A pair of astrophysicists at Tianjin University, in China, has proposed ways that humans in the distant future might use black holes as an energy source. In their paper published in the journal Physical Review D, Zhan-Feng Mai and Run-Qiu Yang outline two possible scenarios in which energy could potentially be harvested from primordial black holes.
As scientists continue to look for ways to meet the energy needs of a growing global population, some have begun to look for options that may not have been considered in the past. In this new effort, the researchers consider the possibility of tapping black holes as a way to power human needs of the future by turning them into batteries.
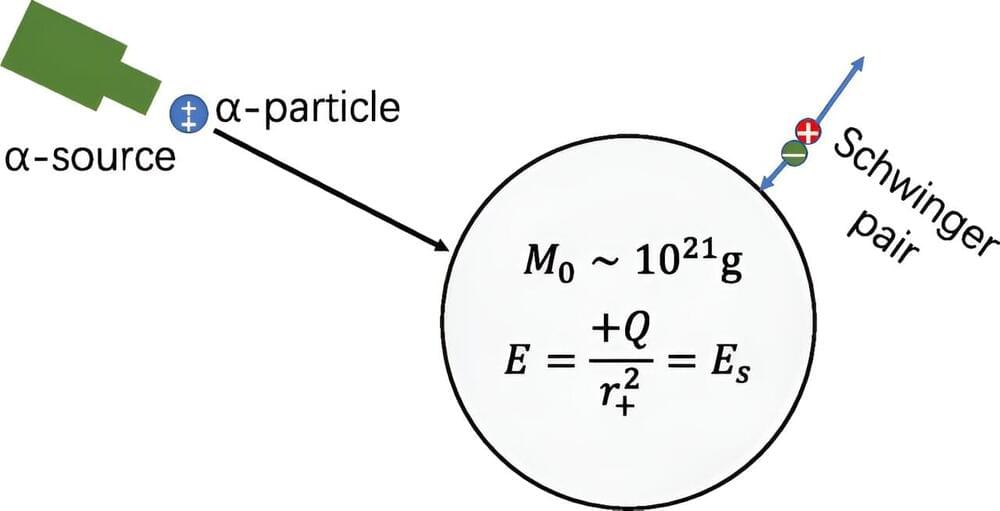
The first option suggests future astro-engineers could “charge” a primordial black hole (a very small black hole with no spin that formed soon after the Big Bang) by feeding it electrically charged particles until the black hole begins to repel them, signaling it is fully charged, like a battery. Energy could then be collected from the black hole through the use of superradiance, whereby some of the electromagnetic or gravitational waves carrying more energy than was fed in are deflected into the black hole, captured first and converted into a usable energy source.