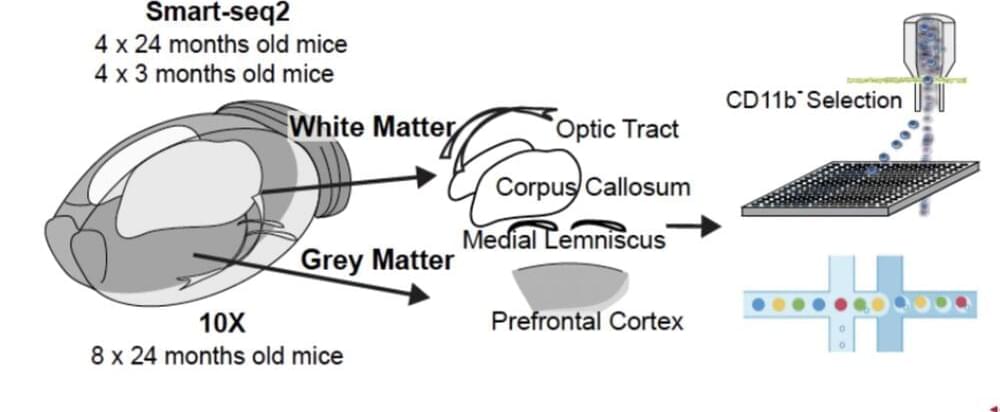
Summary: Mutations of the PTEN gene cause neurons to grow to twice the size and form four times the number of synaptic connections to other neurons as a normal neuron. Removing the RAPTOR gene, an essential gene in the mTORC1 signaling pathway, prevents the neuronal and synaptic overgrowth associated with PTEN mutations. Using Rapamycin to inhibit mTORC1 rescues all the changes in neuronal overgrowth.
Source: the geisel school of medicine at dartmouth.
Findings from a new study published in Cell Reports, involving a collaborative effort between researchers at the Luikart Laboratory at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine and the Weston Laboratory at the University of Vermont, are providing further insight into the neurobiological basis of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) and pointing to possible treatments.