An accelerated five-day TMS protocol may rival the standard six-week treatment for depression.


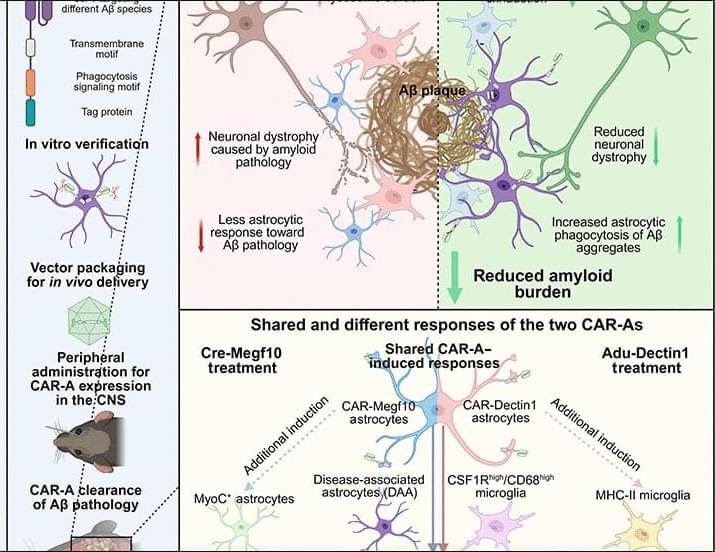
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed a novel cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease using genetically modified astrocytes — the brain’s most abundant cells. By equipping these cells with a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), scientists enabled them to specifically target and clear beta-amyloid plaques, the toxic protein deposits that accumulate in brain tissue and drive neurodegeneration. In mouse trials, a single injection prevented plaque formation in young healthy rodents and reduced existing plaque levels by half in older mice. While the approach is still being refined to minimize side effects and must be evaluated for human safety, it holds promise both as a preventive measure and as a treatment at various stages of Alzheimer’s. The same technology may eventually be adapted for cancer therapy by reprogramming the cells to target tumor markers.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia and is characterized by progressive amyloid accumulation followed by tau-mediated neurodegeneration. Despite advances in anti-amyloid immunotherapies, important limitations remain, highlighting the need for new therapeutic strategies. Here, we introduce anti-amyloid chimeric antigen receptors expressed in astrocytes (CAR-A) and validate their function in vitro. We show that two CAR-A designs reduce amyloid and associated pathology after plaque formation and prevent early plaque deposition in vivo. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing shows that CAR-A treatment induces a distinct glial response to amyloid pathology involving coordinated activity of astrocytes and microglia. Each construct additionally elicits distinctive, receptor-specific effects in astrocytes or microglia.
We are living in the age of maximum AI hype: A superintelligence that surpasses humanity is going to emerge at any moment, according to the most breathless corners of the tech world.
There are basic technical grounds to be skeptical of that claim, but beyond that, a much deeper issue lies at the boundary between science and philosophy: What makes life different from non-life? Why is a rock inert and insensate, while even the simplest cell manifests open-ended activity in the relentless pursuit of staying alive? Since the only systems that indisputably display intelligence are alive, if we can’t understand life, we’re probably missing something essential about intelligence.
Sixty years ago, an influential but little-known philosopher named Hans Jonas gave a potent, creative, and radical answer to this question of what makes life different from non-life. In the decades since, the power and reach of his perspective have gained traction. Today, for a growing group of researchers — in fields ranging from neuroscience to the physics of complex systems — Jonas has become an incisive voice arguing forcefully that organisms are more than just machines, and minds are more than just computers.
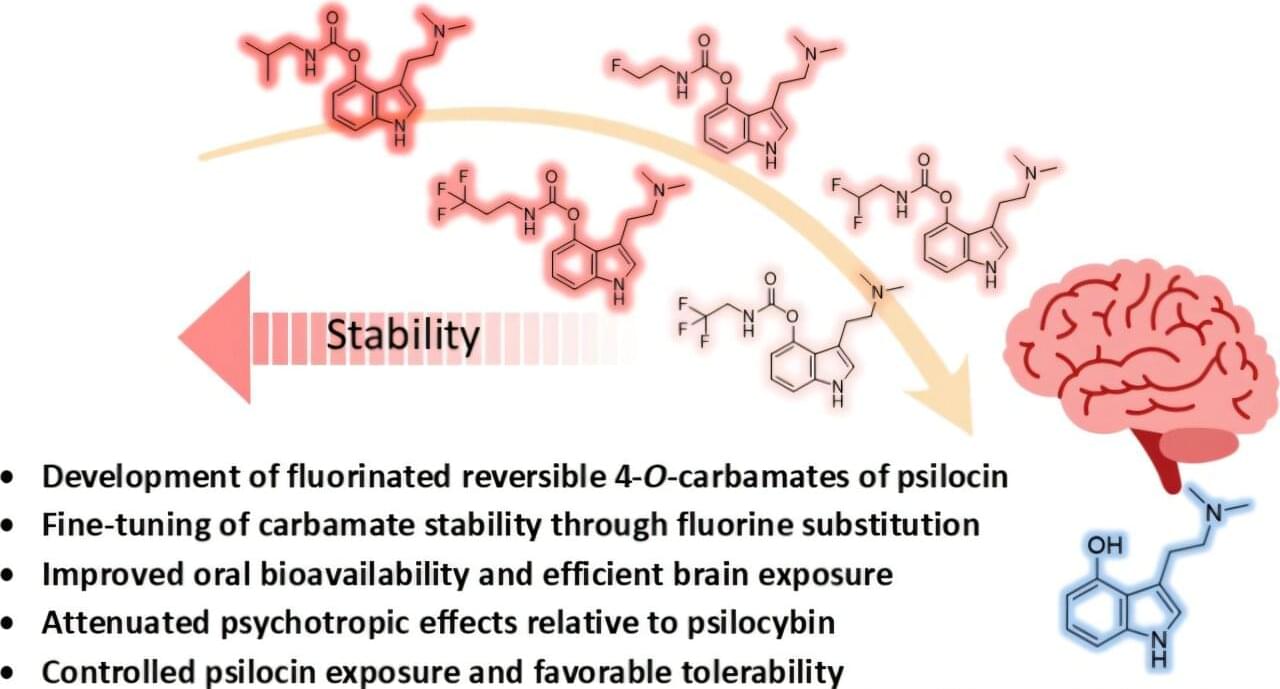
Psilocybin—the psychoactive compound in “magic mushrooms”—is gaining scientific attention for its potential in treating neuropsychiatric conditions including depression, anxiety, substance use disorders and certain neurodegenerative diseases. However, its hallucinogenic effects may limit broader therapeutic applications. Researchers publishing in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry synthesized modified versions of psilocin, the active form of psilocybin, that retained its activity while producing fewer hallucinogenic-like effects than pharmaceutical-grade psilocybin in a preliminary study in mice.
“Our findings are consistent with a growing scientific perspective suggesting that psychedelic effects and serotonergic activity may be dissociated,” says Andrea Mattarei, a corresponding author of the study. “This opens the possibility of designing new therapeutics that retain beneficial biological activity while reducing hallucinogenic responses, potentially enabling safer and more practical treatment strategies.”
Mood disorders and some neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, involve imbalances of the neurotransmitter molecule serotonin, which helps regulate mood and other brain functions. For decades, scientists have been investigating the therapeutic use of psychedelics such as psilocybin on serotonin-signaling pathways. However, the hallucinations that can accompany these drugs may make people wary of taking them, even if there is a medical benefit.

Growing neurons rely on chemical cues to find their targets, but new research shows that the brain’s physical properties help shape those signals. Scientists discovered that tissue stiffness can trigger the production of guidance molecules through a force-sensing protein called Piezo1. This protein not only detects mechanical forces but also helps maintain the structure of brain tissue. The discovery reveals a powerful link between the brain’s physical environment and how its wiring is built.

In a randomized clinical trial including older bereaved adults, group-format grief-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (ProlongedGriefDisorder) was noninferior to individual therapy for reducing symptoms of prolonged grief, posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, and anxiety at 6 months.
Both formats produced large reductions in symptom burden, suggesting either delivery method is effective for older adults seeking treatment after loss.
This study examines whether cognitive behavioral therapy delivered in a group format is noninferior to cognitive behavioral therapy delivered in an individual format in reducing prolonged grief disorder symptoms in older adults.
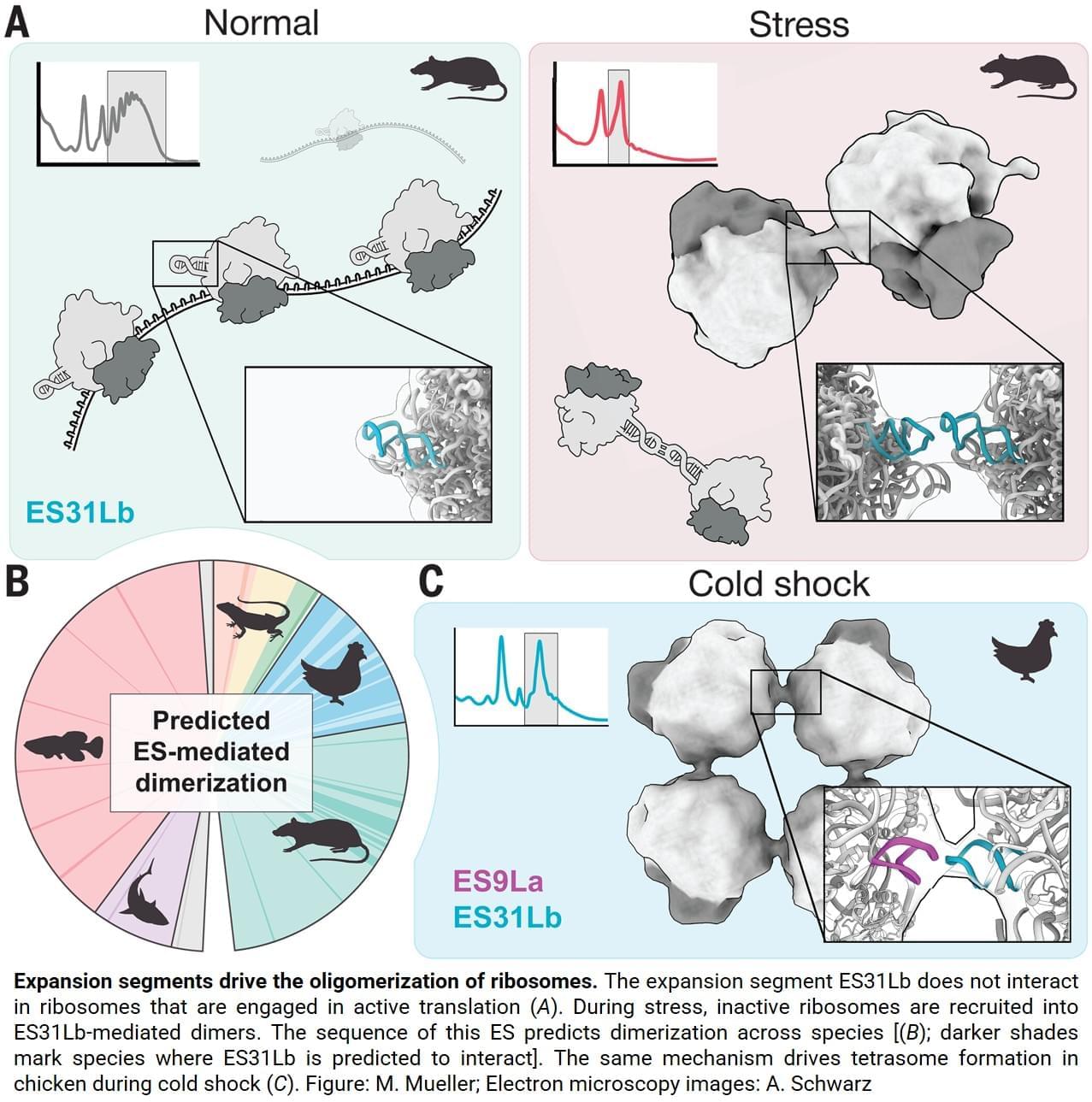
“Surprisingly, the two ribosomes are not held together by proteins, as is common in bacteria. Instead, the connection is made by a specific piece of ribosomal RNA called an expansion segment”, explains one of the lead authors.
Expansion segments are long, flexible RNA “tentacles” that protrude from ribosomes and have grown larger over the course of evolution. Although they are a prominent feature of animal ribosomes, their functions only just started to emerge. This study now shows that one particular expansion segment, called “31b”, is both necessary and sufficient to link ribosomes together during stress. At the molecular level, the expansion segment forms a precise RNA-RNA interaction — a so-called “kissing loop” — in which identical RNA loops bind each other through complementary sequences. Disrupting this interaction prevents disome formation, stunts cellular growth and makes cells more sensitive to stress. Science Mission sciencenewshighlights.
Ribosomes, the cell’s protein-making factories, consume large amounts of energy as they build the proteins that keep cells alive and functioning. When cells experience stress — such as lack of nutrients or sudden drops in temperature — they quickly switch into survival mode. New research now reveals an unexpected way cells manage this transition: By pairing up inactive ribosomes using a ribosomal RNA link. This RNA-based mechanism reveals a previously unknown role for ribosomal RNA in the cellular stress response.
Ribosomes are large molecular machines made of protein and RNA that build all proteins in the cell. Because protein production is extremely energy-intensive, cells rapidly reduce protein synthesis when stressed. It has long been known that bacterial cells pair their inactive ribosomes into so-called “hibernating disomes” however, such structures had not previously been identified in animal cells.
Using advanced imaging techniques, the team discovered that stressed animal cells — including neurons — assemble inactive ribosomes into tightly linked pairs, known as disomes. These ribosome pairs are not accidental collisions or artifacts, but a regulated and reversible response to stress. The new study was published in Science.

Alzheimer’s disease has long been viewed as something that originates inside the brain, but an in-depth genomic analysis suggests it may initially triggered by inflammation in distant organs like the skin, lungs or gut – perhaps decades before a person’s memory starts to decline.
This radical reframing of the disease may explain why Alzheimer’s drugs have been disappointing to date, because they act too late in the disease process. Instead, we may need to redirect our efforts towards addressing inflammation in other parts of the body.
“As neuroscientists, we tend to be very brain-centric, but this study really shines a spotlight on the fact that the brain is not disconnected from the rest of the body, and when changes happen in the rest of the body, it affects how the brain functions,” says Donna Wilcock at Indiana University, who wasn’t involved in the research. “Even though Alzheimer’s is a brain disease, we need to think about the whole body when we think about how it begins.”
Image: Alamy
The Alzheimer’s field is being turned on its head as mounting evidence points to the disease beginning outside the brain many years before symptoms start. This may mean we have to totally rethink how we approach preventing and treating the condition.
By Alice Klein

Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Chronic pain, with a prevalence of 20–30% is the major cause of human suffering worldwide, because effective, specific and safe therapies have yet to be developed. It is unevenly distributed among sexes, with women experiencing more pain and suffering. Chronic pain can be anatomically and phenomenologically dissected into three separable but interacting pathways, a lateral ‘painfulness’ pathway, a medial ‘suffering’ pathway and a descending pain inhibitory pathway. One may have pain(fullness) without suffering and suffering without pain(fullness). Pain sensation leads to suffering via a cognitive, emotional and autonomic processing, and is expressed as anger, fear, frustration, anxiety and depression.

The brain relies on real-time delivery of oxygen and nutrients through its microvasculature, which threads through neural tissue like electrical wires. While modern imaging technologies allow researchers to follow the activity of individual neurons in the brain, they are not yet advanced enough to dissect the microvascular function at a comparable spatial scale. This gap hinders our understanding of cerebral small vessel disease and its contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia.
To address this challenge, a team of researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and Northwestern University, led by Song Hu, professor of biomedical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering, have developed super-resolution functional photoacoustic microscopy (SR-fPAM).
By tracking the movement and oxygenation-dependent color change of red blood cells, SR-fPAM allows researchers to image blood flow and oxygenation at single-cell resolution in the mouse brain, which bridges a critical gap in functional microvascular imaging and could provide new insight into microvascular health and disease, such as stroke, vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.