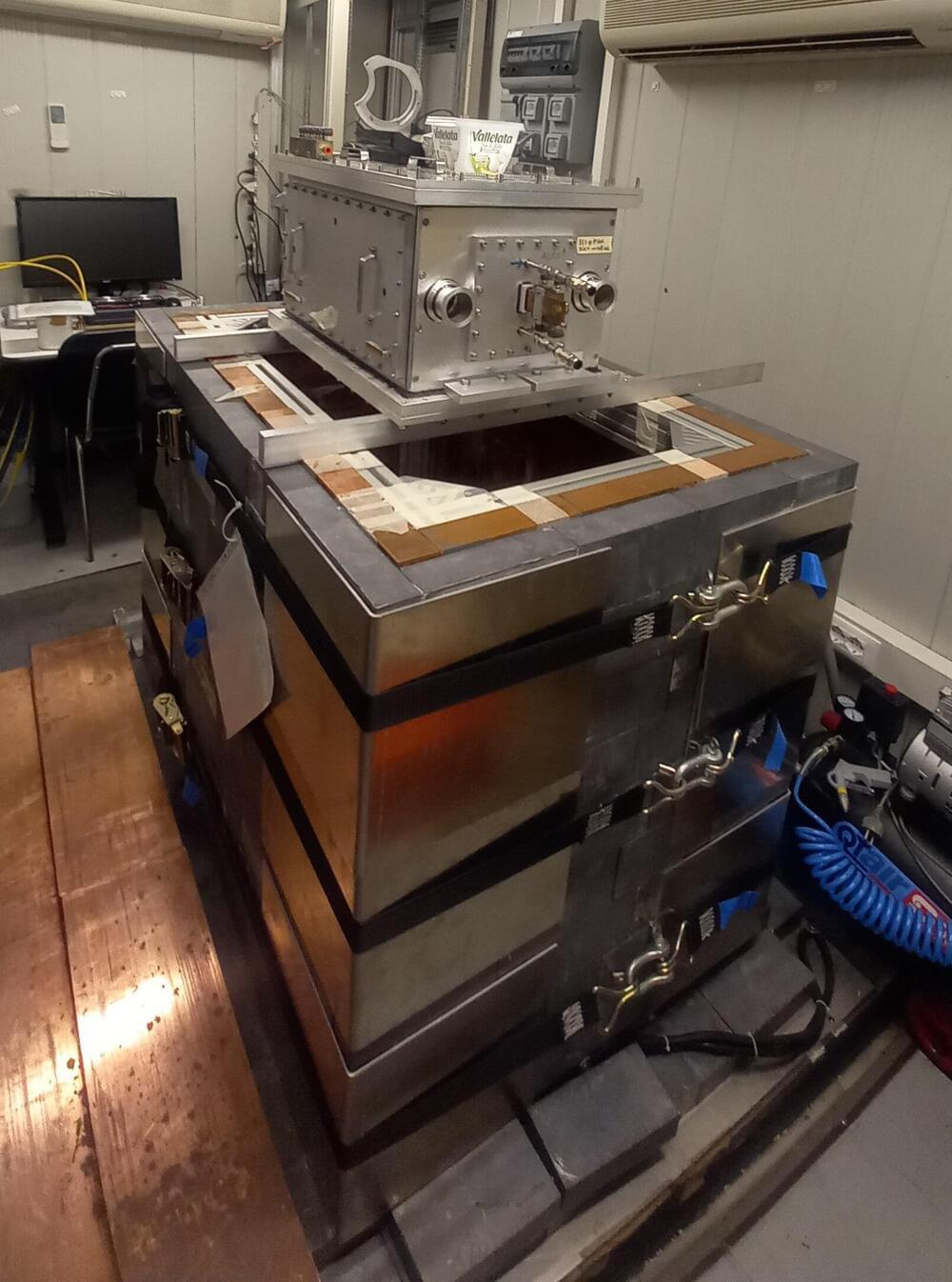
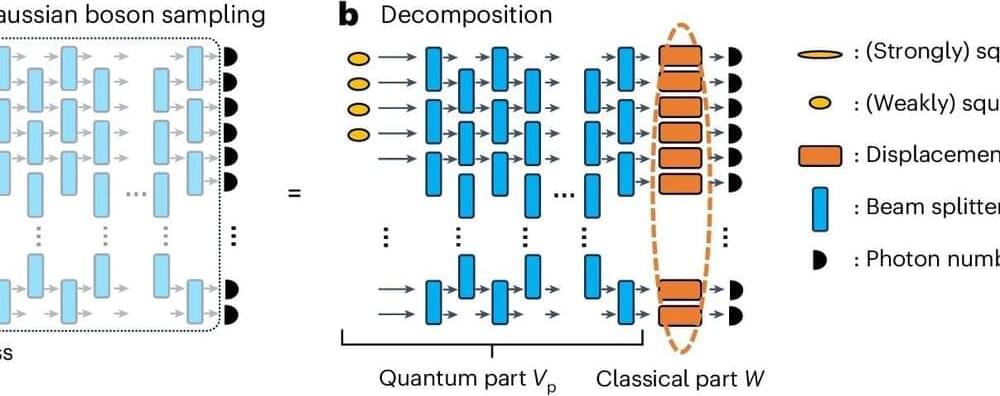
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics in Heidelberg have succeeded in selectively manipulating the motion of the electron pair in the hydrogen molecule.

👉 Head to https://brilliant.org/spacetime/ for a 30-day free trial + 20% off your annual subscription.
Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!
/ pbsspacetime.
If we discover how to connect quantum mechanics with general relativity we’ll pretty much win physics. There are multiple theories that claim to do this, but it’s notoriously difficult to test them. They seem to require absurd experiments like a particle collider the size of a galaxy. Or we could try to physics smarter, instead of physicsing harder. Let’s talk about some ideas for quantum gravity experiments that can be done on a non-galaxy-sized lab bench, and in some cases already have been done.
PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
Check out the Space Time Merch Store.
https://www.pbsspacetime.com/shop.


The principles of thermodynamics are cornerstones of our understanding of physics. But they were discovered in the era of steam-driven technology, long before anyone dreamed of quantum mechanics. In this episode, the theoretical physicist Nicole Yunger Halpern talks to host Steven Strogatz about how physicists today are reinterpreting concepts such as work, energy and information for a quantum world.
Listen on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, TuneIn or your favorite podcasting app, or you can stream it from Quanta.
As its name implies, the Bose glass exhibits certain glass-like properties, with all particles in the system becoming localized. This means that each particle remains confined to its position, without interacting or blending with its neighbors.
If coffee behaved in this way, for example, stirring milk into it would result in a permanent pattern of black and white stripes that never mix into a uniform color.
In a localized system like the Bose glass, particles don’t mix with their environment, which suggests that quantum information stored within such a system could be retained for much longer periods. This property has significant implications for quantum computing and information storage.