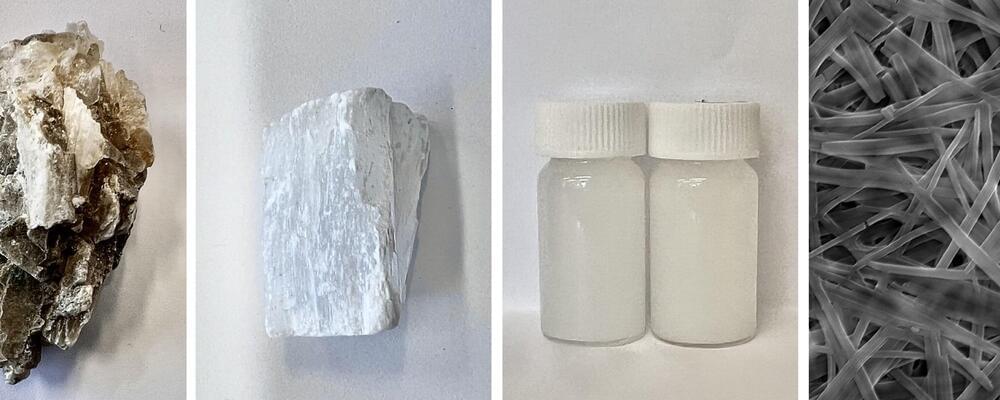
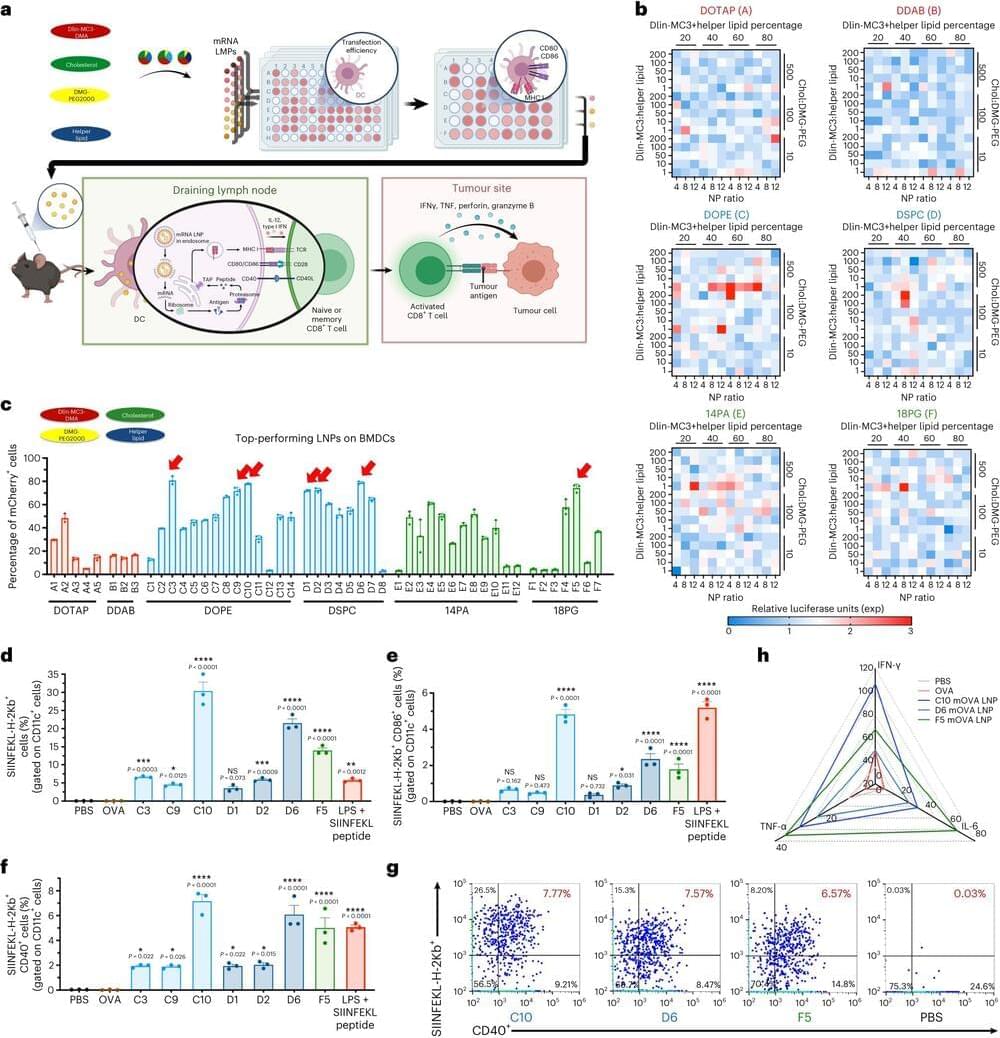
Researchers at the University of Sussex have discovered the transformative potential of Martian nanomaterials, potentially opening the door to sustainable habitation on the red planet.
Using resources and techniques currently applied on the International Space Station and by NASA, Dr. Conor Boland, a Lecturer in Materials Physics at the University of Sussex, led a research group that investigated the potential of nanomaterials—incredibly tiny components thousands of times smaller than a human hair —for clean energy production and building materials on Mars.
Taking what was considered a waste product by NASA and applying only sustainable production methods, including water-based chemistry and low-energy processes, the researchers have successfully identified electrical properties within gypsum nanomaterials—opening the door to potential clean energy and sustainable technology production on Mars.