𝙏𝙝𝙚 𝙘𝙤𝙣𝙙𝙞𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣𝙨 𝙘𝙖𝙣 𝙖𝙡𝙡 𝙖𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙘𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣, 𝙙𝙖𝙢𝙖𝙜𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙗𝙡𝙤𝙤𝙙 𝙫𝙚𝙨𝙨𝙚𝙡𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙡𝙚𝙖𝙙𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙩𝙤 𝙨𝙩𝙧𝙤𝙠𝙚𝙨. 𝘽𝙪𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙘𝙤𝙣𝙣𝙚𝙘𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙗𝙚𝙩𝙬𝙚𝙚𝙣 𝙫𝙖𝙨𝙘𝙪𝙡𝙖𝙧 𝙙𝙞𝙨𝙚𝙖𝙨𝙚 𝙞𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝘼𝙡𝙯𝙝𝙚𝙞𝙢𝙚𝙧’𝙨 𝙝𝙖𝙨 𝙧𝙚𝙢𝙖𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙙 𝙪𝙣𝙚𝙭𝙥𝙡𝙖𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙙 𝙙𝙚𝙨𝙥𝙞𝙩𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙞𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙨𝙚 𝙚𝙛𝙛𝙤𝙧𝙩𝙨 𝙤𝙛 … See more.
The Neuro-Network.
𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐦𝐚𝐲 𝐡𝐚𝐯𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐝 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐤 𝐛𝐞𝐭𝐰𝐞𝐞𝐧 𝐀𝐥𝐳𝐡𝐞𝐢𝐦𝐞𝐫’𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐯𝐚𝐬𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞
𝙁𝙤𝙧 𝙢𝙤𝙧𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙣 20 𝙮𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙨, 𝙨𝙘𝙞𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙨𝙩𝙨 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙠𝙣𝙤𝙬𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙥𝙚𝙤𝙥𝙡𝙚 𝙬𝙞𝙩𝙝 𝙝𝙮𝙥𝙚𝙧𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙨𝙞𝙤𝙣… See more.
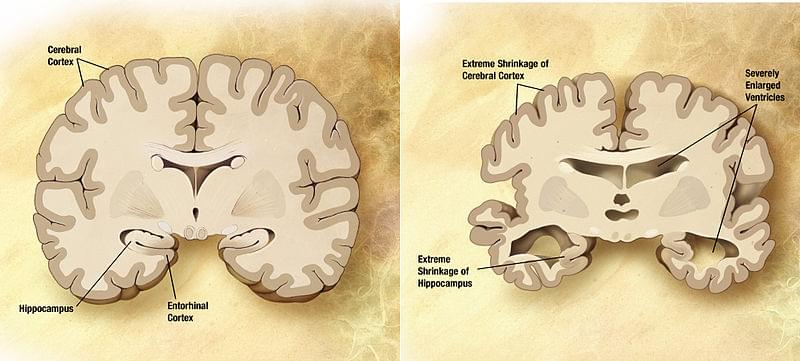
For more than 20 years, scientists have known that people with hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, or obesity have a higher likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
The conditions can all affect the brain, damaging blood vessels and leading to strokes. But the connection between vascular disease in the brain and Alzheimer’s has remained unexplained despite the intense efforts of researchers.