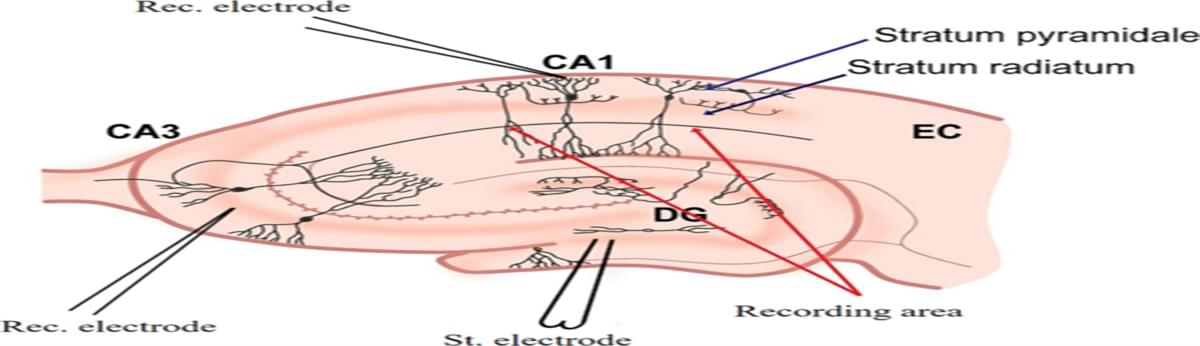
A brain implant used for the first time is helping a patient with paralysis regain use of his limbs. The use of artificial intelligence is helping in the process, also making it possible for the man to feel objects again. NBC News’ Sam Brock reports.
» Subscribe to NBC News: http://nbcnews.to/SubscribeToNBC
» Watch more NBC video: http://bit.ly/MoreNBCNews.
NBC News Digital is a collection of innovative and powerful news brands that deliver compelling, diverse and engaging news stories. NBC News Digital features NBCNews.com, MSNBC.com, TODAY.com, Nightly News, Meet the Press, Dateline, and the existing apps and digital extensions of these respective properties. We deliver the best in breaking news, live video coverage, original journalism and segments from your favorite NBC News Shows.
Connect with NBC News Online!
NBC News App: https://apps.nbcnews.com/mobile.
Breaking News Alerts: https://link.nbcnews.com/join/5cj/bre… NBCNews. Com: http://nbcnews.to/ReadNBC Find NBC News on Facebook: http://nbcnews.to/LikeNBC Follow NBC News on Twitter: http://nbcnews.to/FollowNBC Follow NBC News on Instagram: http://nbcnews.to/InstaNBC #health #implant #brain.
Visit NBCNews. Com: http://nbcnews.to/ReadNBC
Find NBC News on Facebook: http://nbcnews.to/LikeNBC
Follow NBC News on Twitter: http://nbcnews.to/FollowNBC
Follow NBC News on Instagram: http://nbcnews.to/InstaNBC
#health #implant #brain