Circa 2017
The future Internet is very likely the mixture of all-optical Internet with low power consumption and quantum Internet with absolute security. The optical regular Internet would be used by default, but switched over to quantum Internet when sensitive data need to be transmitted. PT and and its counterpart in the quantum limit SPT would be the core components for both OIP and QIP in future Internet. Compared with electronic transistors, PTs/SPTs potentially have higher speed, lower power consumption and compatibility with fibre-optic communication systems.
Several schemes for PT6,7,8,9,10 and SPT11,12,13,14,15,16,17 have been proposed or even proof-of-principle demonstrated. All these prototypes exploit optical nonlinearities, i.e., photon-photon interactions18. However, photons do not interact with each other intrinsically, so indirect photon-photon interactions via electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)19, photon blockade20 and Rydberg blockade21 were intensively investigated in this context over last two decades in either natural atoms22,23 or artificial atoms including superconducting boxes24,25 and semiconductor quantum dots (QDs)12,13. PT can seldom work in the quantum limit as SPT with the gain greater than 1 because of two big challenges, i.e., the difficulty to achieve the optical nonlinearities at single-photon levels and the distortion of single-photon pulse shape and inevitable noise produced by these nonlinearities26. The QD-cavity QED system is a promising solid-state platform for information and communication technology (ICT) due to their inherent scalability and matured semiconductor technology. But the photon blockade resulting from the anharmonicity of Jaynes-Cummings energy ladder27 is hard to achieve due to the small ratio of the QD-cavity coupling strength to the system dissipation rates12,13,28,29,30,31,32 and the strong QD saturation33. Moreover, the gain of this type of SPT based on the photon blockade is quite limited and only 2.2 is expected for In(Ga)As QDs12,13.
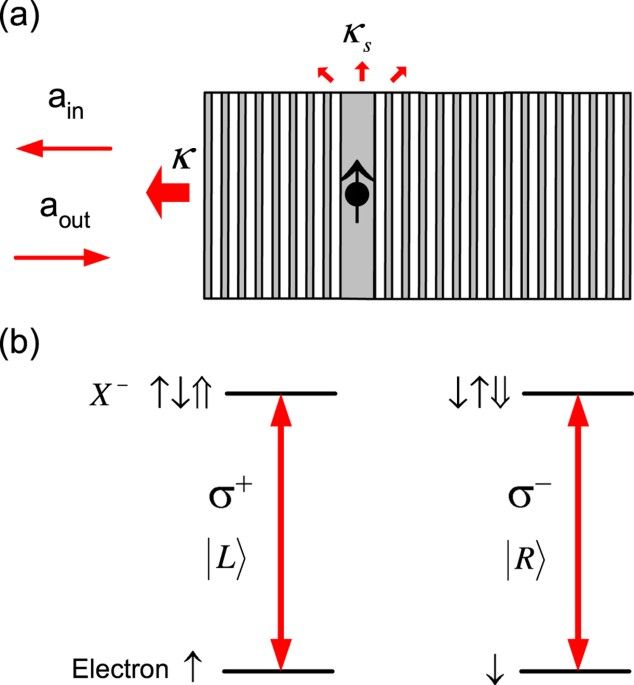
In this work, a different PT and SPT scheme exploiting photon-spin interactions rather than photon-photon interactions is proposed based on a linear quantum-optical effect — giant optical Faraday rotation (GFR) induced by a single QD-confined spin in a single-sided optical microcavity34. This spin-cavity transistor is genuinely a quantum transistor in three aspects: it is based on a quantum effect, i.e., the linear GFR; it has the duality as a quantum gate for QIP and a classical transistor for OIP; it can work in the quantum limit as a SPT to amplify a single-photon state to Schrödinger cat state. Therefore this new-concept transistor can be more powerful than the traditional electronic transistors. Theoretically the maximum gain can reach ~105 in the state-of-the-art pillar microcavity, several orders of magnitude greater than previous PT/SPT schemes6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17. The large gain is attributed to the linear GFR that is robust against classical and quantum fluctuations and the long spin coherence time compared with the cavity lifetime. The maximal speed which is determined by the cavity lifetime has the potential to break the terahertz (THz) barrier for electronic transistors35,36. Based on this versatile spin-cavity transistor, optical Internet1, quantum computers (QCs)37,38 (either spin-cavity hybrid QCs or all-optical QCs), and quantum Internet4 could become reality even with current semiconductor technology.