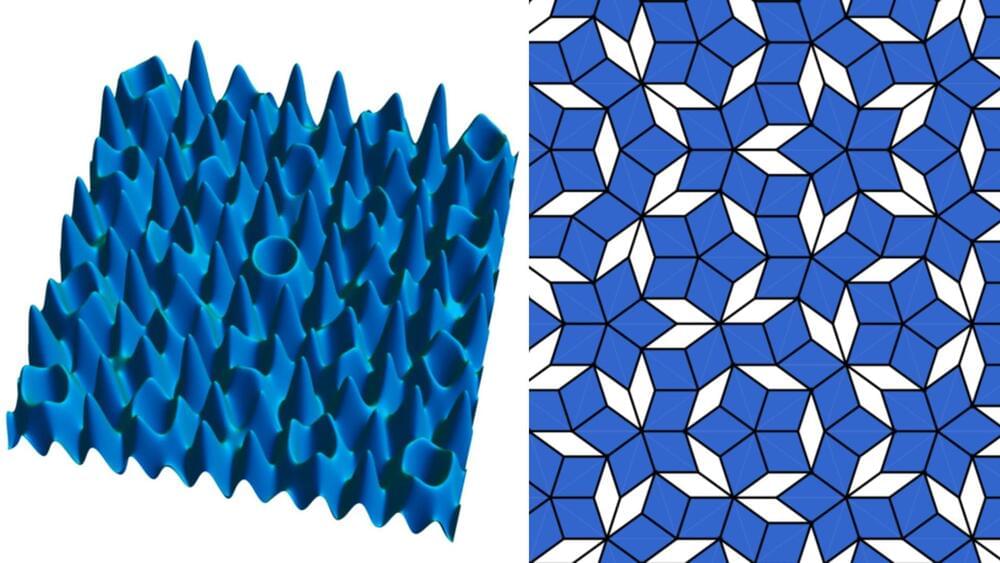
As its name implies, the Bose glass exhibits certain glass-like properties, with all particles in the system becoming localized. This means that each particle remains confined to its position, without interacting or blending with its neighbors.
If coffee behaved in this way, for example, stirring milk into it would result in a permanent pattern of black and white stripes that never mix into a uniform color.
In a localized system like the Bose glass, particles don’t mix with their environment, which suggests that quantum information stored within such a system could be retained for much longer periods. This property has significant implications for quantum computing and information storage.