Category: particle physics – Page 485

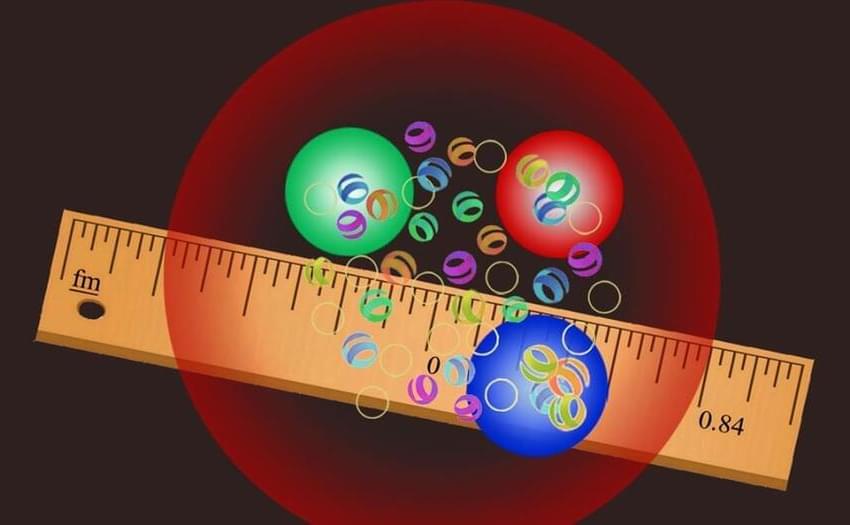
Protons are probably actually smaller than long thought
A few years ago, a novel measurement technique showed that protons are probably smaller than had been assumed since the 1990s. The discrepancy surprised the scientific community; some researchers even believed that the Standard Model of particle physics would have to be changed. Physicists at the University of Bonn and the Technical University of Darmstadt have now developed a method that allows them to analyze the results of older and more recent experiments much more comprehensively than before. This also results in a smaller proton radius from the older data. So there is probably no difference between the values — no matter which measurement method they are based on. The study appeared in Physical Review Letters.

Discovery unravels how atomic vibrations emerge in nanomaterials
A hundred years of physics tells us that collective atomic vibrations, called phonons, can behave like particles or waves. When they hit an interface between two materials, they can bounce off like a tennis ball. If the materials are thin and repeating, as in a superlattice, the phonons can jump between successive materials.
Now there is definitive, experimental proof that at the nanoscale, the notion of multiple thin materials with distinct vibrations no longer holds. If the materials are thin, their atoms arrange identically, so that their vibrations are similar and present everywhere. Such structural and vibrational coherency opens new avenues in materials design, which will lead to more energy efficient, low-power devices, novel material solutions to recycle and convert waste heat to electricity, and new ways to manipulate light with heat for advanced computing to power 6G wireless communication.
The discovery emerged from a long-term collaboration of scientists and engineers at seven universities and two U.S. Department of Energy national laboratories. Their paper, “Emergent Interface Vibrational Structure of Oxide Superlattices,” was published January 26 in Nature.

Scientists Create ‘Coldest Temperature Ever’
As far as we can tell from modern science, there’s no upper limit to temperature. There sure is a lower limit, though. We call that absolute zero, measured as −273.15 °C (−459.67 °F). Scientists have yet to reach that limit in any experiment, but they’re getting close. A team of physicists in Germany has gotten closer than ever before, reaching a temperature of 38 trillionths of a degree from absolute zero, according to New Atlas.
This news might sound familiar because it is — scientists have inched closer to absolute zero on numerous occasions. A few years ago, MIT created what was at the time the coldest spot in the universe with sodium and potassium atoms. The International Space Station has also conducted experiments within a fraction of a degree of absolute zero. The problem is that no matter how well insulated your testing setup is, a tiny amount of energy always sneaks in from the environment. When that happens, you can’t reach absolute zero and halt all atomic motion.
The team from the University of Bremen broke the record once again by dropping the experiment (above) from the top of a very tall tower. Yes, really. They started with a cloud of 100,000 rubidium atoms, which were confined inside a magnetic field. When cooled, the atoms clump together and form a mysterious state of matter known as a Bose-Einstein condensate. In this state, the atoms act like one giant atom, making quantum effects visible at the macroscopic scale.

Strongest ever magnetic field fails to make predicted exotic particles
The strongest magnetic field ever measured anywhere in the universe has failed to produce detectable magnetic monopoles. These hypothetical particles are predicted by many calculations of possible phenomena beyond the standard model of particle physics, but more than a century of searching still hasn’t turned up any signs of them.
All magnets that we know of have at least two poles – typically a north and south pole – with opposite magnetic charges. However, some models of the universe predict that there should be particles with only a north or a south pole called magnetic monopoles. For example, the existence of magnetic monopoles would explain why electric charge is quantised, meaning it comes in packets with a minimum size.
Over the past century or so, researchers have searched for magnetic monopoles both in space and in the smash-ups of particles at colliders, but they haven’t been found yet. Igor Ostrovskiy at the University of Alabama and his colleagues looked for monopoles being produced by a proposed phenomenon called the Schwinger effect, wherein extremely powerful magnetic fields could spontaneously produce magnetic particles and their antiparticles.
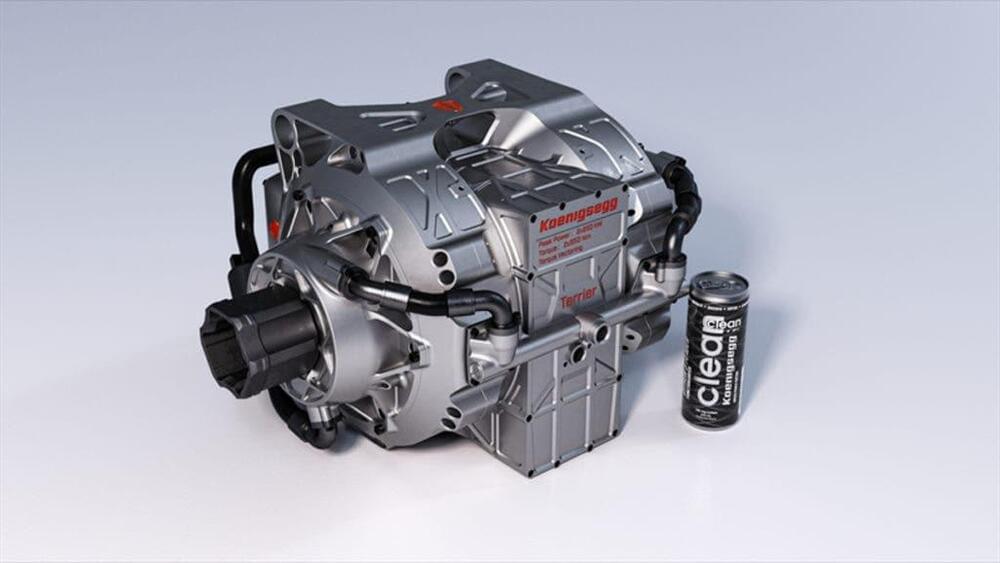

Koenigsegg Quark, Terrier Bring Big Power In Small Package To Electric Cars
Koenigsegg has announced new high power, compact motors and powertrains for electric cars.
Christian von Koenigsegg is an inveterate tinkerer who has built a business on his ability to squeeze extraordinary amounts of power out of internal combustion engines. Lately, he has turned his talents to electric motors and drivetrains. On January 31, his company announced two breakthrough products that could transform the world of electric cars.
[caption id=.
New atomic clock is the most precise ever created
If scientists could measure the oscillations of just one energized cesium atom, they’d be able to keep perfect time, but they can’t due to a weird phenomenon called the standard quantum limit.
Instead, they have to measure thousands of atoms at once and then average out the results for atomic clocks, which leads to a just slightly imprecise second.
Now, MIT researchers have found a way to create a more precise atomic clock by exploiting another weird quantum phenomenon: entanglement.
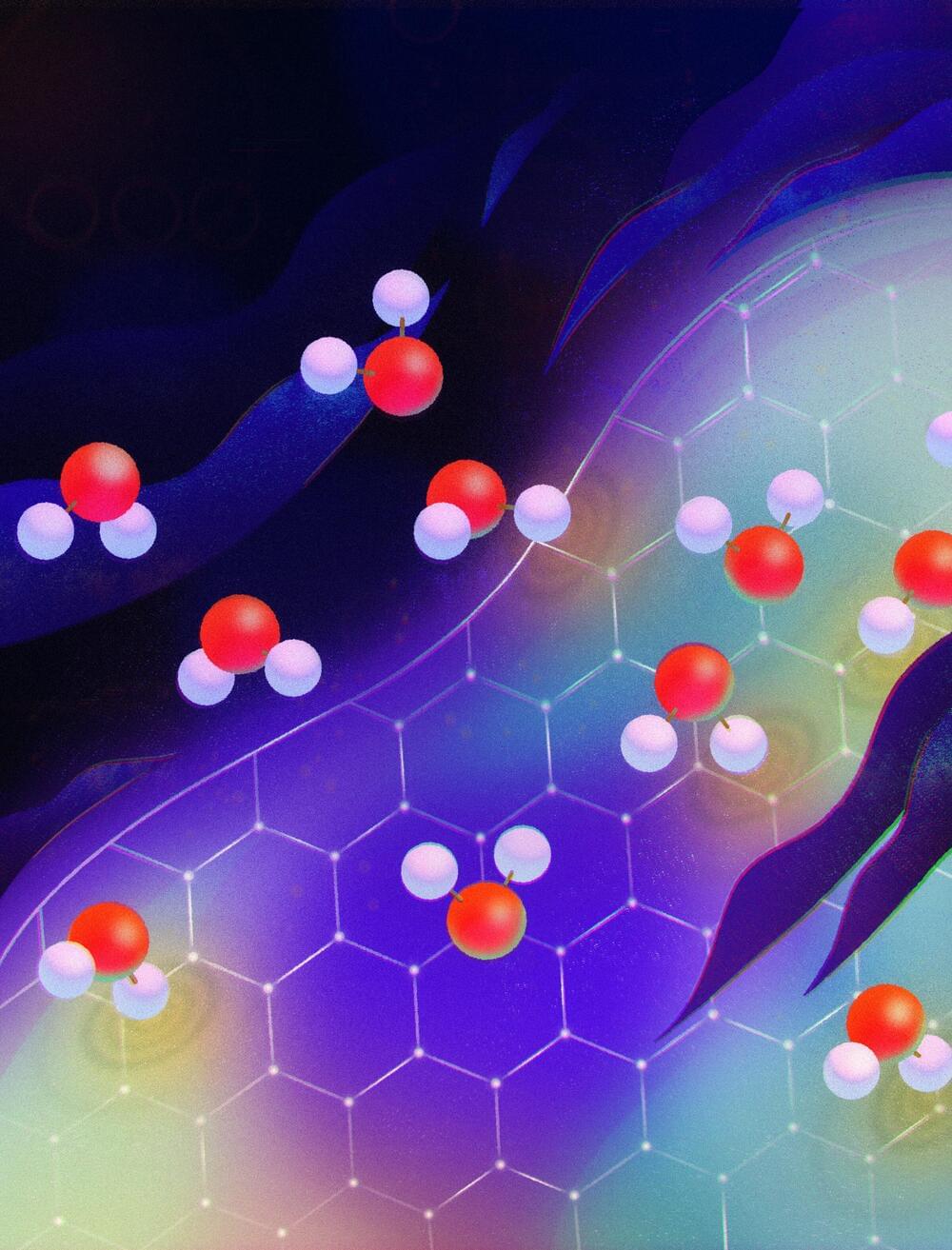
‘Quantum friction’ slows water flow through carbon nanotubes, resolving long-standing fluid dynamics mystery
For 15 years, scientists have been baffled by the mysterious way water flows through the tiny passages of carbon nanotubes—pipes with walls that can be just one atom thick. The streams have confounded all theories of fluid dynamics; paradoxically, fluid passes more easily through narrower nanotubes, and in all nanotubes it moves with almost no friction. What friction there is has also defied explanation.
In an unprecedented mashup of fluid dynamics and quantum mechanics, researchers report in a new theoretical study published February 2 in Nature that they finally have an answer: ‘quantum friction.’
The proposed explanation is the first indication of quantum effects at the boundary of a solid and a liquid, says study lead author Nikita Kavokine, a research fellow at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Quantum Physics (CCQ) in New York City.
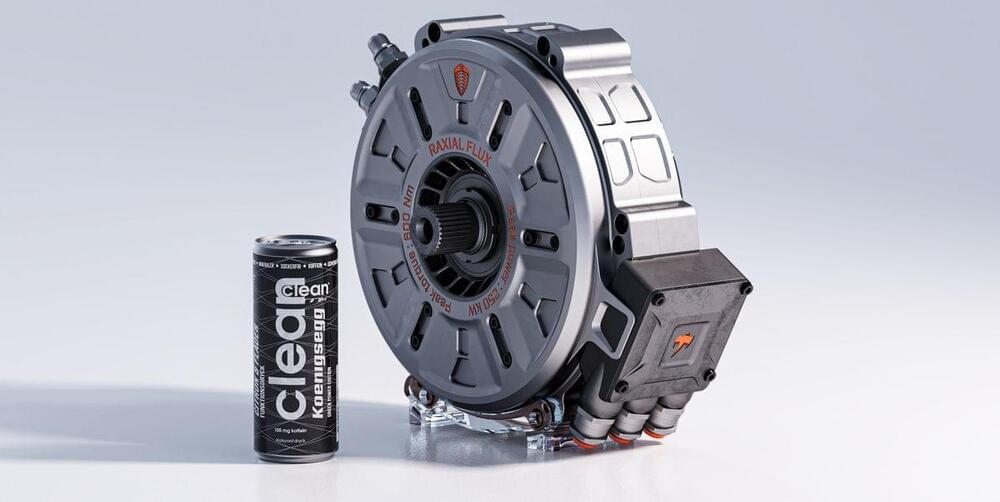

Koenigsegg’s Tiny Electric Motor Makes 335 HP and 443 LB-FT of Torque
Dubbed the “Quark,” the motor weighs just 63 pounds.
Koenigsegg is also marketing an EV drive unit made up of two Quark motors, plus its small-but-powerful inverter, and small low-ratio planetary gearsets at each output shaft. The unit is called the “Terrier,” and serves up 670 hp and 811 lb-ft in a package that weighs just 187 pounds, and which offers torque vectoring across an axle. A Terrier can be bolted directly to a car’s monocoque as well.
More information on the Terrier unit is forthcoming, and presumably, it will be featured on future Koenigsegg products. As ever, the numbers are deeply impressive and entirely unsurprising from the innovative Swedish firm.