Mar 14, 2016
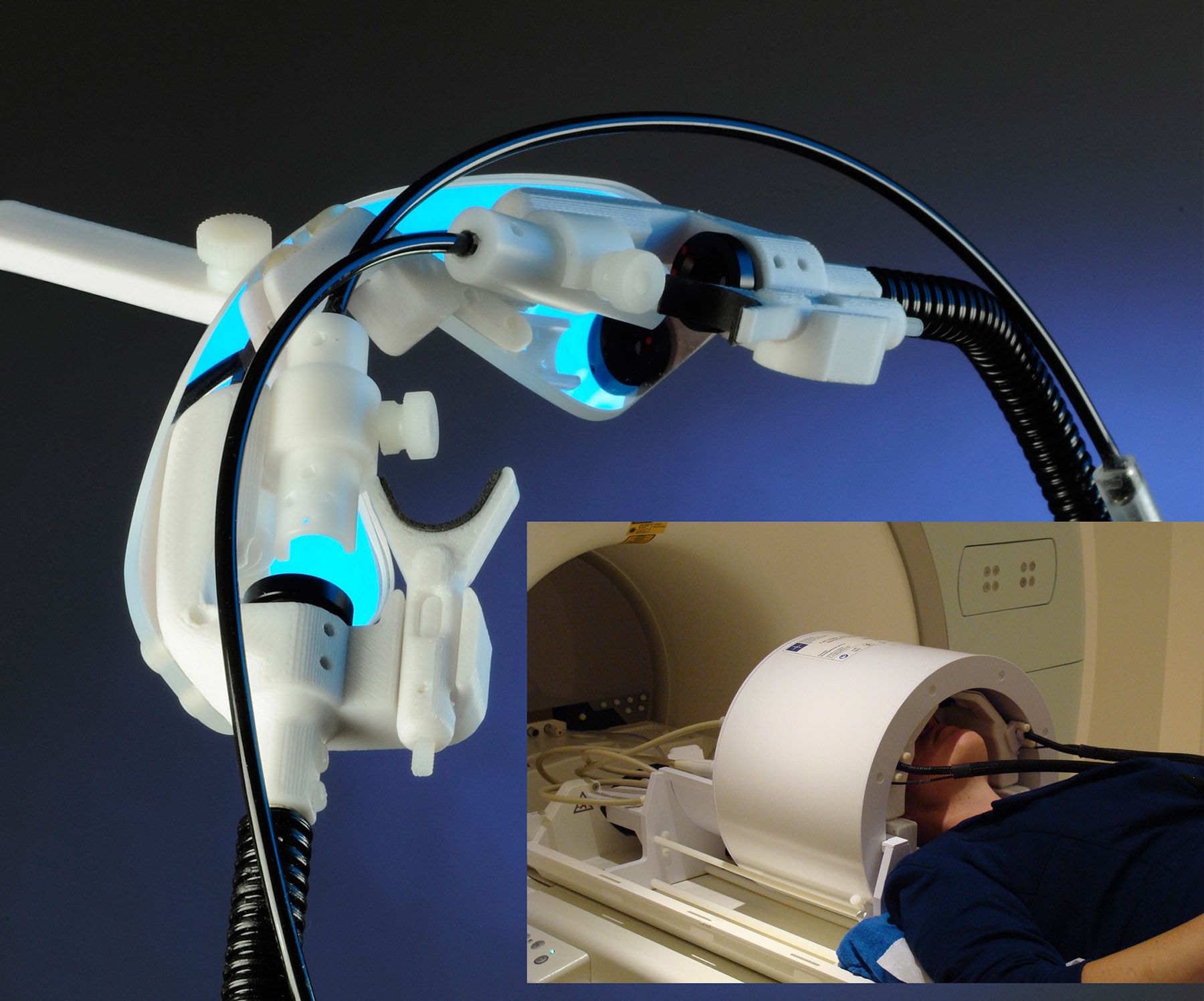
PGO Provides Customized Optical Components For Avotec’s Real Eye Nano
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, materials
Good news for MRIs; maybe witht he precision we also may not have to do any repeat scans as well.
Precision Glass & Optics recently announced the customization of two thin film optical components for a high-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) accessory. They developed the dielectric cold mirror and cylindrical prism mirror for the Real Eye Nano; an advanced visual presentation and eye-tracking system constructed of glass and plastic with a reduced size for operation in confined MRI spaces.