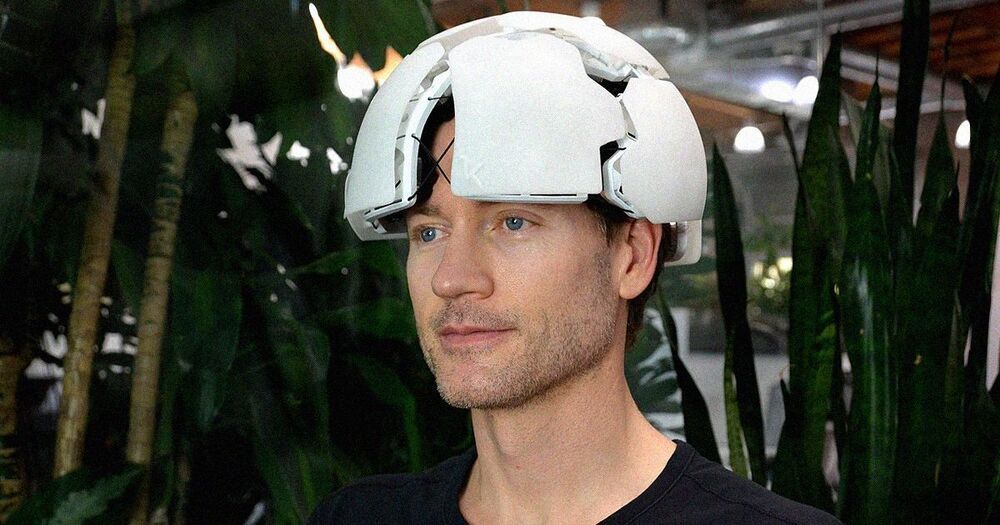
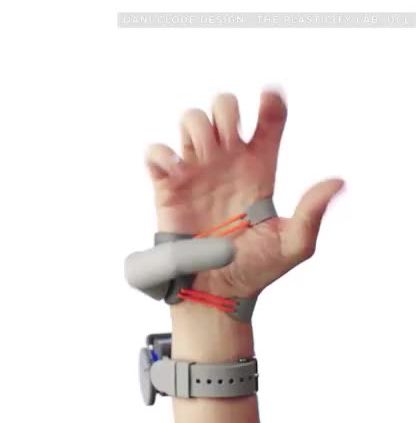
This third thumb is a flexible, 3D-printed extention that’s wirelessly controlled by the user’s big toe.




There are still many unsolved mysteries about the human brain and its development. Now, a novel study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry sheds new light on the neurobiological origins of our individual traits.
Functional connectivity is the coordinated activity – activation or deactivation – through time between separate brain regions, regardless of their physical closeness or the type of neural connections between them. Changes in functional connectivity can be a sign of mental health disorders such as depression, eating disorders, and schizophrenia, and are thought to have developmental origins.

When faced with a predator or sudden danger, the heart rate goes up, breathing becomes more rapid, and fuel in the form of glucose is pumped throughout the body to prepare an animal to fight or flee.
These physiological changes, which constitute the “fight or flight” response, are thought to be triggered in part by the hormone adrenaline.
But a new study from Columbia researchers suggests that bony vertebrates can’t muster this response to danger without the skeleton. The researchers found in mice and humans that almost immediately after the brain recognizes danger, it instructs the skeleton to flood the bloodstream with the bone-derived hormone osteocalcin, which is needed to turn on the fight or flight response.

The plasticizers contained in many everyday objects can impair important brain functions in humans. Biologists from the University of Bayreuth warn of this danger in an article in Communications Biology. Their study shows that even small amounts of the plasticizers bisphenol A and bisphenol S disrupt the transmission of signals between nerve cells in the brains of fish. The researchers consider it very likely that similar interference can also occur in the brains of adult humans. They, therefore, call for the rapid development of alternative plasticizers that do not pose a risk to the central nervous system.
Bisphenols are plasticizers that are found in a large number of plastic products worldwide — for example, in food packaging, plastic tableware, drinking bottles, toys, tooth fillings, and babies’ dummies. In recent years, numerous health risks have already been associated with them, especially with bisphenol A (BPA). The Bayreuth research team led by Dr. Peter Machnik at the Animal Physiology research group (led by Prof. Dr. Stefan Schuster) has now for the first time investigated the effects of plasticizers on signal transmission between nerve cells in the adult brain. The study covers not only BPA, but also bisphenol S (BPS), which is often considered less harmful to health. Their findings: Both plasticizers impair communication between the nerve cells of the brain.
Hemp has been celebrated and vilified in equal measure over the centuries. It has fantastic properties for textiles and ropes, but it comes from the cannabis plant, so it arouses deep suspicion among some policymakers. What is unarguable though, is that it is an extremely fast growing plant that stores a large amount of carbon. So is it really possible to convert it into graphene and diamond in a sustainable, environmentally friendly way?
Video Transcripts available at our website.
http://www.justhaveathink.com.
Help support this channels independence at http://www.patreon.com/justhaveathink.
Or with a donation via Paypal by clicking here.
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted_b…source=url.
You can also help keep my brain ticking over during the long hours of research and editing via the nice folks at BuyMeACoffee.com.
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/justhaveathink.
Download the Just Have a Think App from the AppStore or Google Play.
The population on Earth is increasingly growing and people are expected to live longer in the future. Thus, better and more reliable therapies to treat human diseases such as Alzheimer’s and cardiovascular diseases are crucial. To cope with the challenge of ensuring healthy aging, a group of international scientists investigated the potential of biosynthesising several polyamines and polyamines analogs with already known functionalities in treating and preventing age-related diseases.
One of the most interesting molecules to study was spermidine, which is a natural product already present in people’s blood and an inducer of autophagy that is an essential cellular process for clearing damaged proteins, e.g., misfolded proteins in brain cells that can cause Alzheimer’s. When people get older the level of spermidine in the blood decrease and dietary supplements, or certain food products are needed to maintain a stable and high level of spermidine in the blood. However, those products are difficult to produce with traditional chemistry due to their structural complexity and extraction of natural resources is neither a commercially viable nor a sustainable approach.
Therefore, the researchers instead decided to open their biochemical toolbox and use classical metabolic engineering strategies to engineer the yeast metabolism to produce polyamines and polyamines analogs.
Research conducted by Qiang et al has discovered a link between a protein in red blood cells and age-related decline in cognitive performance. Published in the open access journal PLOS Biology on 17th June 2021, the study shows that depleting mouse blood of the protein ADORA2B leads to faster declines in memory, delays in auditory processing, and increased inflammation in the brain.
As life expectancies around the world increase, so are the number of people who will experience age-related cognitive decline. Because the amount of oxygen in the blood also declines with age, the team hypothesized that aging in the brain might be naturally held at bay by adenosine receptor A2B (ADORA2B), a protein on the membrane of red blood cells which is known to help release oxygen from the blood cells so it can be used by the body. To test this idea, they created mice that lacked ADORA2B in their blood and compared behavioral and physiological measures with control mice.
The team found that as the mice got older, the hallmarks of cognitive decline—poor memory, hearing deficits, and inflammatory responses in the brain—were all greater in the mice lacking ADORA2B than in the control mice. Additionally, after experiencing a period of oxygen deprivation, the behavioral and physiological effects on young mice without ADORA2B were much greater than those on normal young mice.