“This gamma-ray burst was extremely bright. We expect to see one like this only every 10,000 years or so.”
A team of astronomers led by the University of Alabama in Huntsville has detected the brightest gamma-ray burst.
These bursts are thought to be among the most luminous explosions in the universe and created during the birth of black holes. GRBs generally last from less than a second to several minutes.
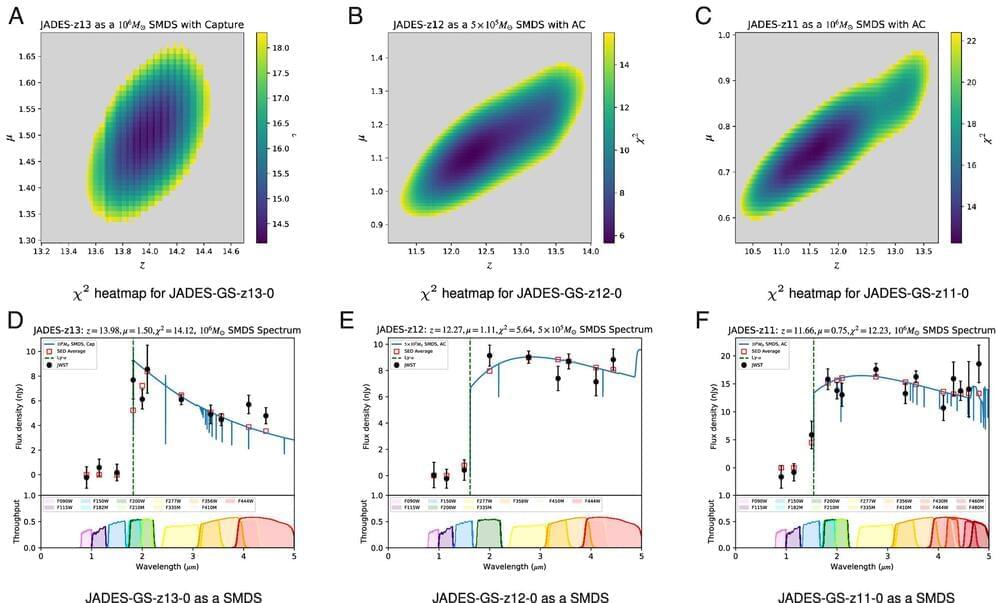
The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH) has announced that three researchers associated with the UAH Center for Space Plasma and Aeronomic Research (CSPAR) have discovered a gamma-ray burst (GRB) approximately 2.4 billion light-years away in the constellation Sagitta that ranks as the brightest ever observed. Believed to have been triggered by collapse of a massive star, it is accompanied by a supernova explosion, giving birth to a black hole.
Dr. Peter Veres, an assistant professor with CSPAR, Dr. Michael S. Briggs, CSPAR principal research scientist and assistant director, and Stephen Lesage, a UAH graduate research assistant, collaborated on the discovery and analysis of the gamma-ray burst. The researchers operate the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM) at UAH, a part of the University of Alabama System. The GBM is an instrument in low-Earth orbit aboard the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope that can see the entire gamma-ray sky not blocked by the Earth and hunts for GRBs as part of its main program.
The development of the GBM and analysis of its data is a collaborative effort between the National Space Science and Technology Center in the U.S. and the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany. The instrument is managed at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL.




 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)