Data-centric applications benefit from dense, low-power memory. Here the authors use a combination of chalcogenide superlattices and nanocomposites to achieve low switching voltage (0.7 V) and fast speed (40 ns) in 40-nm-scale phase-change memory.

Natasha and Max also appear in a recent video titled “Transhumanism. What it is not” in conversation with David Wood and two representatives of the anti-transhumanist camp, Alexander Thomas and Émile Torres. I’m not familiar with the work of Thomas. I’m more familiar with the work of Torres. I very strongly disagree with most of what Torres says, but I must concede that Torres seems an intelligent and perceptive person, not without a certain endearing grace. However, BS is BS.
I’ve watched and listened again to the awesome conversation between Lex Fridman and Guillaume Verdon aka Beff Jezos, the founder of the movement called effective accelerationism (e/acc) and the company Extropic AI. This long conversation (almost 3 hours) touches a lot of things including physics, quantum, thermodynamics, Artificial Intelligence, LLMs, space, e/acc philosophy & metaphysics, and of course the meaning of life & all that. This is the most complete talk on e/acc so far and is likely to remain so for some time. Watch it all, and let’s accelerate the fuck away from mediocrity toward unlimited extropian and cosmist greatness.
See my previous posts on e/acc (1, 2). I see e/acc as the new kid on the historic block of futurism, cosmism, and extropy. The next Terasem Colloquium on July 20, the (alas 55th!) anniversary of the first human landing on the Moon, and the next issue of Terasem ’s Journal of Geoethical Nanotechnology, to be published in July, will explore the old and new futurisms on the block: parallels, differences, philosophical foundations.
The engineers believe that their method, referred to as superluminescent light projection, represents a breakthrough that could enable revolutionary technological advancements in a wide range of industrial, commercial, and scientific applications, including advances in nanotechnology.
Printing Infinitesimally Small Objects by Harnessing the Power of Light
As technologies continue to advance, scientists and engineers have developed an increasing need for objects printed at the nanoscale, meaning hundreds of times smaller than a human hair. This is especially true in extremely advanced nanotechnologies like power generation and sensing, as well as novel medical procedures that previously only existed in science fiction.
NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has successfully bounced a laser off of India’s Vikram lander, which successfully touched down on the Moon’s surface in August.
The LRO’s laser altimeter aimed its sights at Vikram in December, shooting it with a series of laser pulses. Vikram’s 2-inch-wide retroreflector, which comes courtesy of NASA, bounced these signals right back, with scientists confirming the first-of-its-kind “ping” moments later.
The feat could revolutionize the way we locate objects and determine their exact locations on the Moon’s surface from vast distances using a surprisingly low-tech solution.
Instruments smaller than a human hair are being designed to eradicate antibiotic-resistant bacteria and fight cancer.
Dr. Ana Santos becomes emotional when describing what happened several years ago: Her grandfather and an uncle died of urinary tract infections and a good friend succumbed after an accidental cut got infected.
She was shocked. In an age of antibiotics, such misfortunes weren’t supposed to happen.
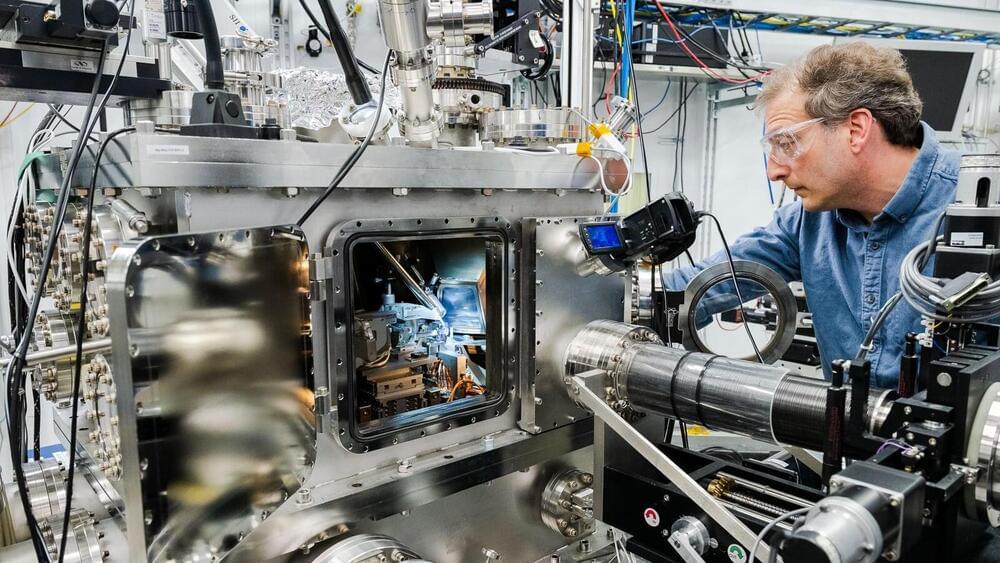
Silicon carbide is becoming a major player on the quantum scene. Widely used in specialized electronics goods such as LEDs and electric vehicles, silicon carbide boasts versatility, wide commercial availability, and growing use in high-power electronics, making it an attractive material for quantum information science, whose impact is expected to be profound.
Drawing on physics at the atomic scale, technologies such as quantum computers, networks, and sensors will likely revolutionize areas as varied as communication, drug development, and logistics in the coming decades.
Now, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, DOE’s Sandia National Laboratories, and partner institutions have conducted a comprehensive study on the creation of qubits—the fundamental units of quantum information processing—in silicon carbide.
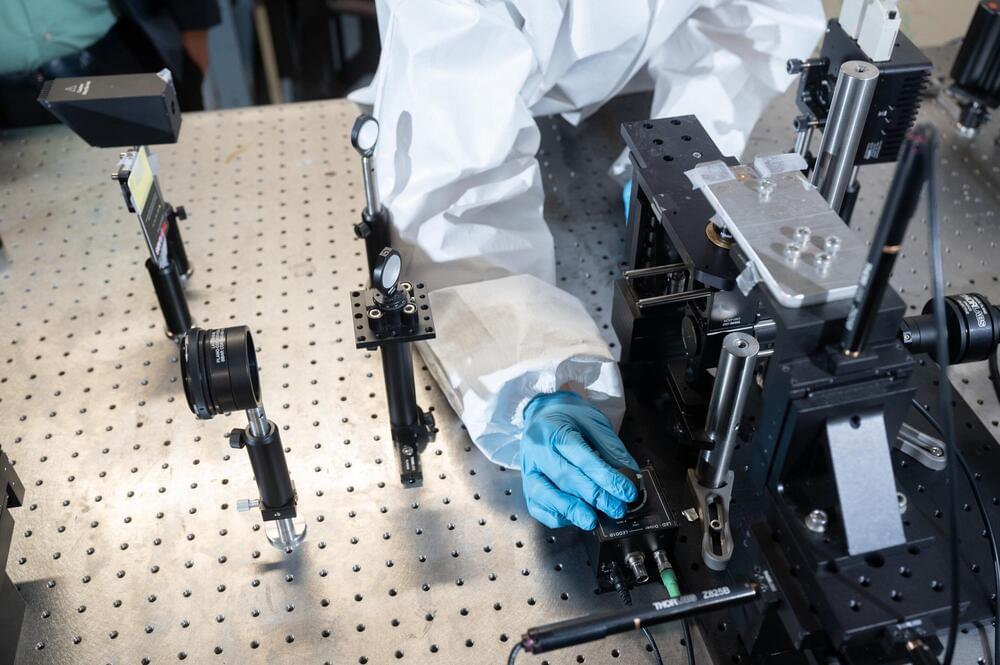
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed a light-based means of printing nano-sized metal structures that is significantly faster and cheaper than any technology currently available. It is a scalable solution that could transform a scientific field long reliant on technologies that are prohibitively expensive and slow. The breakthrough has the potential to bring new technologies out of labs and into the world.
Technological advances in many fields rely on the ability to print metallic structures that are nano-sized—a scale hundreds of times smaller than the width of a human hair. Sourabh Saha, assistant professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering, and Jungho Choi, a Ph.D. student in Saha’s lab, developed a technique for printing metal nanostructures that is 480 times faster and 35 times cheaper than the current conventional method.
Their research is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
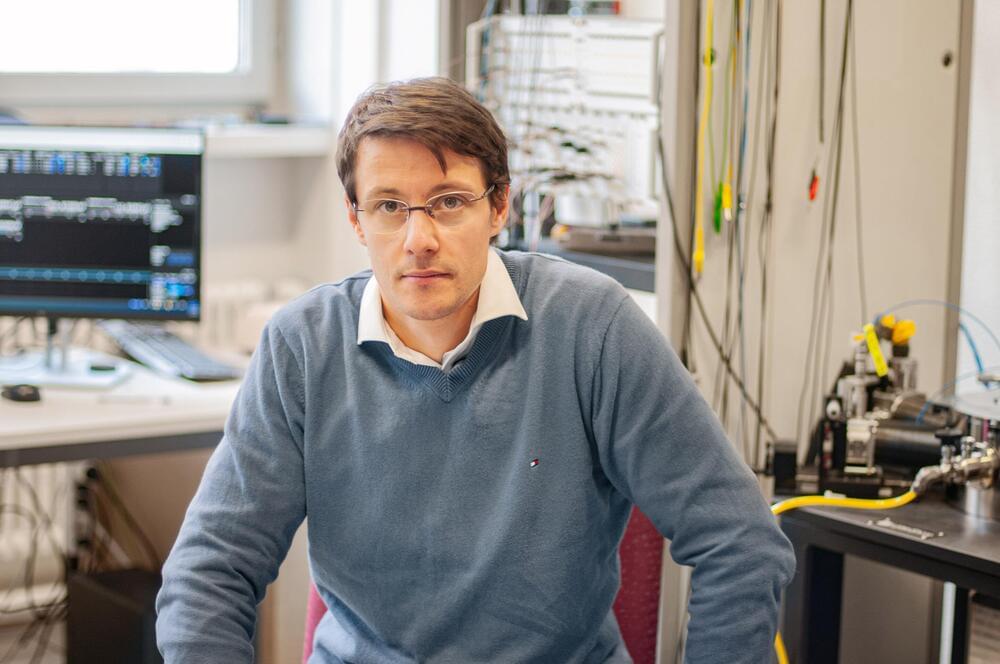

When Mickael Perrin started out on his scientific career 12 years ago, he had no way of knowing he was conducting research in an area that would be attracting wide public interest only a few years later: Quantum electronics. “At the time, physicists were just starting to talk about the potential of quantum technologies and quantum computers,” he recalls.
“Today there are dozens of start-ups in this area, and governments and companies are investing billions in developing the technology further. We are now seeing the first applications in computer science, cryptography, communications and sensors.” Perrin’s research is opening up another field of application: Electricity production using quantum effects with almost zero energy loss. To achieve this, the 36-year-old scientist combines two usually separate disciplines of physics: thermodynamics and quantum mechanics.
In the past year, the quality of Perrin’s research and its potential for future applications has brought him two awards. He received not only one of the ERC Starting Grants that are so highly sought-after by young researchers, but also an Eccellenza Professorial Fellowship of the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNS)F. He now leads a research group of nine at Empa as well as being an Assistant Professor of Quantum Electronics at ETH Zurich.

In a paper published in Science Jan. 18, scientists Chad Mirkin and Sharon Glotzer and their teams at Northwestern University and University of Michigan, respectively, present findings in nanotechnology that could impact the way advanced materials are made.
The paper describes a significant leap forward in assembling polyhedral nanoparticles. The researchers introduce and demonstrate the power of a novel synthetic strategy that expands possibilities in metamaterial design. These are the unusual materials that underpin “invisibility cloaks” and ultrahigh-speed optical computing systems.
“We manipulate macroscale materials in everyday life using our hands,” said Mirkin, the George B. Rathmann Professor of Chemistry at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences.