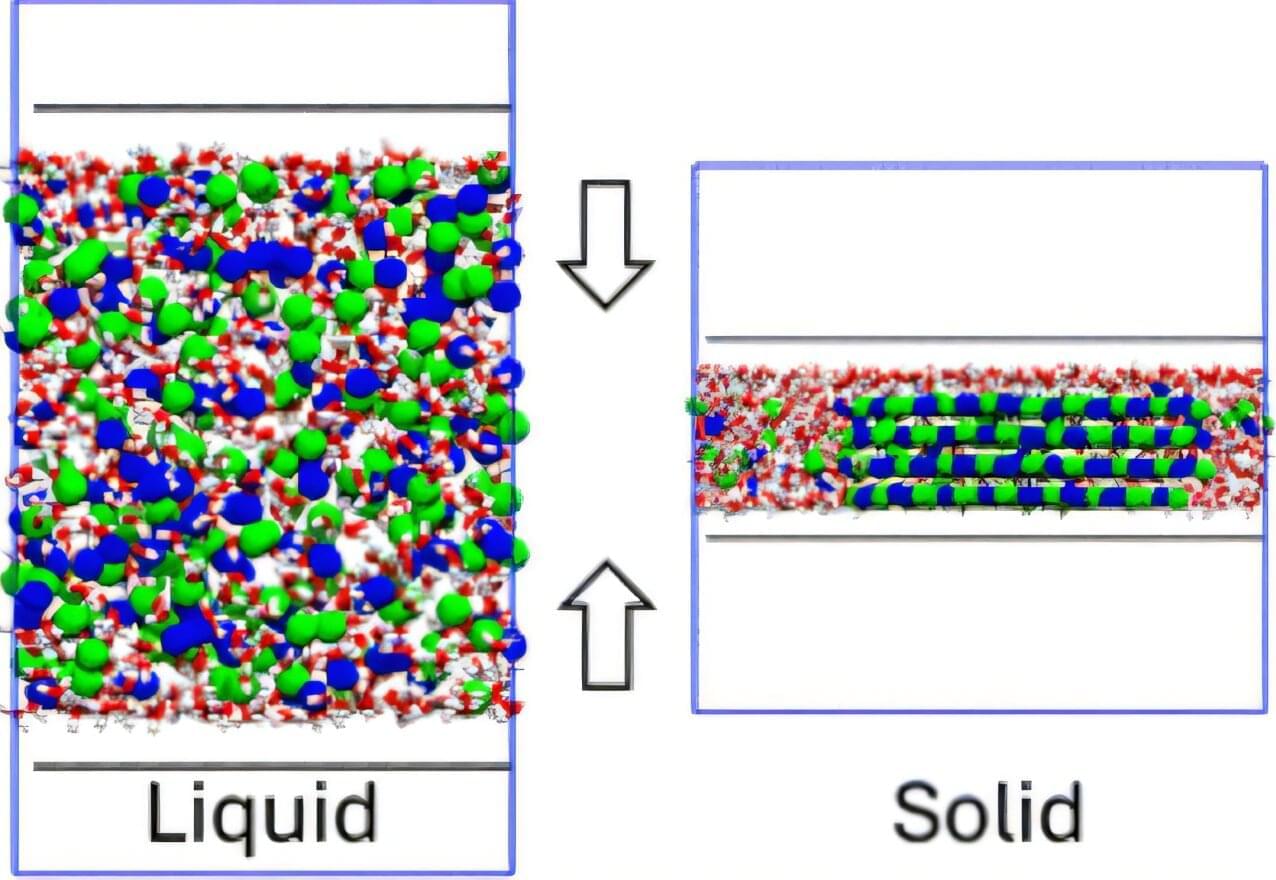
Suppose you want to make a tiny robot to perform surgery inside a human patient. To avoid damaging healthy tissue and to squeeze into tight spots, the robot should be squishy. And manipulating the robot’s movements with magnetic fields would make sense, as tissues don’t respond to magnetism. But what material would you use for the robot’s limbs? Magnetic materials are stiff and brittle. Embedding tiny particles of them in a rubbery matrix could work, but the thinner—and therefore bendier—you make the composite material, the less it responds to a magnetic field. Heinrich Jaeger of the University of Chicago, Monica Olvera de la Cruz of Northwestern University, Illinois, and their collaborators have now overcome that obstacle by making thin, flexible sheets out of self-assembled nanoparticles of magnetite [1]. Even a modest field of 100 milliteslas can lift a sheet and bend it by 50°, they found.
At room temperature, magnetite (Fe3O4) is ferrimagnetic—that is, the magnetic moments in its two sublattices align in opposite directions but with unequal magnitudes, yielding a net magnetization. The smaller a ferrimagnet, the greater the chance that it has a single domain, and therefore the lower the temperature at which the domain’s magnetization will flip. When the sample size gets down to a few tens of nanometers, a ferrimagnet made of randomly flipping particles becomes, in effect, a paramagnet—that is, it lacks a net magnetization and is attracted by an applied magnetic field. The attraction can be strong. The discoverers of this phenomenon in 1959 dubbed it superparamagnetism [2].
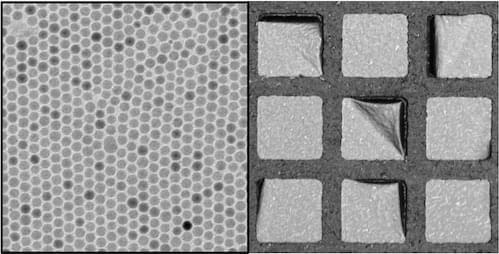
The researchers realized that a sheet made from a single layer of superparamagnetic particles could serve as a viable material for the magnetic actuation of small soft robots. To create the layers, they suspended magnetite nanoparticles in droplets of water coated with an organic solvent. The solvent attracted the nanoparticles, which migrated to a droplet’s surface. The water slowly evaporated, leaving behind a layer of closely packed nanoparticles draped on the droplet’s support structure, a square copper grid. Each of the 20 × 20 µm squares supported a single sheet. As shown in the figure, some of the sheets happened to have a single unattached corner.