Farzad
Category: robotics/AI – Page 274


Fuel your creativity with new generative media models and tools
Today, we’re announcing our newest generative media models, which mark significant breakthroughs. These models create breathtaking images, videos and music, empowering artists to bring their creative vision to life. They also power amazing tools for everyone to express themselves.
Veo 3 and Imagen 4, our newest video and image generation models, push the frontier of media generation, with their groundbreaking new capabilities. We’re also expanding access to Lyria 2, giving musicians more tools to create music. Finally, we’re inviting visual storytellers to try Flow, our new AI filmmaking tool. Using Google DeepMind’s most advanced models, Flow lets you weave cinematic films with more sophisticated control of characters, scenes and styles, to bring your story to life.
We’ve partnered closely with the creative industries — filmmakers, musicians, artists, YouTube creators — to help shape these models and products responsibly and to give creators new tools to realize the possibilities of AI in their art.

Conversational agent can create executable quantum chemistry workflows
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents and large-language models (LLMs), such as the model underpinning OpenAI’s conversational platform ChatGPT, are now widely used by people worldwide, both in informal and professional settings. Over the past decade or so, some of these models have also been adapted to tackle complex research problems rooted in various fields, including biology, physics, medical sciences and chemistry.
Existing computational tools employed by chemists are often highly sophisticated and complex. Their complexity makes them inaccessible to non-expert users and often even difficult for expert chemists to use.
Researchers at Matter Lab at the University of Toronto and NVIDIA have developed El Agente Q, a new LLM-based system that could allow chemists, particularly those specialized in quantum chemistry, to easily generate and execute quantum chemistry workflows, sequences of computational tasks required to study specific chemical systems at the quantum mechanical level.

President of European Commission expects human-level AI by 2026
On May 20, during her speech at the Annual EU Budget Conference 2025, Ursula von der Leyen, President of the European Commission, stated:
When the current budget was negotiated, we thought AI would only approach human reasoning around 2050. Now we expect this to happen already next year. It is simply impossible to determine today where innovation will lead us by the end of the next budgetary cycle. Our budget of tomorrow will need to respond fast.
This is remarkable coming from the highest-ranking EU official. It suggests the Overton window for AI policy has shifted significantly.
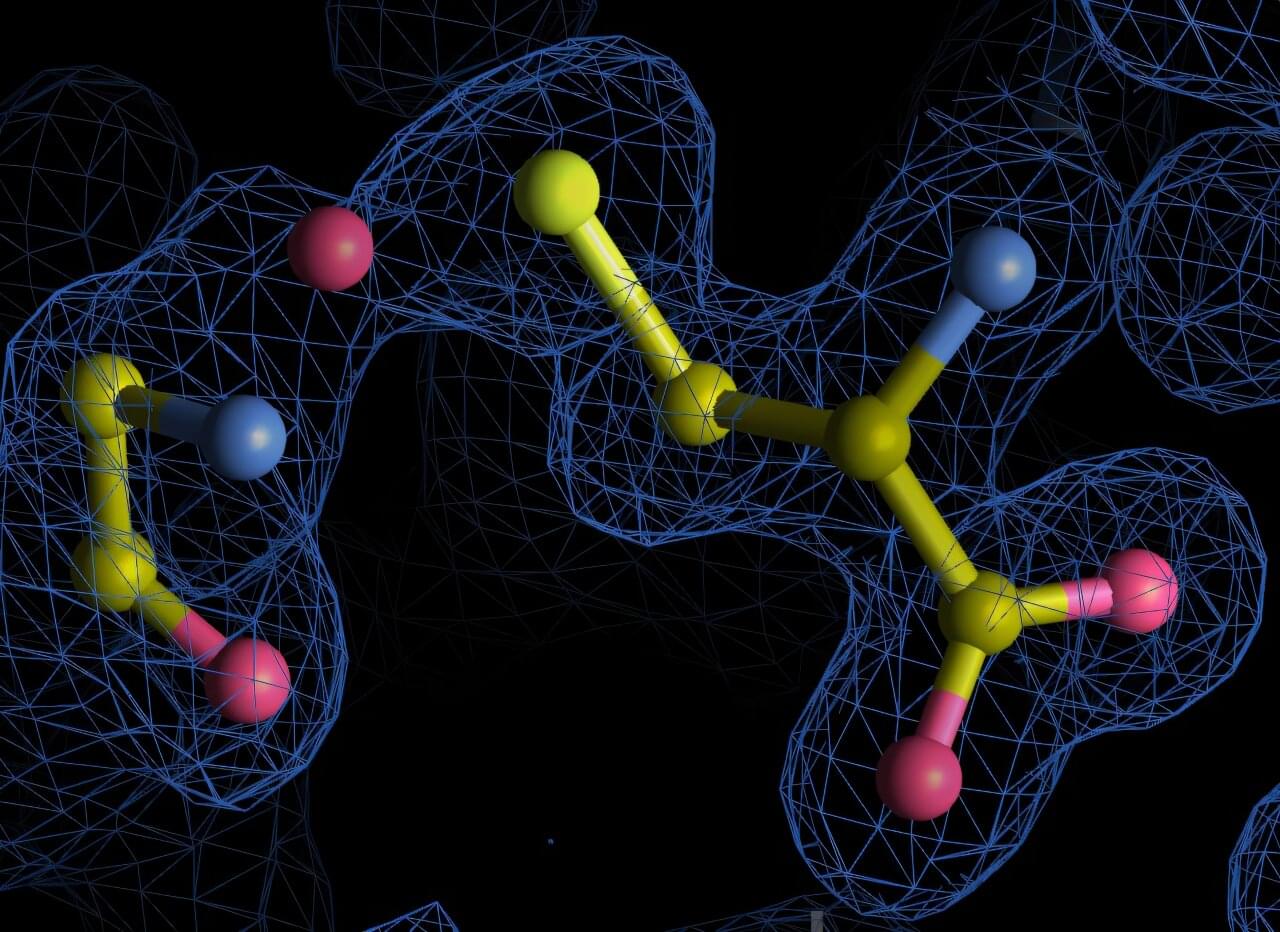
A new complexity in protein chemistry: Algorithm uncovers overlooked chemical linkages
Proteins are among the most studied molecules in biology, yet new research from the University of Göttingen shows they can still hold surprising secrets. Researchers have discovered previously undetected chemical bonds within archived protein structures, revealing an unexpected complexity in protein chemistry.
These newly identified nitrogen-oxygen-sulfur (NOS) linkages broaden our understanding of how proteins respond to oxidative stress, a condition where harmful oxygen-based molecules build up and can damage proteins, DNA, and other essential parts of the cell. The new findings are published in Communications Chemistry.
The research team systematically re-analyzed over 86,000 high-resolution protein structures from the Protein Data Bank, a global public repository of protein structures, using a new algorithm that they developed inhouse called SimplifiedBondfinder. This pipeline combines machine learning, quantum mechanical modeling, and structural refinement methods to reveal subtle chemical bonds that were missed by conventional analyses.
Project Astra | Exploring the Capabilities of a Universal AI Assistant
Last year we introduced Project Astra, our research prototype of a universal AI assistant. Since then we’ve improved memory, added computer control and enhanced voice output, and are working to bring these new capabilities to Gemini Live and other products.
Learn more about Project Astra: https://deepmind.google/technologies/.… #AIAssistant #ProjectAstra Subscribe to our Channel: / google Find us on X:
/ google Watch us on TikTok:
/ google Follow us on Instagram:
/ google Join us on Facebook:
/ google.
#GoogleIO #AIAssistant #ProjectAstra.
Find us on X: / google.
Watch us on TikTok: / google.
Follow us on Instagram: / google.
Join us on Facebook: / google.