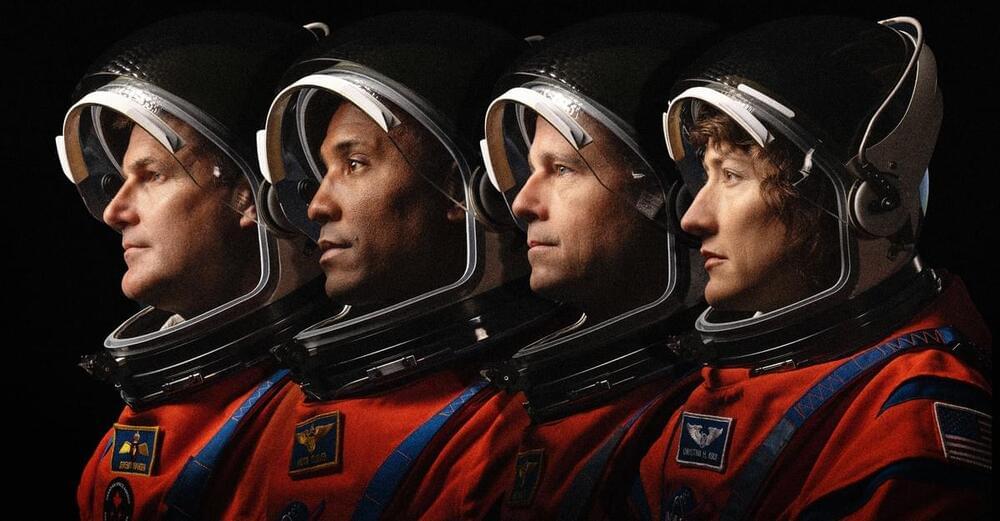
NASA has picked the four astronauts who will fly to the moon next year—and this lineup looks different than the Apollo crews did.


The FAA has Starship on their launch calendar! The biggest step towards colonizing Mars is perhaps a week away. But the question remains: why are humans going to make the choice to spend the rest of their lives on such a hostile planet? Well, for the main reasons that humans do anything.
Money.
#space #spacex #nasa.
Please support my channel! EARLY VIDEO RELEASES, DISCORD MEMBERSHIP AND EXCLUSIVE CONTENT PLUS 15% OFF MERCH!
https://www.patreon.com/AngryAstronaut.
https://www.paypal.com/paypalme/AngryAstro.
The Case for Mars by Robert Zubrin.
https://space.nss.org/the-case-for-colonizing-mars-by-robert-zubrin/
https://www.youtube.com/@spaceboffin.
https://www.youtube.com/@NickHenning3D
Putting two forms of semiconductor material called gallium oxide together seems to make it completely resistant to radiation.
By Alex Wilkins

A spaceship traveling at warp speed wouldn’t be firing its engines to travel that fast; it’s just being carried by a spacetime bubble. Then if you want to exponentially increase your speed, you build another bubble around that bubble, which in the world of Star Trek is referred to as warp factor two, and then warp factor three, Macdonald says.
Spacetime as we know it is finite, and as such, there is a limit to the number of warp bubbles, or level of warp speed one could theoretically reach. In some shows, this is arbitrarily called warp factor 10, which is when all of spacetime is wrapped around the spaceship. At that point, “you’ve broken all the laws of infinity and you experience all time at all moments,” Macdonald says. “And in the classic Voyager episode of Star Trek, you evolve into lizard people.”

An artificial black hole produced using sound waves and a dielectric medium has been created in the lab, according to researchers with an international think tank featuring more than 30 Ph.D. research scientists from around the world.
The researchers say their discovery is significantly more cost-effective and efficient than current methods in use by researchers who want to simulate the effects of a black hole in a laboratory environment.
New York-based Applied Physics first achieved recognition with the 2021 publication of a peer-reviewed theoretical paper detailing the mathematics behind the construction of a physical warp drive. More recently, the organization published a method for using Cal Tech’s Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) to detect the use of warp drives in outer space, co-authored by Dr. Manfred Paulini, the Associate Dean of Physics at Carnegie Mellon University.
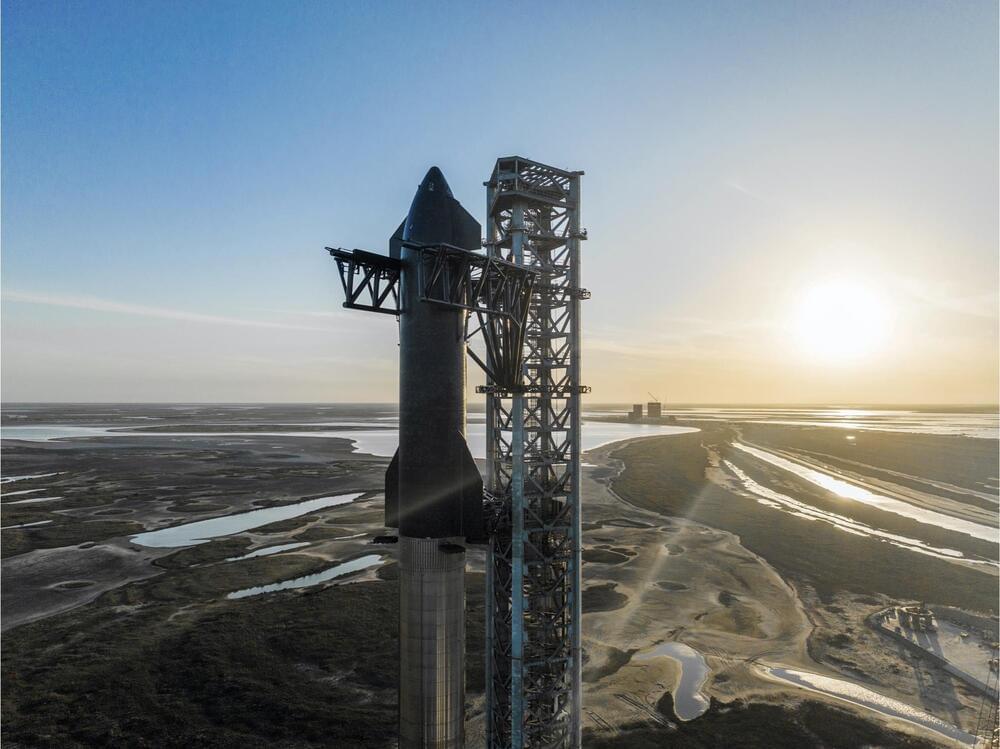

SpaceX has moved the Super Heavy Starship and NASA has reserved observation planes for April 10 and 11.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
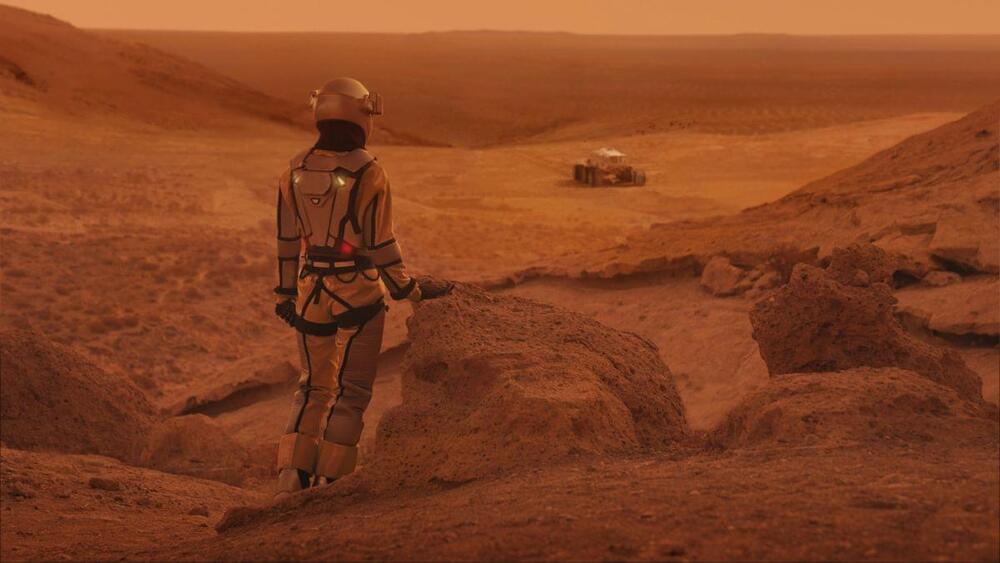

10 SpaceX Starships are carrying 120 robots to Mars. They are the first to colonize the Red Planet. Building robot habitats to protect themselves, and then landing pads, structures, and the life support systems for the humans who will soon arrive.
This Mars colonization mini documentary also covers they type of robots that will be building on Mars, the solar fields, how Elon Musk and Tesla could have a battery bank station at the Mars colony, and how the Martian colony expands during the 2 years when the robots are building. Known as the Robotic Age of Mars.
Additional footage from: SpaceX, NASA/JPL/University of Arizona, ICON, HASSEL, Tesla, Lockhead Martin.
A building on Mars sci-fi documentary, and a timelapse look into the future.
See more of Venture City at my website: https://vx-c.com.
_______
Books.
• The Martian book showcases the science, math, and physics of living on the red planet — told through the story of someone who has to survive there.
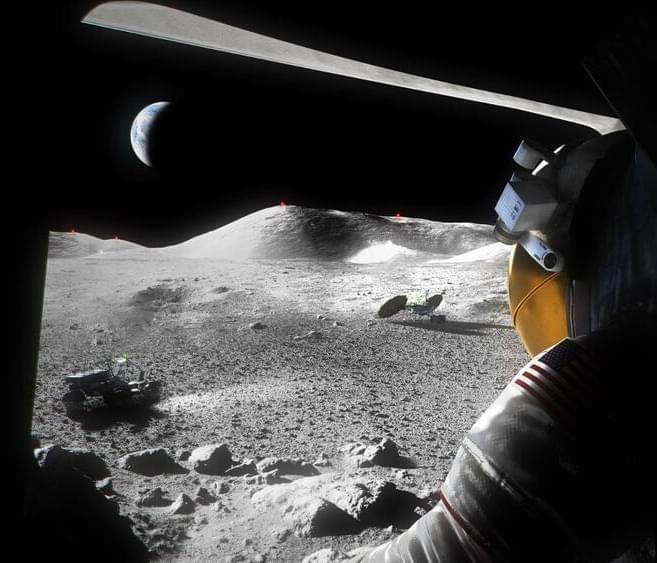

In a quest to expand human settlement to the moon and beyond, NASA and industry partners are developing landing systems to take astronauts from orbit to the lunar surface with its mission Artemis. However, a small but pertinent issue of excessive dust on the surface is posing a considerable challenge for fulfilling such explorations.
To counter this, the agency is seeking ideas from university students for solutions to mitigate the issue related to dusty landings. NASA’s new Human Lander Challenge invites college students to research ways to regulate the plume effect, the process in which a cloud of dust is stirred up by lunar vehicles when rocket engines are used to provide thrust for a smooth landing on unprepared surfaces. NASA had conducted a similar program for students, through its Breakthrough, Innovative, and Game-changing challenge in 2020 for solutions to the same issue.