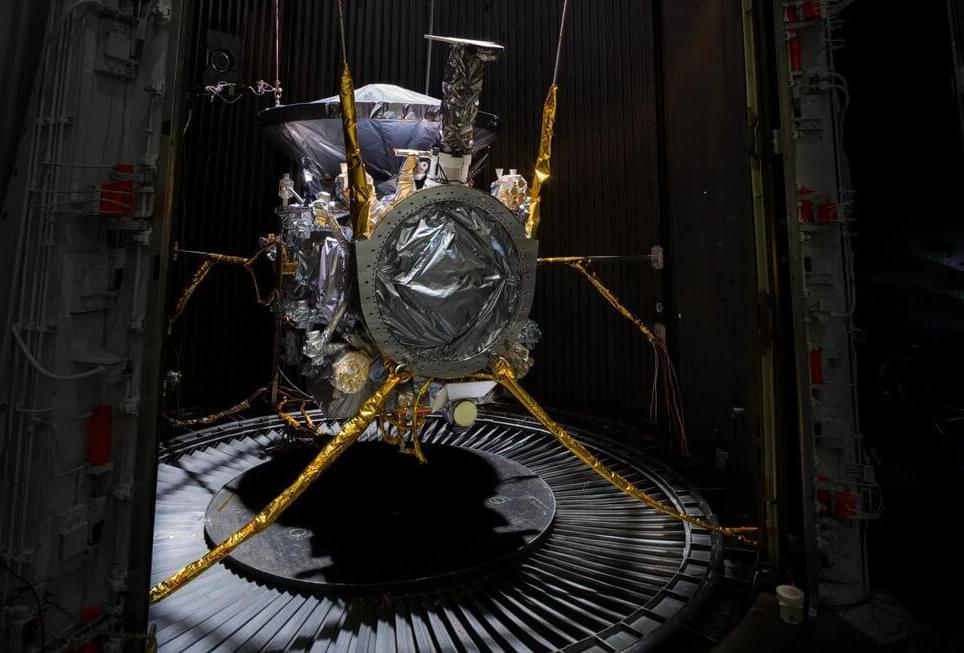
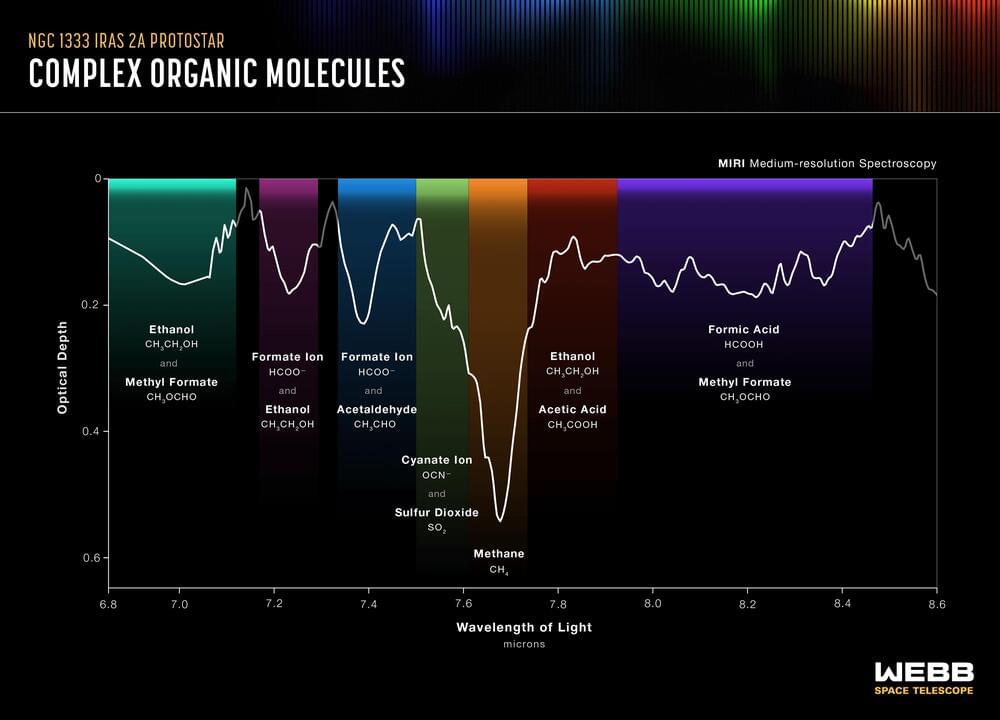
“There still is work to be done, but we’re on track for an on-time launch,” said Europa Clipper Project Manager, Jordan Evans. “And the fact that this testing was so successful is a huge positive and helps us rest more easily.”
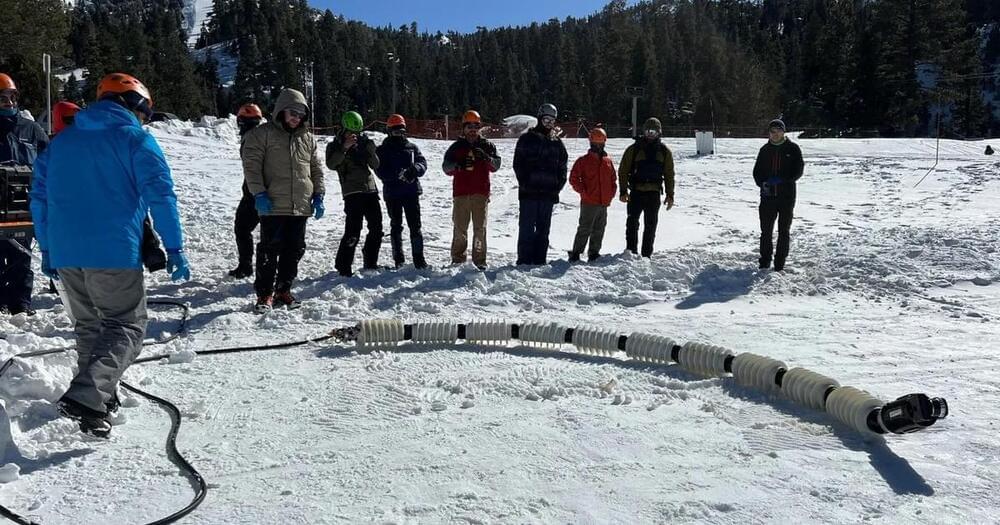
Like all spacecraft leading up to their launch date, NASA’s Europa Clipper has been undergoing rigorous tests and checkouts to ensure all systems are functioning properly, with NASA engineers recently subjecting the bus-sized orbiter to extreme environmental testing over a 16-day period to ensure the spacecraft can withstand the harsh conditions it will face during its 4-year science mission to the small, ocean world. These harsh conditions not only include the vacuum of space, but also electromagnetic radiation since it will be flying through Jupiter’s massive and powerful magnetic field throughout its mission.
“These were the last big tests to find any flaws,” said Jordan Evans, who is the Europa Clipper Project Manager at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). “Our engineers executed a well-designed and challenging set of tests that put the system through its paces. What we found is that the spacecraft can handle the environments that it will see during and after launch. The system performed very well and operates as expected.”
The tests included putting Europa Clipper into NASA’s well-known thermal vacuum chamber (TVAC), more commonly known as the 25-foot Space Simulator, where engineers not only removed all the air in the chamber but reduced the temperatures to ensure Europa Clipper’s hundreds of heating sensors could keep the spacecraft warm enough to function properly. Additionally, the engineers performed checkouts of Clipper’s electrical and magnetic systems, vibrations, sounds, and shock tests, essentially performing an entire shakedown of Europa Clipper prior to its delivery for launch later this spring.